
In mathematics, many sets of transformations form a group under function composition; for example, the rotations around a point in the plane. It is often useful to consider the group as an abstract group, and to say that one has a group action of the abstract group that consists of performing the transformations of the group of transformations. The reason for distinguishing the group from the transformations is that, generally, a group of transformations of a structure acts also on various related structures; for example, the above rotation group acts also on triangles by transforming triangles into triangles.
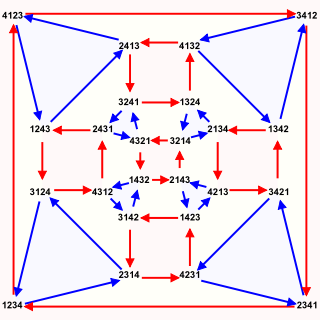
In abstract algebra, the symmetric group defined over any set is the group whose elements are all the bijections from the set to itself, and whose group operation is the composition of functions. In particular, the finite symmetric group defined over a finite set of symbols consists of the permutations that can be performed on the symbols. Since there are such permutation operations, the order of the symmetric group is .

In the mathematical classification of finite simple groups, there are 26 or 27 groups which do not fit into any infinite family. These are called the sporadic simple groups, or the sporadic finite groups, or just the sporadic groups.

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Conway groups are the three sporadic simple groups Co1, Co2 and Co3 along with the related finite group Co0 introduced by (Conway 1968, 1969).

In group theory, a topic in abstract algebra, the Mathieu groups are the five sporadic simple groups M11, M12, M22, M23 and M24 introduced by Mathieu. They are multiply transitive permutation groups on 11, 12, 22, 23 or 24 objects. They are the first sporadic groups to be discovered.

In mathematics, especially in the group theoretic area of algebra, the projective linear group (also known as the projective general linear group or PGL) is the induced action of the general linear group of a vector space V on the associated projective space P(V). Explicitly, the projective linear group is the quotient group

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Suzuki groupSuz or Sz is a sporadic simple group of order

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Higman–Sims group HS is a sporadic simple group of order
In mathematical graph theory, the Higman–Sims graph is a 22-regular undirected graph with 100 vertices and 1100 edges. It is the unique strongly regular graph srg(100,22,0,6), where no neighboring pair of vertices share a common neighbor and each non-neighboring pair of vertices share six common neighbors. It was first constructed by Mesner (1956) and rediscovered in 1968 by Donald G. Higman and Charles C. Sims as a way to define the Higman–Sims group, a subgroup of index two in the group of automorphisms of the Hoffman–Singleton graph.

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Mathieu groupM11 is a sporadic simple group of order

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Mathieu groupM12 is a sporadic simple group of order

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Mathieu groupM22 is a sporadic simple group of order

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Mathieu groupM24 is a sporadic simple group of order

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the McLaughlin group McL is a sporadic simple group of order
In mathematical finite group theory, a rank 3 permutation group acts transitively on a set such that the stabilizer of a point has 3 orbits. The study of these groups was started by Higman. Several of the sporadic simple groups were discovered as rank 3 permutation groups.

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Conway groupCo2 is a sporadic simple group of order

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Conway group is a sporadic simple group of order

In the area of modern algebra known as group theory, the Conway groupCo1 is a sporadic simple group of order





