Ancient Egyptian religion was a complex system of polytheistic beliefs and rituals that formed an integral part of ancient Egyptian culture. It centered on the Egyptians' interactions with many deities believed to be present in, and in control of the world. Rituals such as prayer and offerings were provided to the gods to gain their favor. Formal religious practice centered on the pharaohs, the rulers of Egypt, believed to possess divine powers by virtue of their positions. They acted as intermediaries between their people and the gods, and were obligated to sustain the gods through rituals and offerings so that they could maintain Ma'at, the order of the cosmos, and repel Isfet, which was chaos. The state dedicated enormous resources to religious rituals and to the construction of temples.

Aten also Aton, Atonu, or Itn was the focus of Atenism, the religious system formally established in ancient Egypt by the late Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh Amenhotep IV, better known as Akhenaten. Exact dating for the 18th dynasty is contested, though a general date range places the dynasty in the years 1550 to 1292 B.C.E.. The worship of Aten and the coinciding rule of Akhenaten are major identifying characteristic of a period within the 18th dynasty referred to as the Amarna Period.

Horus, also known as Hor in Ancient Egyptian, is one of the most significant ancient Egyptian deities who served many functions, most notably as god of kingship, healing, protection, the sun and the sky. He was worshipped from at least the late prehistoric Egypt until the Ptolemaic Kingdom and Roman Egypt. Different forms of Horus are recorded in history, and these are treated as distinct gods by Egyptologists. These various forms may be different manifestations of the same multi-layered deity in which certain attributes or syncretic relationships are emphasized, not necessarily in opposition but complementary to one another, consistent with how the Ancient Egyptians viewed the multiple facets of reality. He was most often depicted as a falcon, most likely a lanner falcon or peregrine falcon, or as a man with a falcon head.

The Osiris myth is the most elaborate and influential story in ancient Egyptian mythology. It concerns the murder of the god Osiris, a primeval king of Egypt, and its consequences. Osiris's murderer, his brother Set, usurps his throne. Meanwhile, Osiris's wife Isis restores her husband's body, allowing him to posthumously conceive their son, Horus. The remainder of the story focuses on Horus, the product of the union of Isis and Osiris, who is at first a vulnerable child protected by his mother and then becomes Set's rival for the throne. Their often violent conflict ends with Horus's triumph, which restores maat to Egypt after Set's unrighteous reign and completes the process of Osiris's resurrection.

Akhenaten, also spelled Akhenaton or Echnaton, was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning c. 1353–1336 or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV.

Nut, also known by various other transcriptions, is the goddess of the sky, stars, cosmos, mothers, astronomy, and the universe in the ancient Egyptian religion. She was seen as a star-covered nude woman arching over the Earth, or as a cow. She was depicted wearing the water-pot sign (nw) that identifies her. Nut is comparable to the Mesopotamian goddess Ninhursag also sharing her role as mother of the gods.

Shu was one of the primordial Egyptian gods, spouse and brother to the goddess Tefnut, and one of the nine deities of the Ennead of the Heliopolis cosmogony. He was the god of peace, lions, air, and wind.

Unut, also known as Wenut or Wenet, was a prehistoric Egyptian hare and snake goddess of fertility and new birth.

Atenism, also known as the Aten religion, the Amarna religion, and the Amarna heresy, was a religion in ancient Egypt. It was founded by Akhenaten, a pharaoh who ruled the New Kingdom under the Eighteenth Dynasty. The religion is typically described as monotheistic or monolatristic, although some Egyptologists argue that it was actually henotheistic. Atenism was centred on the cult of Aten, a god depicted as the disc of the Sun. Aten was originally an aspect of Ra, Egypt's traditional solar deity, though he was later asserted by Akhenaten as being the superior of all deities. In the 14th century BC, Atenism was Egypt's state religion for around 20 years, and Akhenaten met the worship of other gods with persecution; he closed many traditional temples, instead commissioning the construction of Atenist temples, and also suppressed religious traditionalists. However, subsequent pharaohs toppled the movement in the aftermath of Akhenaten's death, thereby restoring Egyptian civilization's traditional polytheistic religion. Large-scale efforts were then undertaken to remove from Egypt and Egyptian records any presence or mention of Akhenaten, Atenist temples, and Atenist assertions of a uniquely supreme god.

