Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving live birth to female nymphs—who may also be already pregnant, an adaptation scientists call telescoping generations—without the involvement of males. Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonize new plants. In temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn, with the insects often overwintering as eggs.

Tsuga is a genus of conifers in the subfamily Abietoideae of Pinaceae, the pine family. The English-language common name "hemlock" arose from a perceived similarity in the smell of its crushed foliage to that of the unrelated plant poison hemlock. Unlike the latter, Tsuga species are not poisonous.

Mount Rogers is the highest natural point in Virginia, United States, with a summit elevation of 5,729 feet (1,746 m) above mean sea level. The summit straddles the border of Grayson and Smyth Counties, Virginia, about 6.45 miles (10.38 km) WSW of Troutdale, Virginia. Most of the mountain is contained within the Lewis Fork Wilderness, while the entire area is part of the Mount Rogers National Recreation Area, which itself is a part of the Jefferson National Forest.

The Aphididae are a very large insect family in the aphid superfamily (Aphidoidea), of the order Hemiptera. These insects suck the sap from plant leaves. Several thousand species are placed in this family, many of which are considered plant/crop pests. They are the family of insects containing most plant virus vectors with the green peach aphid being one of the most prevalent and indiscriminate carriers.

Woolly aphids are sap-sucking insects that produce a filamentous waxy white covering which resembles cotton or wool. The adults are winged and move to new locations where they lay egg masses. The nymphs often form large cottony masses on twigs, for protection from predators.

Adelges tsugae, the hemlock woolly adelgid or HWA, is an insect of the order Hemiptera native to East Asia. It feeds by sucking sap from hemlock and spruce trees. In its native range, HWA is not a serious pest because populations are managed by natural predators and parasitoids and by host resistance. In eastern North America it is a destructive pest that threatens the eastern hemlock and the Carolina hemlock. HWA is also found in western North America, where it has likely been present for thousands of years. In western North America, it primarily attacks western hemlock Tsuga heterophylla and has only caused minor damage due to natural predators and host resistance. Accidentally introduced to North America from Japan, HWA was first found in the eastern United States near Richmond, Virginia, in 1951. The pest is now found from northern Georgia to coastal Maine and southwestern Nova Scotia as well as areas of western Michigan near the eastern Lake Michigan shoreline. As of 2015, HWA has affected 90% of the geographic range of eastern hemlock in North America.

The Sternorrhyncha suborder of the Hemiptera contains the aphids, whiteflies, and scale insects, groups which were traditionally included in the now-obsolete order "Homoptera". "Sternorrhyncha" refers to the rearward position of the mouthparts relative to the head.
The gall adelgid is an adelgid species that produces galls in spruce trees. They infect the new buds of native spruce trees in the foothills of the Rocky Mountains in the spring. They also attack blue spruce to a lesser degree. The insects complete two generations within the year. They require two different trees for its life cycle, the second being the Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir. They may also attack Sitka, Engelmann, or white spruce. The many different species of adelgids produce different galls on different spruce species.

Pine and fir trees, grown purposely for use as Christmas trees, are vulnerable to a wide variety of pests, weeds and diseases. Many of the conifer species cultivated face infestations and death from such pests as the balsam woolly adelgid and other adelgids. Aphids are another common insect pest. Christmas trees are also vulnerable to fungal pathogens and their resultant illnesses such as root rot, and, in the U.S. state of California, sudden oak death. Douglas-fir trees in particular are vulnerable to infections from plant pathogens such as R. pseudotsugae.

Laricobius is a genus of beetles in the family Derodontidae, the tooth-necked fungus beetles.
The balsam woolly adelgid is small wingless insect that infests and kills firs. In their native Europe they are a minor parasite on silver fir and Sicilian fir, but they have become a threat especially to balsam fir and Fraser fir after they were introduced to the United States around the beginning of the 20th century. Because this species is not native to North America, the Fraser fir has not evolved any type of defense against it.

The pineapple gall adelgid is a species of conifer-feeding insect that forms pineapple-shaped plant galls on its host species, commonly Norway and Sitka spruce. The adelgids are pear-shaped, soft-bodied green insects with long antennae, closely related to the aphid. Adelges lays up to one hundred eggs at a time, one on each needle. Adelges abietis is one of the most common species; synonyms are A. gallarum-abietis, Chermes abietis and Sacciphantes abietis.

Adelges is a genus of insects which feed on conifers. They have complex life cycles, some species feeding exclusively on spruce, others feeding on spruce and an alternate conifer. However, galls characteristic of each species are formed only on spruce. Six generations are usually needed to complete the 2-year cycle, and in the case of species having an alternate host, winged adults about 2 mm long are formed only in the generations that move from one host to the other.

Phylloxeridae is a small family of plant-parasitic hemipterans closely related to aphids with only 75 described species. This group comprises two subfamilies and 11 genera with one that is fossil. The genus type is Phylloxera. The Phylloxeridae species are usually called phylloxerans or phylloxerids.

Eriosoma lanigerum, the woolly apple aphid, woolly aphid or American blight, is an aphid in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from plants.

Species which are not native to a forest ecosystem can act as an agent of disturbance, changing forest dynamics as they invade and spread. Invasive insects and pathogens (diseases) are introduced to the United States through international trade, and spread through means of natural and human-dispersal. Invasive insects and pathogens are a serious threat to many forests in the United States and have decimated populations of several tree species, including American chestnut, American elm, eastern hemlock, whitebark pine, and the native ash species. The loss of these tree species is typically rapid with both short and long-term impacts to the forest ecosystem.

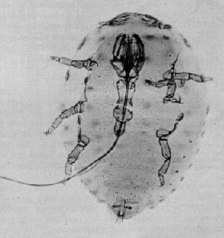
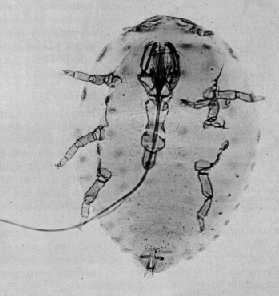
Laricobius nigrinus is a species of tooth-necked fungus beetle in the family Derodontidae. It is native to western North America, and it is being studied as a biological control agent for the hemlock woolly adelgid. It was first released in 2003 and continues to be reared and released across the Northeast to control infestations.

Pineus is a genus of aphids in the family Adelgidae. There are more than 20 described species in Pineus.

Sasajiscymnus tsugae, formerly Pseudoscymnus tsugae, is a species of insect in the family Coccinellidae. It feeds on the hemlock woolly adelgid.
Nathan Peterson Havill is an American entomologist and evolutionary biologist. Havill is a Research Entomologist with the United States Forest Service in Hamden, Connecticut and is internationally recognized on the phylogeny of Adelgidae.