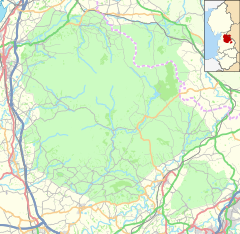
The Forest of Bowland, also known as the Bowland Fells and formerly the Chase of Bowland, is an area of gritstone fells, deep valleys and peat moorland, mostly in north-east Lancashire, England, with a small part in North Yorkshire. It is a western outlier of the Pennines.

Ribble Valley is a local government district with borough status in Lancashire, England. Its council is based in Clitheroe, the largest town. The borough also includes the town of Longridge and numerous villages and surrounding rural areas. It is named after the River Ribble. Much of the district lies within the Forest of Bowland, a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.

Dunsop Bridge is a village in the Borough of Ribble Valley, Lancashire, England, 9 miles (14 km) north-west of Clitheroe, 15 miles (24 km) south-east of Lancaster and 24.5 miles (39 km) west of Skipton. It is in the civil parish of Bowland Forest High. Historically, the village is part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, but was placed under the administration of Lancashire County Council on 1 April 1974.

Bashall Eaves is a village and civil parish in the Ribble Valley district of Lancashire, England, about four miles (6 km) west of Clitheroe. The placename element eaves is Old English and refers to Bashall's location on the borders of the Forest of Bowland. Historically, the village is part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, but was transferred to Lancashire for administrative purposes on 1 April 1974, under the provisions of the Local Government Act 1972.

Slaidburn is a village and civil parish within the Ribble Valley district of Lancashire, England. The parish covers just over 5,000 acres of the Forest of Bowland.

Bolton-by-Bowland is a village and civil parish in the Ribble Valley district of Lancashire, England. Before 1974, the village was part of Bowland Rural District in the West Riding of Yorkshire. According to the census of 2001, the parish had a population of just 498, rising marginally to 499 at the census of 2011.

Bowland Forest Low is a civil parish in the Ribble Valley district of Lancashire, England, covering some 5,500 acres (22 km2) of the Forest of Bowland. According to the 2001 census, the parish had a population of 168, falling to 160 at the 2011 Census. The parish includes the hamlets of Whitewell and Cow Ark. From northwards clockwise, it borders the civil parishes of Newton, Bashall Eaves, Aighton, Bailey and Chaigley, Bowland-with-Leagram and Bowland Forest High. Before 1974, it formed part of Bowland Rural District in the West Riding of Yorkshire.

Bowland Forest High is a civil parish in the Ribble Valley district of Lancashire, England, covering some 20,000 acres (80 km2) of the Forest of Bowland. It fell within the ancient boundaries of the West Riding of Yorkshire. According to the 2001 census, the parish had a population of 163, falling to 144 at the 2011 Census. The parish includes the settlements of Hareden, Sykes, and Dunsop Bridge. It covers Sykes Fell, Whins Brow, Croasdale Fell and Wolfhole Crag. Before 1974, it formed part of Bowland Rural District in the West Riding of Yorkshire.

Bowland-with-Leagram is a civil parish in the Ribble Valley district of Lancashire, England, covering part of the Forest of Bowland. According to the census, the parish had a population of 181 in 1951, 128 in 2001 and 169 at the Census 2011.

Waddington is a small village, 2 miles (3 km) north-west of Clitheroe in the Ribble Valley, Lancashire, England. The population of the civil parish at the 2011 census was 1,028. Before the 1974 county boundary changes, Waddington fell just within the Bowland Rural District of the West Riding of Yorkshire. It covers approximately 2000 acres of the Forest of Bowland.

West Bradford is a village and civil parish in Lancashire, England, 27 miles (43 km) west of the larger city of Bradford, West Yorkshire and 2.5 miles (4 km) north of Clitheroe. The population of the civil parish taken at the 2011 census was 788. It covers some 2000 acres of the Forest of Bowland. In Domesday, it is recorded as Bradeford and in the thirteenth century, Braford in Bouland. It was part of the West Riding of Yorkshire until 1974. "West Bradford" was introduced in the nineteenth century at the time of the introduction of postal services to help distinguish the village from its larger eastern neighbour of the same name.

Pendleton is a small village and civil parish in Ribble Valley, within the county of Lancashire, England. It is close to the towns of Whalley and Clitheroe. The parish lies on the north west side of Pendle Hill below the Nick o' Pendle. The village is just off the A59, Liverpool to York main road, since the construction of the Clitheroe By-Pass. Older roads through the parish include one from Clitheroe to Whalley which passes through the Standen area and another to Burnley which passes Pendleton Hall.

Grindleton is a village and civil parish in the Ribble Valley district of the English county of Lancashire, formerly in the West Riding of Yorkshire. Its 3,700 acres sit within the Forest of Bowland. The population of the civil ward taken at the 2011 census was 772.

Downham is a village and civil parish in Lancashire, England. It is in the Ribble Valley district and at the United Kingdom 2001 census had a population of 156. The 2011 Census includes neighbouring Twiston giving a total for both parishes of 214. The village is on the north side of Pendle Hill off the A59 road about 3 miles (4.8 km) from Clitheroe. Much of the parish, including the village is part of the Forest of Bowland Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB). It adjoins the Ribble Valley parishes of Rimington, Twiston, Worston, Chatburn and Sawley, and the Pendle parish of Barley-with-Wheatley Booth.

Sawley is a village and civil parish in the Borough of Ribble Valley in Lancashire, England. The population of the civil parish was 305 at the 2001 Census, rising to 345 at the 2011 census. It is situated north-east of Clitheroe, on the River Ribble. It was historically part of the West Riding of Yorkshire.
The Lordship of Bowland is a feudal barony associated with the Forest of Bowland in Lancashire, England. The lordship fell into disuse between 1885 and 2008, during which time it was widely believed to have lapsed; it was revived in 2008.

The Honour of Clitheroe is an ancient grouping of manors and royal forests centred on Clitheroe Castle in Lancashire, England; an honour traditionally being the grant of a large landholding complex, not all of whose parts are contiguous. In the case of Clitheroe, this complex was loosely clustered around the ancient wapentake of Blackburnshire.

Great Mitton is a village and a civil parish in the Ribble Valley, Lancashire, England. It is separated from the civil parish of Little Mitton by the River Ribble, both lie about three miles from the town of Clitheroe. The combined population of both civil parishes at the 2011 census was 266. In total, Great and Little Mitton cover less than 2000 acres of the Forest of Bowland, making it the smallest township in the Forest. Historically, the village is part of the West Riding of Yorkshire, but was transferred to Lancashire for administrative purposes on 1 April 1974, under the provisions of the Local Government Act 1972.

Easington is a civil parish within the Ribble Valley district of Lancashire, England, with a population in 2001 of 52. The Census 2011 population details have been grouped with the parish of Slaidburn. Before 1974, it formed part of Bowland Rural District in the West Riding of Yorkshire. It covers just over 9000 acres.