This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2025) |
| Dorsal root of spinal nerve | |
|---|---|
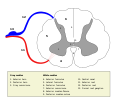
 The formation of the spinal nerve from the dorsal and ventral roots | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | radix posterior nervi spinalis |
| TA98 | A14.2.00.030 |
| TA2 | 6146 |
| FMA | 5980 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
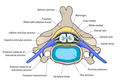
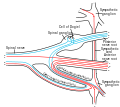
The dorsal root of spinal nerve (or posterior root of spinal nerve or sensory root)[ citation needed ] is one of two "roots" which emerge from the spinal cord. It emerges directly from the spinal cord and travels to the dorsal root ganglion. Nerve fibres with the ventral root then combine to form a spinal nerve. The dorsal root transmits sensory information, forming the afferent sensory root of a spinal nerve.