The Eye of Ra or Eye of Re is a being in ancient Egyptian mythology that functions as a feminine counterpart to the sun god Ra and a violent force that subdues his enemies. The eye is an extension of Ra's power, equated with the disk of the sun, but it often behaves as an independent goddess. This goddess can be equated with several particular deities, including Hathor, Sekhmet, Bastet, Raet-Tawy, and Mut. The eye goddess acts as mother, sibling, consort, and daughter of the sun god. She is his partner in the creative cycle in which he begets the renewed form of himself that is born at dawn. The eye's violent aspect defends Ra against the agents of disorder that threaten his rule. This dangerous aspect of the eye goddess is often represented by a lioness or by the uraeus, or cobra, a symbol of protection and royal authority. The Eye of Ra is similar to the Eye of Horus, which belongs to a different god, Horus, but represents many of the same concepts. The disastrous effects when the eye goddess rampages out of control and the efforts of the gods to return her to a benign state are a prominent motif in Egyptian mythology.

The four sons of Horus were a group of four gods in ancient Egyptian religion, who were essentially the personifications of the four canopic jars, which accompanied mummified bodies. Since the heart was thought to embody the soul, it was left inside the body. The brain was thought only to be the origin of mucus, so it was reduced to liquid, removed with metal hooks, and discarded. This left the stomach, liver, large intestines, and lungs, which were removed, embalmed and stored, each organ in its own jar. There were times when embalmers deviated from this scheme: during the 21st Dynasty they embalmed and wrapped the viscera and returned them to the body, while the canopic jars remained empty symbols.

The ancient Egyptian noble Parennefer was Akhenaten's close advisor before he came to the throne, and in later times served as his Royal Butler, an office which brought him into intimate contact with the king. His titles include "The King's Cup Bearer," "Washer of the King's Hands," "Chief Craftsman," and "Overseer of All the Works in the Mansion of Aten." He was instrumental in imposing the "Amarna style" in architecture.
In ancient Egyptian religion, Aani is the dog-headed ape sacred to the Egyptian god Thoth. "One of the Egyptian names of the Cynocephalus Baboon, which was sacred to the god Thoth."

Ancient Egyptian deities are the gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistory. Deities represented natural forces and phenomena, and the Egyptians supported and appeased them through offerings and rituals so that these forces would continue to function according to maat, or divine order. After the founding of the Egyptian state around 3100 BC, the authority to perform these tasks was controlled by the pharaoh, who claimed to be the gods' representative and managed the temples where the rituals were carried out.

The Book of the Earth is an Ancient Egyptian funerary text that has been called many names such as The Creation of the Sun Disk and the Book of Aker. The Book primarily appears on the tombs of Merneptah, Twosret, Ramesses III, Ramesses VI, and Ramesses VII and serves as a counterpart to the Book of Caverns.

Werethekau was an ancient Egyptian deity. She served as the personification of supernatural powers.

Ra or Re was the ancient Egyptian deity of the sun. By the Fifth Dynasty, in the 25th and 24th centuries BC, he had become one of the most important gods in ancient Egyptian religion, identified primarily with the noon-day sun. Ra ruled in all parts of the created world: the sky, the earth, and the underworld. He was the god of the sun, order, kings and the sky.

Egyptian mythology is the collection of myths from ancient Egypt, which describe the actions of the Egyptian gods as a means of understanding the world around them. The beliefs that these myths express are an important part of ancient Egyptian religion. Myths appear frequently in Egyptian writings and art, particularly in short stories and in religious material such as hymns, ritual texts, funerary texts, and temple decoration. These sources rarely contain a complete account of a myth and often describe only brief fragments.
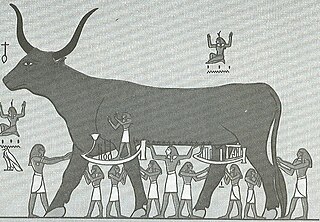
The Book of the Heavenly Cow, or the Book of the Cow of Heaven, is an Ancient Egyptian text thought to have originated during the Amarna Period and, in part, describes the reasons for the imperfect state of the world in terms of humankind's rebellion against the supreme sun god, Ra. Divine punishment was inflicted through the goddess Hathor, with the survivors suffering through separation from Ra, who now resided in the sky on the back of Nut, the heavenly cow.

A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The Oxford Dictionary of English defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater than those of ordinary humans, but who interacts with humans, positively or negatively, in ways that carry humans to new levels of consciousness, beyond the grounded preoccupations of ordinary life".



















