In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously move and deform (flow) under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are substances which cannot resist any shear force applied to them.
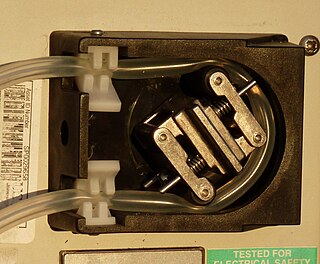
A peristaltic pump, also commonly known as a roller pump, is a type of positive displacement pump used for pumping a variety of fluids. The fluid is contained in a flexible tube fitted inside a circular pump casing. Most peristaltic pumps work through rotary motion, though linear peristaltic pumps have also been made. The rotor has a number of "wipers" or "rollers" attached to its external circumference, which compress the flexible tube as they rotate by. The part of the tube under compression is closed, forcing the fluid to move through the tube. Additionally, as the tube opens to its natural state after the rollers pass, more fluid is drawn into the tube. This process is called peristalsis and is used in many biological systems such as the gastrointestinal tract. Typically, there will be two or more rollers compressing the tube, trapping a body of fluid between them. The body of fluid is transported through the tube, toward the pump outlet. Peristaltic pumps may run continuously, or they may be indexed through partial revolutions to deliver smaller amounts of fluid.
A propellant is a mass that is expelled or expanded in such a way as to create a thrust or another motive force in accordance with Newton's third law of motion, and "propel" a vehicle, projectile, or fluid payload. In vehicles, the engine that expels the propellant is called a reaction engine. Although technically a propellant is the reaction mass used to create thrust, the term "propellant" is often used to describe a substance which contains both the reaction mass and the fuel that holds the energy used to accelerate the reaction mass. For example, the term "propellant" is often used in chemical rocket design to describe a combined fuel/propellant, although the propellants should not be confused with the fuel that is used by an engine to produce the energy that expels the propellant. Even though the byproducts of substances used as fuel are also often used as a reaction mass to create the thrust, such as with a chemical rocket engine, propellant and fuel are two distinct concepts.

A Cartesian diver or Cartesian devil is a classic science experiment which demonstrates the principle of buoyancy and the ideal gas law. The first written description of this device is provided by Raffaello Magiotti, in his book Renitenza certissima dell'acqua alla compressione published in 1648. It is named after René Descartes as the toy is said to have been invented by him.

A water gun is a type of toy gun designed to shoot jets of water. Similar to water balloons, the primary purpose of the toy is to soak another person in a recreational game such as water fight.

A bottle cap or bottle top is a common closure for the top opening of a bottle. A cap is sometimes colorfully decorated with the logo of the brand of contents. Metal caps with plastic backing are used for glass bottles, sometimes wrapped in decorative foil. Metal caps are usually either steel or aluminum, and of the crown cork type. Flip-top caps preceded such caps.

Aerosol spray is a type of dispensing system which creates an aerosol mist of liquid particles. It comprises a can or bottle that contains a payload, and a propellant under pressure. When the container's valve is opened, the payload is forced out of a small opening and emerges as an aerosol or mist.

Bottled gas is a term used for substances which are gaseous at standard temperature and pressure (STP) and have been compressed and stored in carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, or composite containers known as gas cylinders.

A bag-in-box or BiB is a container for the storage and transportation of liquids. It consists of a strong bladder, usually made of several layers of metallised film or other plastics, seated inside a corrugated fiberboard box.

A gas cylinder is a pressure vessel for storage and containment of gases at above atmospheric pressure. Gas storage cylinders may also be called bottles. Inside the cylinder the stored contents may be in a state of compressed gas, vapor over liquid, supercritical fluid, or dissolved in a substrate material, depending on the physical characteristics of the contents. A typical gas cylinder design is elongated, standing upright on a flattened or dished bottom end or foot ring, with the cylinder valve screwed into the internal neck thread at the top for connecting to the filling or receiving apparatus.

A closure is a device used to close or seal a container such as a bottle, jug, jar, tube, or can. A closure may be a cap, cover, lid, plug, liner, or the like. The part of the container to which the closure is applied is called the finish.

A keg is a small cask used for storing liquids. Wooden kegs made by a cooper were used to transport nails, gunpowder, and a variety of liquids. Nowadays a keg is normally constructed of stainless steel, although aluminium can be used if it is coated with plastic on the inside. It is commonly used to store, transport, and serve beer. Other alcoholic or non-alcoholic drinks, carbonated or non-carbonated, may be housed in a keg as well. Carbonated drinks are generally kept under pressure in order to maintain carbon dioxide in solution, preventing the beverage from becoming flat.

A soap dispenser is a device that, when manipulated or triggered appropriately, dispenses soap. They can be automatic or manually operated by a handle and are often found in public toilets or private bathrooms

A surgical drain is a tube used to remove pus, blood or other fluids from a wound, body cavity, or organ. They are commonly placed by surgeons or interventional radiologists after procedures or some types of injuries, but they can also be used as an intervention for decompression. There are several types of drains, and selection of which to use often depends on the placement site and how long the drain is needed.

A spray bottle is a bottle that can squirt, spray or mist fluids.

An eye dropper, also called Pasteur pipette or simply dropper, is a device used to transfer small quantities of liquids. They are used in the laboratory and also to dispense small amounts of liquid medicines. A very common use was to dispense eye drops into the eye. The commonly recognized form is a glass tube tapered to a narrow point and fitted with a rubber bulb at the top, although many styles of both plastic and glass droppers exist. The combination of the pipette and rubber bulb has also been referred to as a teat pipette. The Pasteur pipette name is from the French scientist Louis Pasteur, who used a variant of them extensively during his research. In the past, there was no equipment to transfer a chemical solution without exposing it to the external environment. The hygiene and purity of chemical compounds is necessary for the expected result of each experiment. The eye dropper, both glass and plastic types, can be sterilized and plugged with a rubber bulb at the open end of the pipette preventing any contamination from the atmosphere. Generally, they are considered cheap enough to be disposable, however, so long as the glass point is not chipped, the eye dropper may be washed and reused indefinitely.

A tube, squeeze tube, or collapsible tube is a collapsible package which can be used for viscous liquids such as toothpaste, artist's paint, adhesive, caulk, & ointments. Basically, a tube is a cylindrical, hollow piece with a round or oval profile, made of plastic, paperboard, aluminum, or other metal. In general, on one end of the tube body there is a round orifice, which can be closed by different caps and closures. The orifice can be shaped in many different ways: plastic nozzles in various styles and lengths are most typical. The other end is sealed either by welding or by folding.

A foam pump, or squeeze foamer and dispensing device is a non-aerosol way of dispensing liquid materials. The foam pump outputs the liquid in the form of foam and it is operated by squeezing. The parts of the foam pump, mostly made from polypropylene (PP), are similar to those of other pump devices. The foaming pump often comes with a protective cap.

A pump dispenser is used on containers of liquids to help dispensing. They might be used on bottles, jars, or tubes. Often the contents are viscous liquids such as creams and lotions. Some are metered to provide uniform usage. Some mix contents from two or more sources prior to dispensing.

A fuel container is a container such as a steel can, bottle, drum, etc. for transporting, storing, and dispensing various fuels.


















