
An anticyclone is a weather phenomenon defined as a large-scale circulation of winds around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above. Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure.
The North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) is a weather phenomenon over the North Atlantic Ocean of fluctuations in the difference of atmospheric pressure at sea level (SLP) between the Icelandic Low and the Azores High. Through fluctuations in the strength of the Icelandic Low and the Azores High, it controls the strength and direction of westerly winds and location of storm tracks across the North Atlantic.
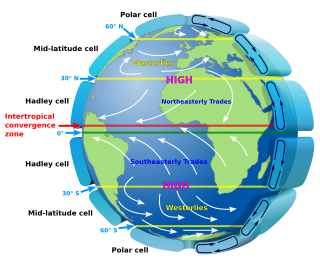
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller-scale weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory.

A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation.

In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather, while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places:

In meteorology, the synoptic scale is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1,000 km (620 mi) or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions. Most high- and low-pressure areas seen on weather maps are synoptic-scale systems, driven by the location of Rossby waves in their respective hemisphere. Low-pressure areas and their related frontal zones occur on the leading edge of a trough within the Rossby wave pattern, while high-pressure areas form on the back edge of the trough. Most precipitation areas occur near frontal zones. The word synoptic is derived from the Ancient Greek word συνοπτικός (sunoptikós), meaning "seen together".
The Siberian High is a massive collection of cold dry air that accumulates in the northeastern part of Eurasia from September until April. It is usually centered on Lake Baikal. It reaches its greatest size and strength in the winter when the air temperature near the center of the high-pressure area is often lower than −40 °C (−40 °F). The atmospheric pressure is often above 1,040 millibars (31 inHg). The Siberian High is the strongest semi-permanent high in the northern hemisphere and is responsible for both the lowest temperature in the Northern Hemisphere outside Greenland, of −67.8 °C (−90.0 °F) on 15 January 1885 at Verkhoyansk, and the highest pressure, 1083.8 mbar at Agata, Krasnoyarsk Krai, on 31 December 1968, ever recorded. The Siberian High is responsible both for severe winter cold and attendant dry conditions with little snow and few or no glaciers across Asian part of Russia, Mongolia, and China. During the summer, the Siberian High is largely replaced by the Asiatic low.
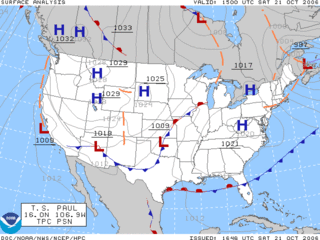
A pressure system is a peak or lull in the sea level pressure distribution. The surface pressure at sea level varies minimally, with the lowest value measured 87 kilopascals (26 inHg) and the highest recorded 108.57 kilopascals (32.06 inHg). High- and low-pressure systems evolve due to interactions of temperature differentials in the atmosphere, temperature differences between the atmosphere and water within oceans and lakes, the influence of upper-level disturbances, as well as the amount of solar heating or radiationized cooling an area receives. Pressure systems cause weather to be experienced locally. Low-pressure systems are associated with clouds and precipitation that minimize temperature changes throughout the day, whereas high-pressure systems normally associate with dry weather and mostly clear skies with larger diurnal temperature changes due to greater radiation at night and greater sunshine during the day. Pressure systems are analyzed by those in the field of meteorology within surface weather maps.

Berg wind is the South African name for a katabatic wind: a hot dry wind blowing down the Great Escarpment from the high central plateau to the coast.

Blocks in meteorology are large-scale patterns in the atmospheric pressure field that are nearly stationary, effectively "blocking" or redirecting migratory cyclones. They are also known as blocking highs or blocking anticyclones. These blocks can remain in place for several days or even weeks, causing the areas affected by them to have the same kind of weather for an extended period of time. In the Northern Hemisphere, extended blocking occurs most frequently in the spring over the eastern Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Whilst these events are linked to the occurrence of extreme weather events such as heat waves, particularly the onset and decay of these events is still not well captured in numerical weather forecasts and remains an open area of research.

