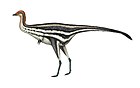
Archaeopteryx, sometimes referred to by its German name, "Urvogel" is a genus of bird-like dinosaurs. The name derives from the ancient Greek ἀρχαῖος (archaīos), meaning "ancient", and πτέρυξ (ptéryx), meaning "feather" or "wing". Between the late 19th century and the early 21st century, Archaeopteryx was generally accepted by palaeontologists and popular reference books as the oldest known bird. Older potential avialans have since been identified, including Anchiornis, Xiaotingia, and Aurornis.

Vertebrate paleontology is the subfield of paleontology that seeks to discover, through the study of fossilized remains, the behavior, reproduction and appearance of extinct vertebrates. It also tries to connect, by using the evolutionary timeline, the animals of the past and their modern-day relatives.

Theropoda whose members are known as theropods, is an extant dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally carnivorous, although a number of theropod groups evolved to become herbivores and omnivores. Theropods first appeared during the Carnian age of the late Triassic period 231.4 million years ago (Ma) and included the majority of large terrestrial carnivores from the Early Jurassic until at least the close of the Cretaceous, about 66 Ma. In the Jurassic, birds evolved from small specialized coelurosaurian theropods, and are today represented by about 11,000 living species.

Deinonychosauria is a clade of paravian dinosaurs which lived from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found across the globe in North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, South America, and Antarctica, with fossilized teeth giving credence to the possibility that they inhabited Australia as well. This group of dinosaurs are known for their sickle-shaped toe claws and features in the shoulder bones.
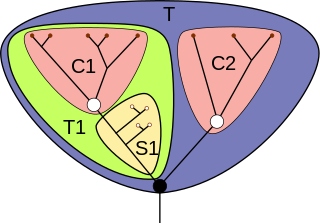
In phylogenetics, the crown group or crown assemblage is a collection of species composed of the living representatives of the collection, the most recent common ancestor of the collection, and all descendants of the most recent common ancestor. It is thus a way of defining a clade, a group consisting of a species and all its extant or extinct descendants. For example, Neornithes (birds) can be defined as a crown group, which includes the most recent common ancestor of all modern birds, and all of its extant or extinct descendants.

Alvarezsauridae is a family of small, long-legged dinosaurs. Although originally thought to represent the earliest known flightless birds, they are now thought to be an early diverging branch of maniraptoran theropods. Alvarezsaurids were highly specialized. They had tiny but stout forelimbs, with compact, bird-like hands. Their skeletons suggest that they had massive breast and arm muscles, possibly adapted for digging or tearing. They had long, tube-shaped snouts filled with tiny teeth. They have been interpreted as myrmecophagous, adapted to prey on colonial insects such as termites, with the short arms acting as effective digging instruments to break into nests.

Confuciusornis is a genus of basal crow-sized avialan from the Early Cretaceous Period of the Yixian and Jiufotang Formations of China, dating from 125 to 120 million years ago. Like modern birds, Confuciusornis had a toothless beak, but closer and later relatives of modern birds such as Hesperornis and Ichthyornis were toothed, indicating that the loss of teeth occurred convergently in Confuciusornis and living birds. It was thought to be the oldest known bird to have a beak, though this title now belongs to an earlier relative Eoconfuciusornis. It was named after the Chinese moral philosopher Confucius. Confuciusornis is one of the most abundant vertebrates found in the Yixian Formation, and several hundred complete specimens have been found.
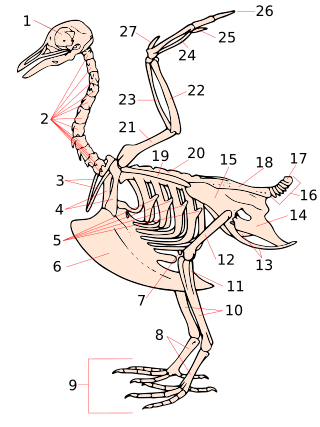
Pygostyle describes a skeletal condition in which the final few caudal vertebrae are fused into a single ossification, supporting the tail feathers and musculature. In modern birds, the rectrices attach to these. The pygostyle is the main component of the uropygium, a structure colloquially known as the bishop's nose, parson's nose, pope's nose, or sultan's nose. This is the fleshy protuberance visible at the posterior end of a bird that has been dressed for cooking. It has a swollen appearance because it also contains the uropygial gland that produces preen oil.

