| Elph Temporal range: Late Permian, | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Suborder: | † Anomodontia |
| Clade: | † Dicynodontia |
| Family: | † Elphidae |
| Subfamily: | † Elphinae |
| Genus: | † Elph Kurkin, 1999 |
| Species: | †E. borealis |
| Binomial name | |
| †Elph borealis Kurkin, 1999 | |
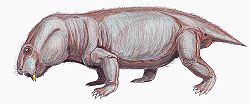
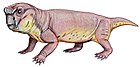
Elph (an arbitrary combination of letters [1] ) is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsids from Russia. Four specimens have been found from the Sokolki Assemblage in European Russia, representing a fauna that dates back to the Late Permian. [2] The holotype, PIN 2353/37, was originally considered a juvenile specimen due to its small size (with a total skull length of 106 mm), before being recognized as a mature individual. [1]
Elph was a small herbivore that lived alongside carnivorous akidnognathids and inostranceviids, as well as larger herbivores like Dicynodon and pareiasaurids. [3] The type species E. borealis was named in 1999. Elph has a short snout and tusks and is closely related to Interpresosaurus and Katumbia . [4]