| Ventral root of spinal nerve | |
|---|---|
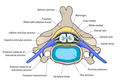
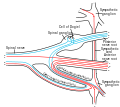
 The formation of the spinal nerve from the dorsal and ventral roots | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | radix anterior nervi spinalis |
| TA98 | A14.2.00.029 |
| TA2 | 6145 |
| FMA | 5979 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In anatomy and neurology, the ventral root of spinal nerve, anterior root, or motor root[ citation needed ] is the efferent motor root of a spinal nerve.
Contents
At its distal end, the ventral root joins with the dorsal root to form a mixed spinal nerve.