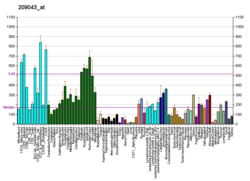
| PAPSS1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | PAPSS1 , ATPSK1, PAPSS, SK1, 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate synthase 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 603262; MGI: 1330587; HomoloGene: 81740; GeneCards: PAPSS1; OMA:PAPSS1 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Bifunctional 3'-phosphoadenosine 5'-phosphosulfate synthetase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PAPSS1 gene. [5] [6] [7]
Three-prime-phosphoadenosine 5-prime-phosphosulfate (PAPS) is the sulfate donor cosubstrate for all sulfotransferase (SULT) enzymes (Xu et al., 2000). SULTs catalyze the sulfate conjugation of many endogenous and exogenous compounds, including drugs and other xenobiotics. In humans, PAPS is synthesized from adenosine 5-prime triphosphate (ATP) and inorganic sulfate by 2 isoforms, PAPSS1 and PAPSS2 (MIM 603005).[supplied by OMIM] [7]