
Panhard was a French motor vehicle manufacturer that began as one of the first makers of automobiles. It was a manufacturer of light tactical and military vehicles. Its final incarnation, now owned by Renault Trucks Defense, was formed by the acquisition of Panhard by Auverland in 2005, and then by Renault in 2012. In 2018 Renault Trucks Defense, ACMAT and Panhard combined under a single brand, Arquus.

Crosley was a small, independent American manufacturer of economy cars or subcompact cars, bordering on microcars. At first called the Crosley Corporation and later Crosley Motors Incorporated, the Cincinnati, Ohio, firm was active from 1939 to 1952, interrupted by World War II production. Their station wagons were the most popular model, but also offered were sedans, pickups, convertibles, a sports car, and even a tiny jeep-like vehicle. For export, the cars were badged Crosmobile.

The Apperson was a brand of American automobile manufactured from 1901 to 1926 in Kokomo, Indiana.

The Atla is a French automobile that was manufactured from 1957 to 1959 in the commune of Garches in the western suburbs of Paris.
Berliet was a French manufacturer of automobiles, buses, trucks and military vehicles among other vehicles based in Vénissieux, outside of Lyon, France. Founded in 1899, and apart from a five-year period from 1944 to 1949 when it was put into 'administration sequestre' it was in private ownership until 1967 when it then became part of Citroën, and subsequently acquired by Renault in 1974 and merged with Saviem into a new Renault Trucks company in 1978. The Berliet marque was phased out by 1980.

The Renault Estafette is a light commercial front-wheel drive van, first introduced in 1959 and made by the French automaker Renault between 1959 and 1980, initially using the water-cooled Renault Ventoux engine, then later the Cléon-Fonte engine in a range of body styles. It was replaced by the Renault Trafic.

The Renault NN, generally known to contemporaries simply as the Renault 6 CV, is a compact car or small family car manufactured by Renault from 1924 until 1930.

The Citroën Type C was a light car made by the French Citroën car company between 1922 and 1926 with almost 81,000 units being made. Known as Citroën 5HP or 5CV in France and 7.5HP in Britain, it was the second model of automobile designed and marketed by André Citroën, between 1922 and 1926. It followed the 10HP "Type A " (1919), then 10HP "B2" (1921); they were the first European mass-produced cars.

The Peugeot 601 was a range-topping car produced between 1934 and 1935 by Peugeot. It had its formal launch on 5 May 1934 and marked a return by the manufacturer to six-cylinder engines.

The Renault MT is a compact sports car manufactured by Renault from 1923 until 1925.
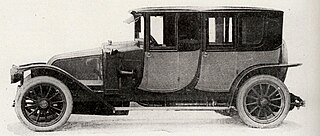
The Renault GS was a mid-size car manufactured by Renault from 1919 to 1920. It was also known as the 10CV.

The Lincoln L series is the first automobile that was produced by the Lincoln Motor Company. Introduced in 1920, the L series would continue to be produced after the bankruptcy of Lincoln in 1922 and its purchase by Ford Motor Company.

The Bignan was a French automobile manufactured between 1918 and 1931 on the north side of central Paris, in Courbevoie. The business was created, and till the mid-1920s, headed-up by Jacques Bignan.

The Citroën B10 is an automobile produced by Citroën at André Citroën's factory in central Paris between 1924 and 1925.

Th. Schneider was a French automobile manufacturer.

Octo was a French automobile manufactured at Courbevoie by Louis Vienne between 1921 and 1928.

Automobiles Oméga-Six was a French automobile manufactured in the Paris region by Gabriel Daubeck between 1922 and 1930.

The Vivaquatre is a car produced by Renault between 1932 and 1939. Its large 4-cylinder engine placed it initially in the 10CV car tax class, though a larger engine later made it a contender in the 11CV class.

The Renault Nervasport was a straight-eight engined sporting luxury automobile introduced by Renault in March 1932 and produced until 1935. It was based on the larger and heavier Nervastella. A more streamlined version called the Nerva Grand Sport appeared in 1935 and replaced the Nervasport, remaining in production until the summer of 1937. As with many Renaults during the 1930s, type changes as well as small often cosmetic facelifts and upgrades appeared frequently.
Pichon-Parat was a French carrosserie based in the commune of Sens, in the department of Yonne. Established in 1952, it was known for producing custom cabriolet, coupé, estate car, and shooting brake conversions of established models from major automakers, and for building their own distinctive sporting models with completely original bodywork.



















