| Sinokannemeyeria Temporal range: Middle Triassic, | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Mounted skeleton, Paleozoological Museum of China | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Clade: | † Anomodontia |
| Clade: | † Dicynodontia |
| Clade: | † Kannemeyeriiformes |
| Genus: | † Sinokannemeyeria Young, 1937 |
| Type species | |
| †Sinokannemeyeria pearsoni Young, 1937 | |
| Species | |
| |
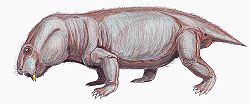
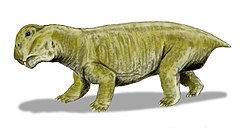
Sinokannemeyeria is a genus of kannemeyeriiform dicynodont that lived during the Anisian age of Middle Triassic period in what is now Shanxi, China. [1] [2]