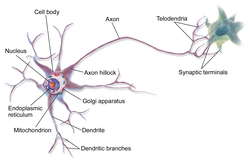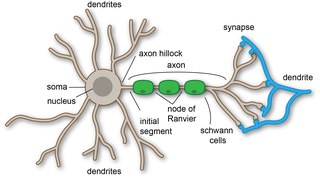
A dendrite or dendron is a branched protoplasmic extension of a nerve cell that propagates the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the neuron from which the dendrites project. Electrical stimulation is transmitted onto dendrites by upstream neurons via synapses which are located at various points throughout the dendritic tree.

A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an excitable cell that fires electric signals called action potentials across a neural network in the nervous system. Neurons communicate with other cells via synapses, which are specialized connections that commonly use minute amounts of chemical neurotransmitters to pass the electric signal from the presynaptic neuron to the target cell through the synaptic gap.

The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response.
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The field of neural development draws on both neuroscience and developmental biology to describe and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which complex nervous systems develop, from nematodes and fruit flies to mammals.
Nervous tissue, also called neural tissue, is the main tissue component of the nervous system. The nervous system regulates and controls body functions and activity. It consists of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) comprising the branching peripheral nerves. It is composed of neurons, also known as nerve cells, which receive and transmit impulses, and neuroglia, also known as glial cells or glia, which assist the propagation of the nerve impulse as well as provide nutrients to the neurons.

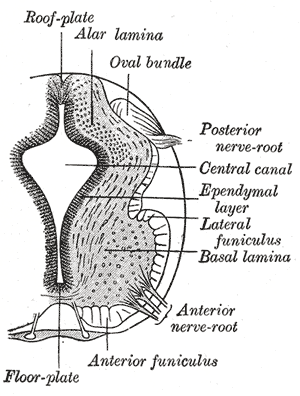
The grey column refers to a somewhat ridge-shaped mass of grey matter in the spinal cord. This presents as three columns: the anterior grey column, the posterior grey column, and the lateral grey column, all of which are visible in cross-section of the spinal cord.

Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal cells are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cortex and the corticospinal tract. One of the main structural features of the pyramidal neuron is the conic shaped soma, or cell body, after which the neuron is named. Other key structural features of the pyramidal cell are a single axon, a large apical dendrite, multiple basal dendrites, and the presence of dendritic spines.

A dorsal root ganglion is a cluster of neurons in a dorsal root of a spinal nerve. The cell bodies of sensory neurons known as first-order neurons are located in the dorsal root ganglia.

Basket cells are inhibitory GABAergic interneurons of the brain, found throughout different regions of the cortex and cerebellum.

A pseudounipolar neuron is a type of neuron which has one extension from its cell body. This type of neuron contains an axon that has split into two branches. They develop embryologically as bipolar in shape, and are thus termed pseudounipolar instead of unipolar.

In neuroscience, Golgi cells are the most abundant inhibitory interneurons found within the granular layer of the cerebellum. Golgi cells can be found in the granular layer at various layers. The Golgi cell is essential for controlling the activity of the granular layer. They were first identified as inhibitory in 1964. It was also the first example of an inhibitory feedback network in which the inhibitory interneuron was identified anatomically. Golgi cells produce a wide lateral inhibition that reaches beyond the afferent synaptic field and inhibit granule cells via feedforward and feedback inhibitory loops. These cells synapse onto the dendrite of granule cells and unipolar brush cells. They receive excitatory input from mossy fibres, also synapsing on granule cells, and parallel fibers, which are long granule cell axons. Thereby this circuitry allows for feed-forward and feed-back inhibition of granule cells.

The superior olivary complex (SOC) or superior olive is a collection of brainstem nuclei that is located in pons, functions in multiple aspects of hearing and is an important component of the ascending and descending auditory pathways of the auditory system. The SOC is intimately related to the trapezoid body: most of the cell groups of the SOC are dorsal to this axon bundle while a number of cell groups are embedded in the trapezoid body. Overall, the SOC displays a significant interspecies variation, being largest in bats and rodents and smaller in primates.

A unipolar neuron is a neuron in which only one process, called a neurite, extends from the cell body. The neurite then branches to form dendritic and axonal processes. Most neurons in the central nervous systems of invertebrates, including insects, are unipolar. The cell bodies of invertebrate unipolar neurons are often located around the edges of the neuropil, in the so-called cell-body rind.
Alpha (α) motor neurons (also called alpha motoneurons), are large, multipolar lower motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle and are directly responsible for initiating their contraction. Alpha motor neurons are distinct from gamma motor neurons, which innervate intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles.
Martinotti cells are small multipolar neurons with short branching dendrites. They are scattered throughout various layers of the cerebral cortex, sending their axons up to the cortical layer I where they form axonal arborization. The arbors transgress multiple columns in layer VI and make contacts with the distal tuft dendrites of pyramidal cells. Martinotti cells express somatostatin and sometimes calbindin, but not parvalbumin or vasoactive intestinal peptide. Furthermore, Martinotti cells in layer V have been shown to express the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α2 subunit (Chrna2).
Neuromorphology is the study of nervous system form, shape, and structure. The study involves looking at a particular part of the nervous system from a molecular and cellular level and connecting it to a physiological and anatomical point of view. The field also explores the communications and interactions within and between each specialized section of the nervous system. Morphology is distinct from morphogenesis. Morphology is the study of the shape and structure of biological organisms, while morphogenesis is the study of the biological development of the shape and structure of organisms. Therefore, neuromorphology focuses on the specifics of the structure of the nervous system and not the process by which the structure was developed. Neuromorphology and morphogenesis, while two different entities, are nonetheless closely linked.

A bipolar neuron, or bipolar cell, is a type of neuron characterized by having both an axon and a dendrite extending from the soma in opposite directions. These neurons are predominantly found in the retina and olfactory system. The embryological period encompassing weeks seven through eight marks the commencement of bipolar neuron development.

In the ventral cochlear nucleus (VCN), auditory nerve fibers enter the brain via the nerve root in the VCN. The ventral cochlear nucleus is divided into the anterior ventral (anteroventral) cochlear nucleus (AVCN) and the posterior ventral (posteroventral) cochlear nucleus (PVCN). In the VCN, auditory nerve fibers bifurcate, the ascending branch innervates the AVCN and the descending branch innervates the PVCN and then continue to the dorsal cochlear nucleus. The orderly innervation by auditory nerve fibers gives the AVCN a tonotopic organization along the dorsoventral axis. Fibers that carry information from the apex of the cochlea that are tuned to low frequencies contact neurons in the ventral part of the AVCN; those that carry information from the base of the cochlea that are tuned to high frequencies contact neurons in the dorsal part of the AVCN. Several populations of neurons populate the AVCN. Bushy cells receive input from auditory nerve fibers through particularly large endings called end bulbs of Held. They contact stellate cells through more conventional boutons.
The development of the cerebral cortex, known as corticogenesis is the process during which the cerebral cortex of the brain is formed as part of the development of the nervous system of mammals including its development in humans. The cortex is the outer layer of the brain and is composed of up to six layers. Neurons formed in the ventricular zone migrate to their final locations in one of the six layers of the cortex. The process occurs from embryonic day 10 to 17 in mice and between gestational weeks seven to 18 in humans.
An anaxonic neuron is a type of neuron where there is no axon or it cannot be differentiated from the dendrites. Being loyal to the etymology of anaxonic there are two types of anaxonic neurons in the human nervous system, the undifferentiated anaxonic neuron where the axon cannot be differentiated from the dendrites, and the unipolar brush cell (UBC), that has no axon and only a dendritic arbour.