Sitka Rocky Gutierrez Airport | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||
| Owner | State of Alaska DOT&PF | ||||||||||
| Serves | Sitka, Alaska | ||||||||||
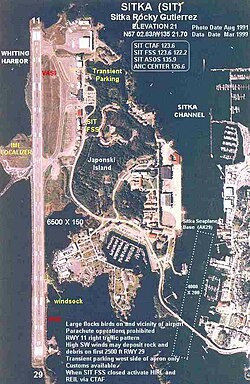
| Location | Japonski Island | ||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 26 ft / 8 m | ||||||||||
| Coordinates | 57°02′50″N135°21′42″W / 57.04722°N 135.36167°W | ||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Statistics (2011) | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Source: Federal Aviation Administration [1] | |||||||||||
Sitka Rocky Gutierrez Airport( IATA : SIT, ICAO : PASI, FAA LID : SIT) is a state-owned, public-use airport located west of the central business district of Sitka, a city and borough in the U.S. state of Alaska.
Contents
- Facilities and aircraft
- Historical airline service
- Airlines and destinations
- Passenger
- Top destinations
- Media appearances
- See also
- References
- External links
The airport is named after Sitka's former mayor Rocky Gutierrez. It features a single terminal with jetway with air service operated year-round by Alaska Airlines. There is a single paved runway located on a causeway that juts off Japonski Island. Deceased tuberculosis patients from the nearby SEARHC/Mt. Edgecumbe Hospital were buried on airport grounds and had to be relocated during construction. That section of the airport is still unofficially called The Mausoleum.
As per Federal Aviation Administration records, the airport had 68,197 passenger boardings (enplanements) in calendar year 2008, [2] 62,498 enplanements in 2009, and 64,536 in 2010. [3] It is included in the National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2015-2019, which categorized it as a primary commercial service (nonhub) airport (more than 10,000 enplanements per year) based on 68,222 enplanements in 2012. [4]
