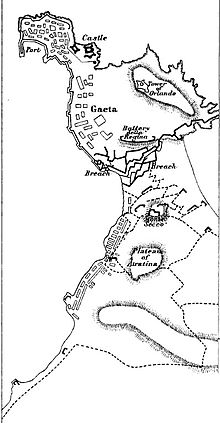
Gaeta is a seaside resort in the province of Latina, in Lazio, Italy. Set on a promontory stretching towards the Gulf of Gaeta, it is 96.5 kilometres from Naples and 133 km (83 mi) from Rome.

The Battle of Maida, fought on 4 July 1806 was a battle between the British expeditionary force and a French force outside the town of Maida in Calabria, Italy during the Napoleonic Wars. John Stuart led 5,236 Anglo-Sicilian troops to victory over about 5,400 Franco-Italian-Polish troops under the command of French general Jean Reynier, inflicting significant losses while incurring relatively few casualties. Maida is located in the toe of Italy, about 30 kilometres (19 mi) west of Catanzaro.

The Neapolitan War, also known as the Austro-Neapolitan War, was a conflict between the Napoleonic Kingdom of Naples and the Austrian Empire. It started on 15 March 1815, when King Joachim Murat declared war on Austria, and ended on 20 May 1815, with the signing of the Treaty of Casalanza. The war occurred during the Hundred Days between Napoleon's return from exile and before he left Paris to be decisively defeated at the Battle of Waterloo. The war was triggered by a pro-Napoleon uprising in Naples and ended with a decisive Austrian victory at the Battle of Tolentino, after which Bourbon monarch Ferdinand IV was reinstated as King of Naples and Sicily. However, the intervention by Austria caused resentment in Italy, which further spurred on the drive towards Italian unification.

The siege of Gaeta was the concluding event of the war between the Kingdom of Sardinia and the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies, part of the unification of Italy. It started on 5 November 1860 and ended on 13 February 1861, and took place in Gaeta, in today's Southern Lazio (Italy).
The siege of Gaeta can refer to several historical sieges of the city of Gaeta in Italy:

The Battle of the Panaro was a victory for King Joachim Murat's Neapolitan forces over a smaller Austrian force under Frederick Bianchi on 3 April 1815 early in the Neapolitan War. This defeat on the banks on the Panaro River, just south of Modena forced the Austrians to retreat behind the Po River.
The Battle of Carpi took place during the Neapolitan War between a brigade of Neapolitan soldiers under the command of Guglielmo Pepe and an Austrian force under the command of Baron Frimont. The battle took place in the town of Carpi and resulted in an Austrian victory, with the Neapolitans being driven from the town.

The Battle of Casaglia was a part of the Neapolitan War. An Austrian force under the command of Johann Friedrich von Mohr engaged a Neapolitan force under their commander, Joachim Murat. The battle took place around the village of Casaglia, seven miles northwest of Ferrara, and resulted in the Austrians recapturing the village from Murat.
The Battle of Ronco took place during the Neapolitan War on 21 April 1815 in the village of Ronco, just south of Forlì. The main Neapolitan army, retreating following the disaster at the Battle of Occhiobello, was being pursued by an Austrian corps under the command of Adam Albert von Neipperg. The Neapolitans, commanded by their king, Joachim Murat, turned to check the Austrians at the Ronco River. The Neapolitans rear guard was defeated by a smaller advanced Austrian force, compelling Murat to retreat further south to the Savio River. The Austrians suffered light casualties, whereas nearly 1,000 Neapolitans were killed or wounded and more deserted Murat altogether.

The Battle of Cesenatico was a minor battle in the Neapolitan War that took place on 23 April 1815 in the town of Cesenatico on Adriatic coast.

The Battle of Pesaro was a minor battle in the Neapolitan War that took place on 28 April 1815 in the town of Pesaro.
The Battle of Scapezzano was a short engagement during the Neapolitan War on 1 May 1815 between an Austrian corps under Adam Albert von Neipperg and a Neapolitan division under Michele Carrascosa.

The Battle of Castel di Sangro was a minor battle in the Neapolitan War that took place on 13 May 1815 in the town of Castel di Sangro in central Italy. The battle resulted in the Neapolitan force being routed.

The Battle of San Germano was the final battle in the Neapolitan War between an Austrian force commanded by Laval Nugent von Westmeath and the King of Naples, Joachim Murat. The battle started on 15 May 1815 and ended on 17 May, after the remaining Neapolitan force was routed at Mignano.

The siege of Ancona took place during the Neapolitan War. It took place beginning on 5 May 1815 and persisted until 30 May 1815. The battle took place mere days after the Battle of Tolentino on 3 May 1815.
The Treaty of Casalanza, which ended the Neapolitan War, was signed on 20 May 1815 between the Napoleonic Kingdom of Naples on the one hand and the Austrian Empire, as well as the Great Britain, on the other. The signature occurred in a patrician villa, owned by the Lanza family, in what is now the commune of Pastorano, Campania, southern Italy.

The Battle of Campo Tenese saw two divisions of the Imperial French Army of Naples led by Jean Reynier attack the left wing of the Royal Neapolitan Army under Roger de Damas. Though the defenders were protected by field fortifications, a French frontal attack combined with a turning movement rapidly overran the position and routed the Neapolitans with heavy losses. The action occurred at Campotenese, a little mountain village in the municipality of Morano Calabro in the north of Calabria. The battle was fought during the War of the Third Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars.

The siege of Gaeta saw the fortress city of Gaeta and its Neapolitan garrison under General Louis of Hesse-Philippsthal besieged by an Imperial French corps led by Marshal André Masséna. After a prolonged defense in which Hesse was severely wounded, Gaeta surrendered, and Masséna granted its garrison generous terms.

The Invasion of Naples was a front during the War of the Third Coalition, in 1806, when an army of the French Empire led by Marshal André Masséna marched from Northern Italy into the Kingdom of Naples, an ally of the Coalition against France ruled by King Ferdinand IV. The Neapolitan army was defeated at Campo Tenese and rapidly disintegrated. The invasion was eventually successful despite some setbacks, including the prolonged Siege of Gaeta, the British victory at Maida, and a stubborn guerrilla war by the peasantry against the French. Total success eluded the French because Ferdinand withdrew to his domain in Sicily, where he was protected by the Royal Navy and a British Army garrison. In 1806, Emperor Napoleon appointed his brother Joseph Bonaparte to rule over Southern Italy as king.

The Army of the Kingdom of Naples was the land force of the Kingdom of Naples. It was in service from 1806 to 1815, reborn from the Army of the Two Sicilies after the French invasion of Naples. It served alongside Napoleon’s Grande Armée in various campaigns of the Napoleonic Wars, until its final demise in the Neapolitan War.