
San Gimignano is a small walled medieval hill town in the province of Siena, Tuscany, north-central Italy. Known as the Town of Fine Towers, San Gimignano is famous for its medieval architecture, unique in the preservation of about a dozen of its tower houses, which, with its hilltop setting and encircling walls, form "an unforgettable skyline". Within the walls, the well-preserved buildings include notable examples of both Romanesque and Gothic architecture, with outstanding examples of secular buildings as well as churches. The Palazzo Comunale, the Collegiate Church and Church of Sant' Agostino contain frescos, including cycles dating from the 14th and 15th centuries. The "Historic Centre of San Gimignano" is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The town also is known for saffron, the dry aged and saffron infused Golden Ham, pecorino cheese and its white wine, Vernaccia di San Gimignano, produced from the ancient variety of Vernaccia grape grown on the sandstone hillsides of the area.

Piazza Navona is a public open space in Rome, Italy. It is built on the site of the 1st century AD Stadium of Domitian and follows the form of the open space of the stadium in an elongated oval. The ancient Romans went there to watch the agones ("games"), and hence it was known as "Circus Agonalis". It is believed that over time the name changed to in avone to navone and eventually to navona.
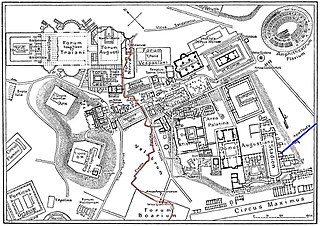
The Cloaca Maxima or, less often, Maxima Cloaca, was one of the world's earliest sewage systems. Its name is related to that of Cloacina, a Roman goddess. Built during either the Roman Kingdom or early Roman Republic, it was constructed in Ancient Rome in order to drain local marshes and remove waste from the city. It carried effluent to the River Tiber, which ran beside the city. The sewer started at the Forum Augustum and ended at the Ponte Rotto and Ponte Palatino. It began as an open air canal, but it developed into a much larger sewer over the course of time. Agrippa renovated and reconstructed much of the sewer. This would not be the only development in the sewers. By the first century CE all eleven Roman aqueducts were connected to the sewer. After the Roman Empire fell the sewer still was used. By the 19th century, it became a tourist attraction. Some parts of the sewer are still used today. Whilst still being used, it was highly valued as a sacred symbol of Roman culture, and Roman engineering.

The Suburra, or Subura was a vast and populous neighborhood of Ancient Rome, located below the Murus Terreus on the Carinae and stretching on the slopes of the Quirinal and Viminal hills up to the offshoots of the Esquiline.

Largo di Torre Argentina is a large open space in Rome, Italy, with four Roman Republican temples and the remains of Pompey's Theatre. It is in the ancient Campus Martius.

Trajan's Market is a large complex of ruins in the city of Rome, Italy, located on the Via dei Fori Imperiali, at the opposite end to the Colosseum. The surviving buildings and structures, built as an integral part of Trajan's Forum and nestled against the excavated flank of the Quirinal Hill, present a living model of life in the Roman capital and a glimpse at the restoration in the city, which reveals new treasures and insights about ancient Roman architecture.

The Torre delle Milizie is a fortified tower in Rome, Italy, located between Trajan's Market in the Imperial fora to the southwest and the Pontifical University of Saint Thomas Aquinas, or Angelicum, to the east.

Mentana is a town and comune, former bishopric and present Latin Catholic titular see in the Metropolitan City of Rome, Lazio, central Italy. It is located 29 kilometres (18 mi) north-east of Rome and has a population of about 23,000.
Montemagno is a comune (municipality) in the Province of Asti in the Italian region Piedmont, located about 50 kilometres (31 mi) east of Turin and about 13 kilometres (8 mi) northeast of Asti. As of 31 December 2010 it had a population of 1,228 and an area of 15.9 square kilometres (6.1 sq mi).

The Towers of Bologna are a group of medieval structures in Bologna, Italy. The two most prominent ones remaining, known as the Two Towers, are a landmark of the city.

The Torre dei Conti is a medieval fortified tower in Rome, Italy, located near the Colosseum and the Roman Forum. The tower was one of the most impressive towers that dominated medieval Rome.
The Torre dei Della Bella is an old tower of Florence, Italy and is located in Via dei Tavolini.

The Torre dei Pulci is a historical tower in Florence, Italy. The tower was the residence of the Pulci family in medieval and Renaissance times, including poet Luigi Pulci. It was in origin a purely defensive tower, which was enlarged until it became a sort of palazzetto or small residential palace.

The Gregorian Tower or Tower of the Winds is a square tower and early modern observatory located above the Gallery of Maps, which connects the Villa Belvedere with the Apostolic Palace in Vatican City. The tower was built between 1578 and 1580 to a design by the Bolognese architect Ottaviano Mascherino mainly to promote the study of astronomy for the Gregorian Calendar Reform which was commissioned by Pope Gregory XIII and promulgated in 1582. It was then also known as the Tower of Winds. The tower was also called "Specola Astronomica Vaticana", a reference to the Vatican Observatory. Four stages of progressive development have occurred since it was first established. The tower was an edifice of great value for astronomical observations made using a sundial as they provided essential confirmation of the need to reform the Julian calendar.

Piazza d'Aracoeli is a square of Rome (Italy), placed at the base of the Capitoline Hill, in the Rione X Campitelli.
Pietro Capocci was a Roman Catholic cardinal, nominated by Pope Innocent IV in the consistory of 28 May 1244, with the cardinal-diaconate of San Giorgio in Velabro.

The Cloaca Circi Maximi or Cloaca Circi was one of the three main sewers in ancient Rome. Alongside the Cloaca Maxima and Chiavicone dell'Olmo
Guerrino Mattia Monassi was an Italian medalist and engraver. He was a pupil of Pietro Giampaoli who called him to Rome in 1934 in the workshop of Torre dei Capocci. In 1963 he was appointed chief engraver at the Istituto Poligrafico e Zecca dello Stato.

Characteristic of the historic center of Pavia is the presence of medieval noble towers that survive in its urban fabric, despite having once been more numerous, as evidenced by the sixteenth-century representation of the city frescoed in the church of San Teodoro. They were mostly built between the 11th and 13th centuries when the Ghibelline city was at the height of its Romanesque flowering.
















