Karate terms come almost entirely from Japanese. The following terms are not exclusive to karate. They appear during its study and practice, varying depending on style and school.
Karate terms include:
Gi – Gedan barai - Goju-ryu
Hachiji dachi - Hajime – Heian - Heiko-dachi - Heisoku-dachi
Karate – Karate-ka - Kata – Keri - Kiai - Kihon – Kohai – Kumite – Kyū
Obi - Osu
Seiza - Senpai – Sensei – Shihan – Shotokan – Shuto-uchi - Shuto-uke - Sōke
Yame - Yoi

Shitō-ryū (糸東流) is a form of karate that was founded in 1934 by Kenwa Mabuni. Shitō-ryū is synthesis of the Okinawan Shuri-te and Naha-te schools of karate and today is considered one of the four main styles of the art.
Isshin-Ryū is a style of Okinawan karate created by Tatsuo Shimabuku in approximately 1947/1948. Isshin-Ryū karate is largely a synthesis of Shorin-ryū karate, Gojū-ryū karate, and kobudō. The name means, literally, "one heart method". In 1989 there were 336 branches of Isshin-ryū throughout the world, most of which were concentrated in the United States.
Gojūshiho is a kata practiced in karate. Gojushiho was developed by Sokon Matsumura, one of the key founders of Okinawan martial arts and named it "Uesheishi", which literally means 54 methods in Chinese. In some styles of karate, there are two versions of this kata - Gojūshiho Shō and Gojūshiho Dai. An advantage of the two versions of the kata is to better master the difficult techniques presented therein, but not without facing some confusion, for many sequences are the same and others only slightly different. The embusen of both Gojūshiho Shō and Gojūshiho Dai are nearly identical. Gojūshiho Shō begins straight off with a wide variety of advanced techniques and, as such, is highly recommended for study. Gojūshiho Dai consists of many advanced open-handed techniques and attacks to the collar-bone.
Sōchin (壯鎭) is a kata practiced in several styles of karate. It may have derived from Dragon style kung fu, and was taught in the Naha-te school in Okinawa by Seisho Arakaki. It was then passed down to Shitō-ryū. Later, a variation of it was introduced into the Shotokan style by Gichin Funakoshi's son, Yoshitaka. Some branches of Tang Soo Do have added it to their curriculum under the name "Sojin".
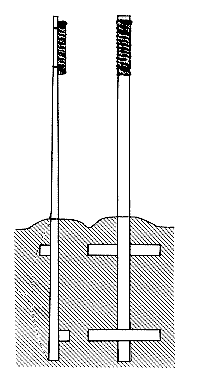
The makiwara (巻藁) is a padded striking post used as a training tool in various styles of traditional karate. It is thought to be uniquely Okinawan in origin. The makiwara is one form of hojo undō, a method of supplementary conditioning used by Okinawan martial artists.
The karate kataSeisan (十三) literally means '13'. Some people refer to the kata as '13 Hands', '13 Fists', '13 Techniques', '13 Steps' or even '13 killing positions'; however, these names have no historical basis.
Naihanchi (ナイハンチ) is a karate kata, performed in straddle stance. It translates to 'internal divided conflict'. The form makes use of in-fighting techniques and grappling. In Shorin-Ryu and Matsubayashi-ryū Naihanchi Shodan is the first ni kyu although it is taught to yon kyu occasionally before evaluations for the ni kyu rank. It is also the first Shorin-ryu and Shindo jinen-ryu kata to start with a technique to the right instead of the left. There are three modern kata derived from this. Some researchers believe Nidan and Sandan were created by Anko Itosu, but others believe that it was originally one kata broken into three separate parts. The fact that only Naihanchi/Tekki Shodan has a formal opening suggests the kata was split.
The Taikyoku series is a series of kata in use in several types of karate. The name Taikyoku (太極) refers to the Chinese philosophical concept of Taiji. The Taikyoku kata were developed by Yoshitaka Funakoshi and introduced by Gichin Funakoshi as a way to simplify the principles of the already simplified Pinan/Heian series. The embusen, or pattern of the kata's movements, are the same as in Heian shodan. Students of karate systems that use the Taikyoku kata series are often introduced to them first, as a preparation for the Pinan/Heian kata. Some Korean Tang Soo Do and Song Moo Kwan Taekwondo schools, also practice these kata (poomsae); they are termed, "Taegeuk", which is a direct Korean translation of the Kanji/Hanja characters used to write "Taikyoku". They are distinctly different from the 8 Taegeuk poomsae practiced in Kukkiwon. Gōjū Kai developed five of its own Taikyoku kata, based on the Shotokan katas and retaining the I-shaped embusen. The embusen (pathway) of all the Taikyoku kata is simple :
*--! | | | | !--#
Rōhai (鷺牌) meaning “image of a heron” or “sign of a heron” is a family of kata practiced in some styles of karate. The kata originated from the Tomari-te school of Okinawan martial arts. It was called Matsumora Rōhai, after Kosaku Matsumora, who was presumably its inventor. Ankō Itosu later took this kata and developed three kata from it: Rōhai shodan, Rōhai nidan, and Rōhai sandan. In Shorin-ryū and Matsubayashi-ryū this kata introduces Gedan Shotei Ate and Ippon Ashi Dachi. It contains a sequence of Tomoe Zuki exactly the same as the one in Bassai, although the ending of the sequence chains into Hangetsu Geri/Uke.
Karate has many different stances, each used for different types of power and movement. In Japanese the general term is tachi (立ち) changed to dachi when used as a suffix. Some stances focus more on mobility than stability, and vice verse.
Shorin-ryu Seibukan, also known as Sukunaihayashi, is one of the many Okinawan Shorin-ryu styles of karate.
Shorin-ryu Shidokan is the main branch of Shorin-ryū style of Okinawan karate, started by Katsuya Miyahira, Hanshi 10th Dan.
Enpi (燕飛), also frequently transliterated as Empi, is a kata practiced by Shotokan and other karate styles. Enpi means Flying Swallow.
Tōon-ryū is a style of Okinawan Karate founded by Kyoda Juhatsu.

