
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving living birth to female nymphs—who may also be already pregnant, an adaptation scientists call telescopic development—without the involvement of males. Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonize new plants. In temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn, with the insects often overwintering as eggs.

The Hemiptera or true bugs are an order of insects comprising some 50,000 to 80,000 species of groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, bed bugs and shield bugs. They range in size from 1 mm (0.04 in) to around 15 cm (6 in), and share a common arrangement of sucking mouthparts. The name "true bugs" is often limited to the suborder Heteroptera. Many insects commonly known as "bugs", especially in American English, belong to other orders; for example, the lovebug is a fly and the May bug and ladybug are beetles.
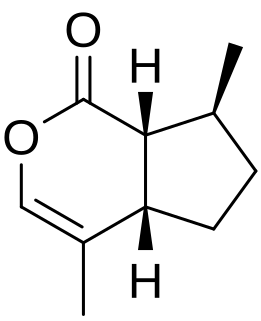
Nepetalactone is a name for multiple iridoid analog stereoisomers. Nepetalactones are produced by Nepeta cataria (catnip) and a many other plants belonging to the genus Nepeta, in which they protect these plants from herbivorous insects by functioning as insect repellents. They are also produced by many aphids, in which they are sex pheromones. Nepetalactones are cat attractants, and cause the behavioral effects that catnip induces in domestic cats. However, they affect visibly only about 2/3 of adult cats. They produce similar behavioral effects in many other Felidae, especially in lions and jaguars. McElvain and colleagues were the first to extract and name nepetalactones, which they did in 1941.

Commonly known as hellebores, the Eurasian genus Helleborus consists of approximately 20 species of herbaceous or evergreen perennial flowering plants in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae, within which it gave its name to the tribe of Helleboreae. Despite names such as "winter rose", "Christmas rose" and "Lenten rose", hellebores are not closely related to the rose family (Rosaceae). Many hellebore species are poisonous.

Green lacewings are insects in the large family Chrysopidae of the order Neuroptera. There are about 85 genera and 1,300–2,000 species in this widespread group. Members of the genera Chrysopa and Chrysoperla are very common in North America and Europe; they are very similar and many of their species have been moved from one genus to the other time and again, and in the nonscientific literature assignment to Chrysopa and Chrysoperla can rarely be relied upon. Since they are the most familiar neuropterans to many people, they are often simply called "lacewings". Since most of the diversity of Neuroptera are properly referred to as some sort of "lacewing", common lacewings is preferable.

Potyviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses that encompasses more than 30% of known plant viruses, many of which are of great agricultural significance. Currently, 228 species are placed in this family, divided among 12 genera with three unassigned species.

The Aphididae are a very large insect family in the aphid superfamily (Aphidoidea), of the order Hemiptera. Several thousand species are placed in this family, many of which are well known for being serious plant pests. They are also the family of insects containing most plant virus vectors with the green peach aphid being one of the most prevalent and indiscriminate carriers.

Woolly aphids are sucking insects that live on plant sap and produce a filamentous waxy white covering which resembles cotton or wool. The adults are winged and move to new locations where they lay egg masses. The nymphs often form large cottony masses on twigs, for protection from predators.

The Sternorrhyncha suborder of the Hemiptera contains the aphids, whiteflies, and scale insects, groups which were traditionally included in the order Homoptera. "Sternorrhyncha" refers to the rearward position of the mouthparts relative to the head.
Citrus tristeza virus (CTV) is a viral species of the genus Closterovirus that causes the most economically damaging disease to its namesake plant genus, Citrus. The disease has led to the death of millions of Citrus trees all over the world and has rendered millions of others useless for production. Farmers in Brazil and other South American countries gave it the name "tristeza", meaning sadness in Portuguese and Spanish, referring to the devastation produced by the disease in the 1930s. The virus is transmitted most efficiently by the brown citrus aphid.

The Adelgidae are a small family of the Hemiptera closely related to the aphids, and often included in the Aphidoidea with the Phylloxeridae or placed within the superfamily Phylloxeroidea as a sister of the Aphidoidea within the infraorder Aphidomorpha. The family is composed of species associated with pine, spruce, or other conifers, known respectively as "pine aphids" or "spruce aphids". This family includes the former family Chermesidae, or "Chermidae", the name of which was declared invalid by the ICZN in 1955. There is still considerable debate as to the number of genera within the family, and the classification is still unstable and inconsistent among competing authors.

Brevicoryne brassicae, commonly known as the cabbage aphid or cabbage aphis, is a destructive aphid native to Europe that is now found in many other areas of the world. The aphids feed on many varieties of produce, including cabbage, broccoli (especially), Brussels sprouts, cauliflower and many other members of the genus Brassica, but do not feed on plants outside of the family Brassicaceae. The insects entirely avoid plants other than those of Brassicaceae; even though thousands may be eating broccoli near strawberries, the strawberries will be left untouched.

Aphis is a genus of insects in the family Aphididae containing at least 600 species of aphids. It includes many notorious agricultural pests, such as the soybean aphid Aphis glycines. Many species of Aphis, such as A. coreopsidis and A. fabae, are myrmecophiles, forming close associations with ants.

Myzus persicae, known as the green peach aphid, greenfly, or the peach-potato aphid, is a small green aphid. It is the most significant aphid pest of peach trees, causing decreased growth, shrivelling of the leaves and the death of various tissues. It is also acts as a vector for the transport of plant viruses such as cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), potato virus Y (PVY) and tobacco etch virus (TEV). Potato virus Y and potato leafroll virus can be passed to members of the nightshade/potato family (Solanaceae), and various mosaic viruses to many other food crops.

Acyrthosiphon pisum, commonly known as the pea aphid, is a sap-sucking insect in the family Aphididae. It feeds on several species of legumes worldwide, including forage crops, such as pea, clover, alfalfa, and broad bean, and ranks among the aphid species of major agronomical importance. The pea aphid is a model organism for biological study whose genome has been sequenced and annotated.

Adelges is a genus of insects which feed on conifers. Excepting galls formed by the spruce gall midge, galls are caused by aphid-like insects of the superfamily Phylloxeroidea commonly known as the spruce gall adelgids. They have complex life cycles, some species feeding exclusively on spruce, others feeding on spruce and an alternate conifer. However, galls characteristic of each species are formed only on spruce. Six generations are usually needed to complete the 2-year cycle, and in the case of species having an alternate host, winged adults about 2 mm long are formed only in the generations that move from one host to the other.

Phylloxeridae is a small family of plant-parasitic hemipterans closely related to aphids with only 75 described species. This group comprises two subfamilies and 11 genera with one that is fossil. The genus type is Phylloxera. The Phylloxeridae species are usually called Phylloxerans or Phylloxerids.

Aphidinae is an aphid subfamily in the family Aphididae.

Megoura viciae is a large, green aphid in the family Aphididae native to Europe that feeds on plants in the genus Vicia. They are commonly known as vetch aphids for this reason.

Aphidomorpha is an infraorder within the insect order Sternorrhyncha which includes the aphids and their allies in the superfamilies Adelgoidea, Phylloxeroidea and Aphidoidea. This group also includes numerous fossil taxa of uncertain placement.


