The geography of South America contains many diverse regions and climates. Geographically, South America is generally considered a continent forming the southern portion of the landmass of the Americas, south and east of the Colombia–Panama border by most authorities, or south and east of the Panama Canal by some. South and North America are sometimes considered a single continent or supercontinent, while constituent regions are infrequently considered subcontinents.

Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of producing anything from cloudiness and mild showers to severe gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes. These types of cyclones are defined as large scale (synoptic) low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth. In contrast with tropical cyclones, extratropical cyclones produce rapid changes in temperature and dew point along broad lines, called weather fronts, about the center of the cyclone.

Cold air damming, or CAD, is a meteorological phenomenon that involves a high-pressure system (anticyclone) accelerating equatorward east of a north-south oriented mountain range due to the formation of a barrier jet behind a cold front associated with the poleward portion of a split upper level trough. Initially, a high-pressure system moves poleward of a north-south mountain range. Once it sloshes over poleward and eastward of the range, the flow around the high banks up against the mountains, forming a barrier jet which funnels cool air down a stretch of land east of the mountains. The higher the mountain chain, the deeper the cold air mass becomes lodged to its east, and the greater impediment it is within the flow pattern and the more resistant it becomes to intrusions of milder air.

The January 1961 nor'easter was a significant winter storm that impacted the Mid-Atlantic and New England regions of the United States. It was the second of three major snowstorms during the 1960–1961 winter. The storm ranked as Category 3, or "major", on the Northeast Snowfall Impact Scale.

A cold-core low, also known as an upper level low or cold-core cyclone, is a cyclone aloft which has an associated cold pool of air residing at high altitude within the Earth's troposphere, without a frontal structure. It is a low pressure system that strengthens with height in accordance with the thermal wind relationship. If a weak surface circulation forms in response to such a feature at subtropical latitudes of the eastern north Pacific or north Indian oceans, it is called a subtropical cyclone. Cloud cover and rainfall mainly occurs with these systems during the day.

The 2013–14 North American winter was one of the most significant for the United States, due in part to the breakdown of the polar vortex in November 2013, which allowed very cold air to travel down into the United States, leading to an extended period of very cold temperatures. The pattern continued mostly uninterrupted throughout the winter and numerous significant winter storms affected the Eastern United States, with the most notable one being a powerful winter storm that dumped ice and snow in the Southeastern United States and the Northeastern United States in mid-February. Most of the cold weather abated by the end of March, though a few winter storms did affect the Western United States towards the end of the winter.
Centers of action are extensive and almost stationary low or high pressure areas which control the movement of atmospheric disturbances over a large area. This does not mean that the position of the center is constant over a specific area but that the monthly atmospheric pressure corresponds to a high or a low pressure.

The Papagayo jet, also referred to as the Papagayo Wind or the Papagayo Wind Jet, are strong intermittent winds that blow approximately 70 km north of the Gulf of Papagayo, after which they are named. The jet winds travel southwest from the Caribbean and the Gulf of Mexico to the Pacific Ocean through a pass in the Cordillera mountains at Lake Nicaragua. The jet follows the same path as the northeast trade winds in this region; however, due to a unique combination of synoptic scale meteorology and orographic phenomena, the jet winds can reach much greater speeds than their trade wind counterparts. That is to say, the winds occur when cold high-pressure systems from the North American continent meet warm moist air over the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico, generating winds that are then funneled through a mountain pass in the Cordillera. The Papagayo jet is also not unique to this region. There are two other breaks in the Cordillera where this same phenomenon occurs, one at the Chivela Pass in México and another at the Panama Canal, producing the Tehuano (Tehuantepecer) and the Panama jets respectively.
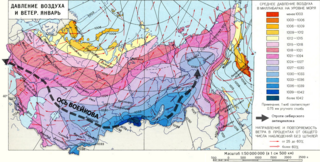
Voeykov axis is the axial portion (ridge) of a high atmospheric pressure band stretching across Eurasia roughly along the 50th parallel. It was named in honor of Alexander Voeikov, a climatologist, who studied this phenomenon.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.