The evolution of birds began in the Jurassic Period, with the earliest birds derived from a clade of theropod dinosaurs named Paraves. Birds are categorized as a biological class, Aves. For more than a century, the small theropod dinosaur Archaeopteryx lithographica from the Late Jurassic period was considered to have been the earliest bird. Modern phylogenies place birds in the dinosaur clade Theropoda. According to the current consensus, Aves and a sister group, the order Crocodilia, together are the sole living members of an unranked reptile clade, the Archosauria. Four distinct lineages of bird survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago, giving rise to ostriches and relatives (Palaeognathae), waterfowl (Anseriformes), ground-living fowl (Galliformes), and "modern birds" (Neoaves).

Odontognathae is a disused name for a paraphyletic group of toothed prehistoric birds. The group was originally proposed by Alexander Wetmore, who attempted to link fossil birds with the presence of teeth, specifically of the orders Hesperornithiformes and Ichthyornithiformes. As such they would be regarded as transitional fossils between the reptile-like "Archaeornithes" like Archaeopteryx and modern birds. They were described by Romer as birds with essentially modern anatomy, but retaining teeth.

The scientific question of within which larger group of animals birds evolved has traditionally been called the "origin of birds". The present scientific consensus is that birds are a group of maniraptoran theropod dinosaurs that originated during the Mesozoic era.

Yandangornis is a genus of theropods from the Late Cretaceous Tangshang Formation of China. It lived 81.5 million years ago in what is now China. The type species, Y. longicaudus, was formally described by Cai and Zhou in 1999.

Sapeornis is a monotypic genus of avialan dinosaurs which lived during the early Cretaceous period. Sapeornis contains only one species, Sapeornis chaoyangensis.

Confuciusornithidae is an extinct family of pygostylian avialans known from the Early Cretaceous, found in northern China. They are commonly placed as a sister group to Ornithothoraces, a group that contains all extant birds along with their closest extinct relatives. Confuciusornithidae contains four genera, possessing both shafted and non-shafted (downy) feathers. Some specimens probably referable to this clade represents one of the earliest known fossil evidence of primary feather moulting. They are also noted for their distinctive pair of ribbon-like tail feathers of disputed function.

John Alan Feduccia is a paleornithologist specializing in the origins and phylogeny of birds. He is S. K. Heninger Distinguished Professor Emeritus at the University of North Carolina. Feduccia's authored works include three major books, The Age of Birds, The Origin and Evolution of Birds, and Riddle of the Feathered Dragons.

Paraves are a widespread group of theropod dinosaurs that originated in the Middle Jurassic period. In addition to the extinct dromaeosaurids, troodontids, anchiornithids, and possibly the scansoriopterygids, the group also contains the avialans, which include diverse extinct taxa as well as the over 10,000 species of living birds.

Sinornis is a genus of enantiornithean birds from the Lower Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation of the People's Republic of China.

Pygostylia is a group of avialans which includes the Confuciusornithidae and all of the more advanced species, the Ornithothoraces.

Protopteryx is an extinct bird and possibly the basalmost enantiornithean, from the Cretaceous period. The type species is P. fengningensis. It was first discovered in the Sichakou Member of the Yixian Formation or Huajiying Formation of Hebei Province, northern China, dating from 131 Ma ago. Protopteryx has been found in the Daibeigou formation, as well. The name Protopteryx means "primitive feather": "proto-" meaning "the first of" and "-pteryx" meaning "feather" or "wing." The name comes from the fact that Protopteryx feathers are more primitive than those of modern birds, such as the two elongated tail feathers that lack barbs and rami.
Bradley Curtis Livezey was an American ornithologist with scores of publications. His main research included the evolution of flightless birds, the systematics of birds, and the ecology and behaviour of steamer ducks.