Constitutional monarchy, also known as limited monarchy, parliamentary monarchy or democratic monarchy, is a form of monarchy in which the monarch exercises their authority in accordance with a constitution and is not alone in making decisions. Constitutional monarchies differ from absolute monarchies in that they are bound to exercise powers and authorities within limits prescribed by an established legal framework.
A monarchy is a form of government in which a person, the monarch, reigns as head of state for life or until abdication. The extent of the authority of the monarch may vary from restricted and largely symbolic, to fully autocratic, and may have representational, executive, legislative, and judicial functions.

Tsarina or tsaritsa is the title of a female autocratic ruler (monarch) of Bulgaria, Serbia or Russia, or the title of a tsar's wife. The English spelling is derived from the German czarin or zarin, in the same way as the French tsarine / czarine, and the Spanish and Italian czarina / zarina. (A tsar's daughter is a tsarevna.)

The prime minister of Spain, officially president of the Government, is the head of government of Spain. The prime minister nominates the ministers and chairs the Council of Ministers. In this sense, the prime minister establishes the Government policies and coordinates the actions of the Cabinet members. As chief executive, the prime minister also advises the monarch on the exercise of their royal prerogatives.
The abolition of monarchy is a legislative or revolutionary movement to abolish monarchical elements in government, usually hereditary. The abolition of an absolute monarchy in favour of limited government under a constitutional monarchy is a less radical form of anti-monarchism that has succeeded in some nations that still retain monarchs, such as Sweden, Spain, and Thailand.

A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family, usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A dynasty may also be referred to as a "house", "family" or "clan", among others.

Simeon Borisov Saxe-Coburg-Gotha is a Bulgarian politician who reigned as the last Tsar of the Tsardom of Bulgaria as Simeon II from 1943 until 1946. In 1946, the monarchy was abolished by a referendum, forcing Simeon into exile. Following the fall of communism in Bulgaria, Simeon returned to his home country in 1996, and founded the National Movement for Stability and Progress party. After winning the 2001 election as its leader, Sakskoburggotski proceeded to govern Bulgaria as prime minister from 2001 to 2005.

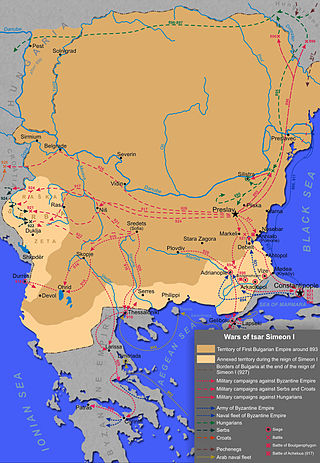
Tsar SimeonI the Great ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927, during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture.
The lieutenancy areas of Scotland are the areas used for the ceremonial lord-lieutenants, the monarch's representatives, in Scotland. The lord-lieutenants' titles chosen by the monarch and his legal advisers are mainly based on placenames of the traditional counties of Scotland. In 1794, permanent lieutenancies were established by Royal Warrant. By the Militia Act 1797, the lieutenants appointed "for the Counties, Stewartries, Cities, and Places" were given powers to raise and command County Militia Units.

The obverse and reverse are the two flat faces of coins and some other two-sided objects, including paper money, flags, seals, medals, drawings, old master prints and other works of art, and printed fabrics. In this usage, obverse means the front face of the object and reverse means the back face. The obverse of a coin is commonly called heads, because it often depicts the head of a prominent person, and the reverse tails.

Knyaz, also knez, knjaz or kniaz, is a historical Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times. It is usually translated into English as "prince", "king", or "duke" depending on specific historical context and the potentially known Latin equivalents at the time, but the word was originally derived from the common Germanic *kuningaz (king).
The Battle of Pegae was fought between 11 and 18 March 921 in the outskirts of Constantinople between the forces of the Bulgarian Empire and the Byzantine Empire during the Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 913–927. The battle took place in a locality called Pegae, named after the nearby Church of St. Mary of the Spring. The Byzantine lines collapsed at the very first Bulgarian attack and their commanders fled the battlefield. In the subsequent rout most Byzantine soldiers were killed by the sword, drowned or were captured.
The Croatian–Bulgarian Wars were a series of conflicts that erupted three times during the 9th and 10th centuries between the medieval realms of Croatia and Bulgaria. During these wars, Croatia formed alliances with East Francia and Byzantium against the Bulgarian Empire.

Hearst San Simeon State Park is a state park of California, United States, preserving rocky coast and rare habitats. It is located between Cambria and San Simeon. The 3,409-acre (1,380 ha) park was first established in 1932. The park includes the Santa Rosa Creek Natural Preserve, the San Simeon Natural Preserve and the Pa-nu Cultural Preserve, which were established in 1990.

Tsar is a title historically used by Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word caesar, which was intended to mean emperor in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official—but was usually considered by Western Europeans to be equivalent to "king".
The Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 913–927 was fought between the Bulgarian Empire and the Byzantine Empire for more than a decade. Although the war was provoked by the Byzantine emperor Alexander's decision to discontinue paying an annual tribute to Bulgaria, the military and ideological initiative was held by Simeon I of Bulgaria, who demanded to be recognized as Tsar and made it clear that he aimed to conquer not only Constantinople but the rest of the Byzantine Empire, as well.
The siege of Constantinople was fought in June 922 at the outskirts of the capital of the Byzantine Empire, Constantinople, between the forces of the First Bulgarian Empire and the Byzantines during the Byzantine–Bulgarian war of 913–927. In the summer the Byzantine Emperor Romanos I Lekapenos sent troops under the commander Saktikios to repel another Bulgarian raid at the outskirts of the Byzantine capital. The Byzantines stormed the Bulgarian camp but were defeated when they confronted the main Bulgarian forces. During his flight from the battlefield Saktikios was mortally wounded and died the following night.

The Bulgarian monarchs used the titles kanasubigi, khan, knyaz and tsar (emperor). When acceding to the throne in the First and Second Bulgarian Empire the occasion was marked with a coronation, conducted by the Bulgarian Orthodox Church. During the Third Bulgarian State accession was marked by an oath on the constitution.