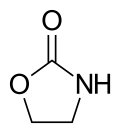
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,3-Oxazolidin-2-one | |||
| Other names 1,3-Oxazolidin-2-one, 2-Oxo-1,3-oxazolidine, 2-Oxotetrahydro-1,3-oxazole | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.129 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID | |||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H5NO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 87.077 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white or colorless solid | ||
| Melting point | 86 to 89 °C (187 to 192 °F; 359 to 362 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 220 °C (428 °F; 493 K) at 48 torr | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds | Oxazolidine | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
2-Oxazolidinone is a heterocyclic organic compound containing both nitrogen and oxygen in a 5-membered ring.