History
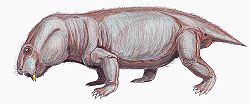
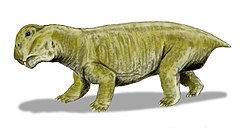
Rechnisaurus has had a long history of confusion with the far more widespread dicynodont Kannemeyeria . Rechnisaurus cristarhynchus was originally described as a new genus and species in 1970, on the basis of fossils from India. Later in the 1970s, additional specimens were found in Africa (namely the Ntawere Formation of Zambia and the Omingonde Formation of Namibia) and referred to the species. These African fossils were noted to be very similar to Kannemeyeria, so Rechnisaurus was renamed as a species of Kannemeyeria, Kannemeyeria cristarhynchus. However, in 1989 the original Indian fossils were re-compared to Kannemeyeria and found to be distinct, so Rechnisaurus was re-established in a more restricted sense including only the Indian fossils. [2]
The African fossils continued to be designated as Kannemeyeria cristarhynchus, but this was later found to be untenable, since that species name was based on Rechnisaurus cristarhynchus, which had been established as a distinct genus. In 2003, the African species of Kannemeyeria was renamed to Kannemeyeria lophorhinus. [3]
Rechnisaurus cristarhynchus has also been reported from the Manda Beds of Tanzania, though the Tanzanian fossils are in need of re-evaluation and are likely not related to Rechnisaurus. PVL 3963, a partial skull from the Quebrada de los Fosiles Formation of Argentina, was initially referred to Rechnisaurus and later designated as a new species of Kannemeyeria, under the species name Kannemeyeria aganosteus. [2]
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.