Vatican City, officially the Vatican City State, is a sovereign country, city-state, microstate, and enclave surrounded by, and historically a part of, Rome, Italy. It became independent from Italy in 1929 with the Lateran Treaty, and is a distinct territory under "full ownership, exclusive dominion, and sovereign authority and jurisdiction" of the Holy See, which is itself a sovereign entity under international law, maintaining the city-state's temporal power, governance, diplomatic, and spiritual independence. The Vatican is also a metonym for the pope, the Holy See, and the Roman Curia. The country has the world's smallest land area and the smallest population, with 764 citizens as of 2023.
Vatican Hill is a hill in Rome, located on the right bank of Tiber river, opposite to the traditional seven hills of Rome. The hill also gave the name to Vatican City. It is the location of St. Peter's Basilica.

Saint Peter's Square is a large plaza located directly in front of St. Peter's Basilica in Vatican City, the papal enclave in Rome, directly west of the neighborhood (rione) of Borgo. Square and basilica are named after Saint Peter, an apostle of Jesus whom Catholics consider the first Pope.

Saint Peter's tomb is a site under St. Peter's Basilica that includes several graves and a structure said by Vatican authorities to have been built to memorialize the location of Saint Peter's grave. St. Peter's tomb is alleged near the west end of a complex of mausoleums, the Vatican Necropolis, that date between about AD 130 and AD 300. The complex was partially torn down and filled with earth to provide a foundation for the building of the first St. Peter's Basilica during the reign of Constantine I in about AD 330. Though many bones have been found at the site of the 2nd-century shrine, as the result of two campaigns of archaeological excavation, Pope Pius XII stated in December 1950 that none could be confirmed to be Saint Peter's with absolute certainty. Following the discovery of bones that had been transferred from a second tomb under the monument, on June 26, 1968, Pope Paul VI said that the relics of Saint Peter had been identified in a manner considered convincing. Only circumstantial evidence was provided to support the claim.

Borgo is the 14th rione of Rome, Italy. It is identified by the initials R. XIV and is included within Municipio I.
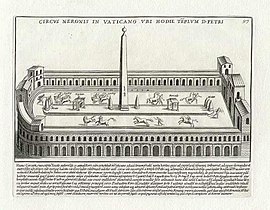
Via Cornelia is an ancient Roman road that supposedly ran east–west along the northern wall of the Circus of Nero on land now covered by the southern wall of St. Peter's Basilica. The location is closely associated with the Via Aurelia and the Via Triumphalis.

Via della Conciliazione is a street in the Rione of Borgo within Rome, Italy. Roughly 500 metres (1,600 ft) in length, it connects Saint Peter's Square to the Castel Sant'Angelo on the western bank of the Tiber River. The road was constructed between 1936 and 1950, and it is the primary access route to the Square. In addition to shops, it is bordered by a number of historical and religious buildings – including the Palazzo Torlonia, the Palazzo dei Penitenzieri and the Palazzo dei Convertendi, and the churches of Santa Maria in Traspontina and Santo Spirito in Sassia.
This is an index of Vatican City–related topics.

The Vatican Necropolis lies under the Vatican City, at depths varying between 5–12 metres below Saint Peter's Basilica. The Vatican sponsored archaeological excavations under Saint Peter's in the years 1940–1949 which revealed parts of a necropolis dating to Imperial times. The work was undertaken at the request of Pope Pius XI who wished to be buried as close as possible to Peter the Apostle. It is also home to the Tomb of the Julii, which has been dated to the third or fourth century. The necropolis was not originally one of the Catacombs of Rome, but an open-air cemetery with tombs and mausolea.

The Pons Neronianus or Bridge of Nero was an ancient bridge in Rome built during the reign of the emperors Caligula or Nero to connect the western part of the Campus Martius with the Ager Vaticanus, where the Imperial Family owned land along the Via Cornelia.
The Horti Agrippinae was a luxurious villa-estate belonging to Agrippina the Elder in ancient Rome. It was located on the west bank of the river Tiber where St. Peter's Basilica is now, and extended to the river where a terrace with a portico was built.
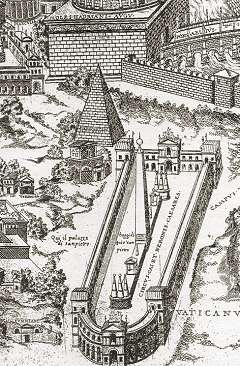
The Meta Romuli was a pyramid built in ancient Rome that is important for historical, religious and architectural reasons. By the 16th century, it was almost completely demolished.

The Terebinth of Nero was a mausoleum built in ancient Rome that is important for historical, religious and architectural reasons. By the 14th century, it was almost completely demolished.

In ancient Rome, the Ager Vaticanus was the alluvial plain on the right (west) bank of the Tiber. It was also called Ripa Veientana or Ripa Etrusca, indicating the Etruscan dominion during the archaic period. It was located between the Janiculum, the Vatican Hill, and Monte Mario, down to the Aventine Hill and up to the confluence of the Cremera creek.

Borgo Nuovo, originally known as via Alessandrina, also named via Recta or via Pontificum, was a road in the city of Rome, Italy, important for historical and architectural reasons. Built by Pope Alexander VI Borgia for the holy year of 1500, the road became one of the main centers of the high Renaissance in Rome. Borgo Nuovo was demolished together with the surrounding quarter in 1936–37 due to the construction of Via della Conciliazione.

Borgo Vecchio, also named in the Middle Ages Via Sancta, Carriera Sancta or Carriera Martyrum, was a road in the city of Rome, Italy, important for historical and architectural reasons. The road was destroyed together with the adjacent quartier in 1936–37 due to the construction of Via della Conciliazione.

Piazza Scossacavalli, also named Piazza di San Clemente, Piazza di Trento, Piazza d'Aragona, Piazza Salviati, was a square in Rome, Italy, important for historical and architectonic reasons. The square was demolished together with the surrounding quarter in 1937 due to the construction of Via della Conciliazione.

Borgo Santo Spirito is a street in Rome, Italy, important for historical and artistic reasons. From a historical point of view, it is considered the most interesting street in the Borgo district. Of medieval origin, it is linked to the foundation of the ancient fortified hospice for pilgrims from England, the Burgus Saxonum. The street houses the oldest Roman hospital, the Arcispedale di Santo Spirito in Saxia, which gave it its name. Heavily altered during the works for the opening of Via della Conciliazione, it nevertheless avoided the fate of the two parallel streets of Borgo Nuovo and Borgo Vecchio, both destroyed.

The Theatre of Nero was the private theatre erected in Rome by Nero, the Roman emperor between AD 53 and AD 68.