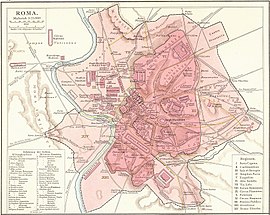
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often considered one body of classical architecture. Roman architecture flourished in the Roman Republic and to even a greater extent under the Empire, when the great majority of surviving buildings were constructed. It used new materials, particularly Roman concrete, and newer technologies such as the arch and the dome to make buildings that were typically strong and well-engineered. Large numbers remain in some form across the former empire, sometimes complete and still in use today.

The Baths of Caracalla in Rome, Italy, were the city's second largest Roman public baths, or thermae, after the Baths of Diocletian. The baths were likely built between AD 212 and 216/217, during the reigns of emperors Septimius Severus and Caracalla. They were in operation until the 530s and then fell into disuse and ruin.

The Baths of Diocletian were public baths in ancient Rome. Named after emperor Diocletian and built from AD 298 to 306, they were the largest of the imperial baths. The project was originally commissioned by Maximian upon his return to Rome in the autumn of 298 and was continued after his and Diocletian's abdication under Constantius, father of Constantine.

The Arch of Septimius Severus at the northwestern end of the Roman Forum is a white marble triumphal arch dedicated in 203 A.D. to commemorate the Parthian victories of Emperor Septimius Severus and his two sons, Caracalla and Geta, in the two campaigns against the Parthians of 194-195 A.D. and 197–199 A.D. After the death of Septimius Severus, his sons Caracalla and Geta were initially joint emperors. Caracalla had Geta assassinated in 212 A.D.; in the practice now known as damnatio memoriae, Geta's memorials were destroyed and all images or mentions of him were removed from public buildings and monuments. Accordingly, Geta's image and inscriptions referring to him were removed from the arch.

The Baths of Titus or Thermae Titi were public baths (Thermae) built in 81 AD at Rome, by Roman emperor Titus. The baths sat at the base of the Esquiline Hill, an area of parkland and luxury estates which had been taken over by Nero for his Golden House or Domus Aurea. Titus' baths were built in haste, possibly by converting an existing or partly built bathing complex belonging to the reviled Domus Aurea. They were not particularly extensive, and the much larger Baths of Trajan were built immediately adjacent to them at the start of the next century.

The Baths of Trajan were a massive thermae, a bathing and leisure complex, built in ancient Rome and dedicated under Trajan during the kalendae of July 109, shortly after the Aqua Traiana was dedicated.

The Ludus Magnus was the largest of the gladiatorial schools in Rome. It was built by the emperor Domitian in the late first century C.E., alongside other building projects undertaken by him such as three other gladiatorial schools across the Roman Empire. The training school is situated directly east of the Colosseum in the valley between the Esquiline and the Caelian hills, an area already occupied by Republican and Augustan structures. While there are remains that are visible today, they belong to a reconstruction that took place under the emperor Trajan where the Ludus plane was raised by about 1.5 metres. The Ludus Magnus was essentially a gladiatorial arena where gladiators from across the Roman Empire would live, eat, and practice while undergoing gladiatorial training in preparation for fighting at the gladiatorial games held at the Colosseum. The Colosseum was where Gladiators would go to fight their opposition.

The Baths of Agrippa was a structure of ancient Rome, Italy, built by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa. It was the first of the great thermae constructed in the city, and also the first public bath.

The Aqua Julia is a Roman aqueduct built in 33 BC by Agrippa under Augustus to supply the city of Rome. It was repaired and expanded by Augustus from 11–4 BC.

Porta Tiburtina or Porta San Lorenzo is a gate in the Aurelian Walls of Rome, Italy, through which the Via Tiburtina exits the city.

The Temple of Hadrian is an ancient Roman structure on the Campus Martius in Rome, Italy, dedicated to the deified emperor Hadrian by his adoptive son and successor Antoninus Pius in 145 CE This temple was previously known as the Basilica of Neptune but has since been properly attributed as the Temple of Hadrian completed under Antoninus Pius. With one cella wall and eleven columns from the external colonnade surviving, the remains of the temple have been incorporated into a later building in the Piazza di Pietra, whereby its facade, alongside the architrave which was reconstructed later on, was incorporated into a 17th-century papal palace by Carlo Fontana, now occupied by Rome's Chamber of commerce. While only part of the structure remains, excavations and scholarship have provided us with information regarding its construction techniques and stylistic influences, helping us recreate the building dynamics and significance of the Temple of Hadrian in Imperial Rome.
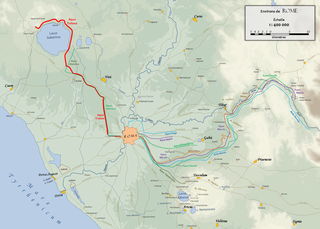
The Aqua Traiana was a 1st-century Roman aqueduct built by Emperor Trajan and inaugurated in 109 AD. It channelled water from sources around Lake Bracciano, 40 km (25 mi) north-west of Rome, to ancient Rome. It joined the earlier Aqua Alsietina to share a common lower route into Rome.
The Baths of Licinius Sura or Thermae Suranae were a private ancient Roman bath complex built by Lucius Licinius Sura on the Aventine Hill in Rome.

The Aqua Alexandrina was a Roman aqueduct located in the city of Rome. The 22.4 km long aqueduct carried water from Pantano Borghese to the Baths of Alexander on the Campus Martius. It remained in use from the 3rd to the 8th century AD.

In ancient Rome, the Piscina Publica was a public reservoir and swimming pool located in Regio XII. The region itself came to be called informally Piscina Publica from the landmark. The piscina was situated in the low-lying area between the Via Appia, the Servian Wall, and the northeast slope of the Aventine Hill, an area later occupied by the Baths of Caracalla.

The Arch of Dolabella and Silanus or Arch of Dolabella is an ancient Roman arch. It was built by senatorial decree in 10 AD by the consuls P. Cornelius Dolabella and C. Junius Silanus.

The Aqua Anio Vetus was an ancient Roman aqueduct, and the second oldest after the Aqua Appia.

The Regio I Porta Capena is the first regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio I took its name from the Porta Capena, a gate of the Servian Walls, through which the Appian Way entered the city prior to the construction of the Aurelian Walls.
The Arch of Scipio was an ancient Roman arch located atop the Capitoline Hill.