Kenkojuku is a style of Shotokan karate previous to the establishment of the Japan Karate Association (JKA) style. It was founded by Tomosaburo Okano. Kenkojuku karate is similar to the teachings of Gichin Funakoshi and modifications made by Funakoshi's son Yoshitaka Funakoshi. JKA Shotokan differs slightly in that it was Masatoshi Nakayama's version of Shotokan. Okano's/Yoshitaka's Kenkojuku karate and JKA karate are becoming more similar compared to other variants of Shotokan karate such as Shigeru Egami's Shotokai, Hirokazu Kanazawa's Shotokan Karate International or SKI.
Ananku (安南空) is a kata from Okinawan karate. Its history in Okinawan martial arts is relatively short in comparison to other kata as it was composed by Chotoku Kyan. Its meaning is "Light from the South" or "Peace from the South", as it is thought to originate when Kyan returned from a trip to Taiwan.

Seigokan (正剛館) is the Goju-Ryu Karate-do organization founded in 1945 by Seigo Tada (1922-1997) Hanshi. With its Hombu Dojo (headquarters) in Himeji, Japan, the Seigokan All Japan Karate-do Association (SAJKA) — its official name — has branches in Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, India, Italy, the Philippines, Portugal, Sri Lanka, the United States, England, Chile, Colombia, Indonesia and Venezuela.

Seigo Tada was the founder of Goju-Ryu Seigokan Karatedo.
Seiunchin (制引戦) is a kaishu kata of Goju-ryu karate. It was taught by Goju-ryu's founder, Chojun Miyagi, who in turn learned it from his teacher, Kanryo Higaonna. Seiunchin can be interpreted to mean "pulling".