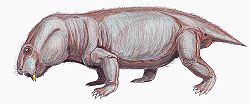
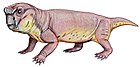
| Colobodectes Temporal range: Middle Permian | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | † Anomodontia |
| Clade: | † Dicynodontia |
| Genus: | † Colobodectes Modesto et al., 2003 |
| Type species | |
| †C. cluveri Modesto et al., 2003 | |
Colobodectes is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid from the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone in the Abrahamskraal Formation (Beaufort Group), South Africa. [1]