The aorta is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart, branching upwards immediately after, and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits at the aortic bifurcation into two smaller arteries. The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation.

Coronary circulation is the circulation of blood in the arteries and veins that supply the heart muscle (myocardium). Coronary arteries supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. Cardiac veins then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the brain, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the level of consciousness of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks, in which the heart muscle is damaged by oxygen starvation. Such interruptions are usually caused by coronary ischemia linked to coronary artery disease, and sometimes to embolism from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels.

In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.

The internal carotid artery is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain.

The celiacartery, also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in humans, it is one of three anterior/ midline branches of the abdominal aorta.

The ophthalmic artery (OA) is an artery of the head. It is the first branch of the internal carotid artery distal to the cavernous sinus. Branches of the ophthalmic artery supply all the structures in the orbit around the eye, as well as some structures in the nose, face, and meninges. Occlusion of the ophthalmic artery or its branches can produce sight-threatening conditions.

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

The facial artery is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face.

In human anatomy, the superficial temporal artery is a major artery of the head. It arises from the external carotid artery when it splits into the superficial temporal artery and maxillary artery.

The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue.

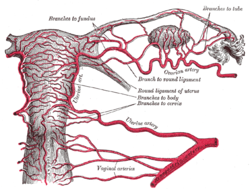
The uterine artery is an artery that supplies blood to the uterus in females.

The vaginal artery is an artery in females that supplies blood to the vagina and the base of the bladder.

The middle rectal artery is an artery in the pelvis that supplies blood to the rectum.

The thyrocervical trunk is a short artery of the neck. It arises from the subclavian artery, then promptly divides into its branches: the inferior thyroid artery, suprascapular artery, and (sometimes) the transverse cervical artery.

The right colic artery is an artery of the abdomen, a branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the ascending colon. It divides into two terminal branches - an ascending branch and a descending branch - which form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and ileocolic artery (respectively).

The middle colic artery is an artery of the abdomen; a branch of the superior mesenteric artery distributed to parts of the ascending and transverse colon. It usually divides into two terminal branches - a left one and a right one - which go on to form anastomoses with the left colic artery, and right colic artery (respectively), thus participating in the formation of the marginal artery of the colon.

The lateral circumflex femoral artery is an artery in the upper thigh. It is usually a branch of the profunda femoris artery, and produces three branches. It is mostly distributed to the muscles of the lateral thigh, supplying arterial blood to muscles of the knee extensor group.

The lacrimal artery is an artery of the orbit. It is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It accompanies the lacrimal nerve along the upper border of the lateral rectus muscle, travelling forward to reach the lacrimal gland. It supplies the lacrimal gland, two rectus muscles of the eye, the eyelids, and the conjunctiva.

The tubal branch of uterine artery is an artery anastamosing with the tubal branches of the ovarian artery.

An interstitial pregnancy is a uterine but ectopic pregnancy; the pregnancy is located outside the uterine cavity in that part of the fallopian tube that penetrates the muscular layer of the uterus. The term cornual pregnancy is sometimes used as a synonym, but remains ambiguous as it is also applied to indicate the presence of a pregnancy located within the cavity in one of the two upper "horns" of a bicornuate uterus. Interstitial pregnancies have a higher mortality than ectopics in general.