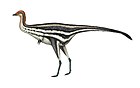
The darters, anhingas, or snakebirds are mainly tropical waterbirds in the family Anhingidae, which contains a single genus, Anhinga. There are four living species, three of which are very common and widespread while the fourth is rarer and classified as near-threatened by the IUCN. The term snakebird is usually used without any additions to signify whichever of the completely allopatric species occurs in any one region. It refers to their long thin neck, which has a snake-like appearance when they swim with their bodies submerged, or when mated pairs twist it during their bonding displays. "Darter" is used with a geographical term when referring to particular species. It alludes to their manner of procuring food, as they impale fishes with their thin, pointed beak. The American darter is more commonly known as the anhinga. It is sometimes called "water turkey" in the southern United States; though the anhinga is quite unrelated to the wild turkey, they are both large, blackish birds with long tails that are sometimes hunted for food.

Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae, Anseranatidae, and Anatidae, the largest family, which includes over 170 species of waterfowl, among them the ducks, geese, and swans. Most modern species in the order are highly adapted for an aquatic existence at the water surface. With the exception of screamers, males have penises, a trait that has been lost in the Neoaves. Due to their aquatic nature, most species are web-footed.

Plotopteridae is an extinct family of flightless seabirds with uncertain placement, generally considered as member of order Suliformes. They exhibited remarkable convergent evolution with the penguins, particularly with the now extinct giant penguins. That they lived in the North Pacific, the other side of the world from the penguins, has led to them being described at times as the Northern Hemisphere's penguins, though they were not closely related. More recent studies have shown, however, that the shoulder-girdle, forelimb and sternum of plotopterids differ significantly from those of penguins, so comparisons in terms of function may not be entirely accurate. Plotopterids are regarded as closely related to Anhingidae (darters) and Phalacrocoracidae (cormorants). On the other hand, there is a theory that this group may have a common ancestor with penguins due to the similarity of forelimb and brain morphology. However, the endocast morphology of stem group Sphenisciformes differs from both Plotopteridae and modern penguins.

Osteodontornis is an extinct seabird genus. It contains a single named species, Osteodontornis orri, which was described quite exactly one century after the first species of the Pelagornithidae was. O. orri was named after Santa Barbara Museum of Natural History paleontologist Phil C. Orr, for his recognition of the importance of the specimen.

The Pelagornithidae, commonly called pelagornithids, pseudodontorns, bony-toothed birds, false-toothed birds or pseudotooth birds, are a prehistoric family of large seabirds. Their fossil remains have been found all over the world in rocks dating between the Early Paleocene and the Pliocene-Pleistocene boundary.
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1976.

Copepteryx is an extinct genus of flightless bird of the family Plotopteridae, endemic to Japan during the Oligocene living from 28.4 to 23 mya, meaning it existed for approximately 5.4 million years.

Odontopteryx is a genus of the extinct pseudotooth birds or pelagornithids. These were probably rather close relatives of either pelicans and storks, or of waterfowl, and are here placed in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty.
Caspiodontornis is a genus of the prehistoric pseudotooth birds of somewhat doubtful validity. These were probably rather close relatives of either pelicans and storks, or of waterfowl, and are here placed in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty.

Dasornis is a genus of prehistoric pseudotooth birds. These were probably close relatives of either pelicans and storks or waterfowl; they are placed in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty.
Gigantornis eaglesomei is a very large prehistoric bird described from a fragmentary specimen from the Eocene of Nigeria. It was originally described as a representative of the albatross family, Diomedeidae, but was later referred to the pseudotooth or bony-toothed bird family, Pelagornithidae. Gigantornis is one of the largest pseudotooth birds, with an inferred wingspan of about 6 m (20 ft) it is among the largest birds ever.
Palaeochenoides is a genus of the prehistoric pseudotooth birds of somewhat doubtful validity. These were probably rather close relatives of either pelicans and storks, or of waterfowl, and are here placed in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty.

Pelagornis is a widespread genus of prehistoric pseudotooth birds. These were probably rather close relatives of either pelicans and storks, or waterfowl, and are placed here in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty.
Pseudodontornis is a rather disputed genus of the prehistoric pseudotooth birds. The pseudotooth birds or pelagornithids were probably rather close relatives of either pelicans and storks, or of waterfowl, and are here placed in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty. Up to five species are commonly recognized in this genus.
Tympanonesiotes is a somewhat doubtfully valid genus of the prehistoric pseudotooth birds. These were probably rather close relatives of either pelicans and storks, or of waterfowl, and are here placed in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty.
Macrodontopteryx is a genus of the prehistoric pseudotooth birds of somewhat doubtful validity. These animals were probably rather close relatives of either pelicans and storks, or of waterfowl, and are here placed in the order Odontopterygiformes to account for this uncertainty.

Tonsala is an extinct genus of Plotopteridae, a family of flightless seabird similar in biology with penguins, but more closely related to modern cormorants. The genus is known from terrains dated from the Late Oligocene of the State of Washington and Japan.

Phocavis is an extinct genus of flightless seabird, belonging to the family Plotopteridae, and distantly related with modern cormorants. Its fossils, found in the Keasey Formation in Oregon, are dated from the Late Eocene.

Klallamornis is an extinct genus of Plotopteridae, a family of large, flightless birds related to modern cormorants, darters, gannets, and boobies. This genus included the largest North American plotopterids. Its remains can be found in Late Eocene to Late Oligocene rocks from the Makah Formation, the overlying Pysht Formation and the Lincoln Creek Formation of the State of Washington. During its existence, Klallamornis was the largest plotopterid on the North American continent. The first fossil remains attributed to the taxon were collected in 1983, although the genus wasn't described until 2016.