Related Research Articles

The autonomic nervous system (ANS), sometimes called the visceral nervous system and formerly the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the nervous system that operates internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, its force of contraction, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response.

The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.
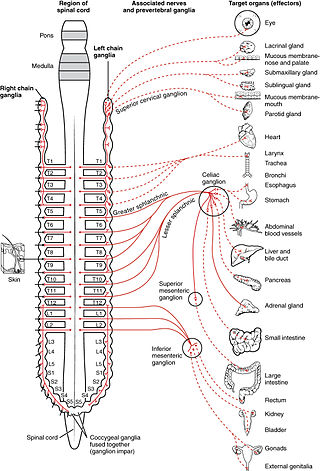
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system.

The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is the upper-most and largest of the cervical sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk. It probably formed by the union of four sympathetic ganglia of the cervical spinal nerves C1–C4. It is the only ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system that innervates the head and neck. The SCG innervates numerous structures of the head and neck.

The sympathetic trunks are a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. They are a major component of the sympathetic nervous system.
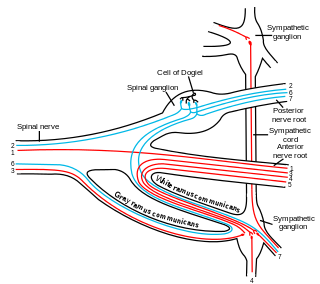
The white ramus communicans from Latin ramus (branch) and communicans (communicating) is the preganglionic sympathetic outflow nerve tract from the spinal cord.

Ramus communicans is the Latin term used for a nerve which connects two other nerves, and can be translated as "communicating branch".

In the autonomic nervous system, nerve fibers from the central nervous system to the ganglion are known as preganglionic nerve fibers. All preganglionic fibers, whether they are in the sympathetic division or in the parasympathetic division, are cholinergic and they are myelinated.

The sympathetic ganglia, or paravertebral ganglia, are autonomic ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Ganglia are 20,000 to 30,000 afferent and efferent nerve cell bodies that run along on either side of the spinal cord. Afferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the body to the brain and spinal cord, while efferent nerve cell bodies bring information from the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. The cell bodies create long sympathetic chains that are on either side of the spinal cord. They also form para- or pre-vertebral ganglia of gross anatomy.

The deep petrosal nerve is a post-ganglionic branch of the (sympathetic) internal carotid (nervous) plexus that enters the cranial cavity through the carotid canal, then passes perpendicular to the carotid canal in the cartilaginous substance which fills the foramen lacerum to unite with the (parasympathetic) greater petrosal nerve to form the nerve of pterygoid canal.

The lateral grey column is one of the three grey columns of the spinal cord ; the others being the anterior and posterior grey columns. The lateral grey column is primarily involved with activity in the sympathetic division of the autonomic motor system. It projects to the side as a triangular field in the thoracic and upper lumbar regions of the postero-lateral part of the anterior grey column.

Sacral splanchnic nerves are splanchnic nerves that connect the inferior hypogastric plexus to the sympathetic trunk in the pelvis.

The esophageal plexus is formed by nerve fibers from two sources, branches of the vagus nerve, and visceral branches of the sympathetic trunk. The esophageal plexus and the cardiac plexus contain the same types of fibers and are both considered thoracic autonomic plexus.

The cervical ganglia are paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system. Preganglionic nerves from the thoracic spinal cord enter into the cervical ganglions and synapse with its postganglionic fibers or nerves. The cervical ganglion has three paravertebral ganglia:

The general visceral afferent (GVA) fibers conduct sensory impulses from the internal organs, glands, and blood vessels to the central nervous system. They are considered to be part of the visceral nervous system, which is closely related to the autonomic nervous system, but 'visceral nervous system' and 'autonomic nervous system' are not direct synonyms and care should be taken when using these terms. Unlike the efferent fibers of the autonomic nervous system, the afferent fibers are not classified as either sympathetic or parasympathetic.

The lumbar ganglia are paravertebral ganglia located in the inferior portion of the sympathetic trunk. The lumbar portion of the sympathetic trunk typically has 4 lumbar ganglia. The lumbar splanchnic nerves arise from the ganglia here, and contribute sympathetic efferent fibers to the nearby plexuses. The first two lumbar ganglia have both white and gray rami communicates.

The thoracic ganglia are paravertebral ganglia. The thoracic portion of the sympathetic trunk typically has 12 thoracic ganglia. Emerging from the ganglia are thoracic splanchnic nerves that help provide sympathetic innervation to thoracic and abdominal structures. The thoracic part of sympathetic trunk lies posterior to the costovertebral pleura and is hence not a content of the posterior mediastinum

The following diagram is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the human nervous system:

The ciliary ganglion is a parasympathetic ganglion located just behind the eye in the posterior orbit. Three types of axons enter the ciliary ganglion but only the preganglionic parasympathetic axons synapse there. The entering axons are arranged into three roots of the ciliary ganglion, which join enter the posterior surface of the ganglion.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ Betts, J Gordon; Desaix, Peter; Johnson, Eddie; Johnson, Jody E; Korol, Oksana; Kruse, Dean; Poe, Brandon; Wise, James; Womble, Mark D; Young, Kelly A (July 22, 2023). Anatomy & Physiology. Houston: OpenStax CNX. 15.1 Divisions of the autonomic nervous system. ISBN 978-1-947172-04-3.
- ↑ F. Netter, Autonomic Nervous System: Schema, Back and Spinal Cord, Plate 153
Wilson-Pauwels, Linda; Stewart, Patricia A.; Akesson, Elizabeth J. (January 1997). Autonomic Nerves . Canada: B. C. Decker, Inc. pp. 71–104. ISBN 978-1-55009-030-7.

