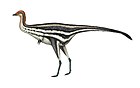
The Enantiornithes, also known as enantiornithines or enantiornitheans in literature, are a group of extinct avialans, the most abundant and diverse group known from the Mesozoic era. Almost all retained teeth and clawed fingers on each wing, but otherwise looked much like modern birds externally. Over eighty species of Enantiornithes have been named, but some names represent only single bones, so it is likely that not all are valid. The Enantiornithes became extinct at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, along with Hesperornithes and all other non-avian dinosaurs.

Vegavis is a genus of extinct bird that lived during the Late Cretaceous of Antarctica, some 68 to 66 mya. Among modern birds, most studies show that Vegavis is most closely related to ducks and geese (Anatidae), but it is not considered to be a direct ancestor of them, although other studies question these results.

Avisaurus is a genus of enantiornithine bird from the Late Cretaceous of North America.

Ampelosaurus is a titanosaurian sauropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now France. Its type species is A. atacis, named by Le Loeuff in 1995. Its remains were found in a level dating from 71.5 million years ago representing the early Maastrichtian.

Elopteryx is a genus of, perhaps troodontid, maniraptoran theropod dinosaur based on fragmentary fossils found in late Cretaceous Period rocks of Romania. The single species, Elopteryx nopcsai, is known only from very incomplete material, and therefore is considered a nomen dubium by most paleontologists.

Denversaurus is a genus of panoplosaurin nodosaurid dinosaur from the late Maastrichtian of Late Cretaceous Western North America. Although at one point treated as a junior synonym of Edmontonia by some taxonomists, current research indicates that it is its own distinct nodosaurid genus.

Elasmosauridae is an extinct family of plesiosaurs, often called elasmosaurs. They had the longest necks of the plesiosaurs and existed from the Hauterivian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Cretaceous, and represented one of the two groups of plesiosaurs present at the end of the Cretaceous alongside Polycotylidae.

The Pteranodontidae are a family of large pterosaurs of the Cretaceous Period of North America and Africa. The family was named in 1876 by Othniel Charles Marsh. Pteranodontids had a distinctive, elongated crest jutting from the rear of the head. The spectacularly-crested Nyctosaurus is sometimes included in this family, though usually placed in its own family, the Nyctosauridae.
The Frenchman Formation is stratigraphic unit of Late Cretaceous age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin. It is present in southern Saskatchewan and the Cypress Hills of southeastern Alberta. The formation was defined by G.M. Furnival in 1942 from observations of outcrops along the Frenchman River, between Ravenscrag and Highway 37. It contains the youngest of dinosaur genera, much like the Hell Creek Formation in the United States.

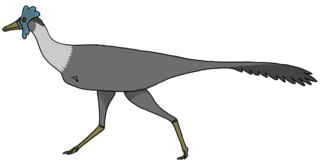
Gargantuavis is an extinct genus of large, primitive bird containing the single species Gargantuavis philoinos. It is the only member of the monotypic family Gargantuaviidae. Its fossils were discovered in several formations dating to 73.5 and 71.5 million years ago in what is now northern Spain, southern France, and Romania. Gargantuavis is the largest known bird of the Mesozoic, a size ranging between the cassowary and the ostrich, and a mass of 141 kg (311 lb) like modern ostriches, exemplifying the extinction of non-avian dinosaurs was not a necessary condition for the emergence of giant terrestrial birds. It was once thought to be closely related to modern birds, but the 2019 discovery of a pelvis from what was Hateg Island shows several primitive features.
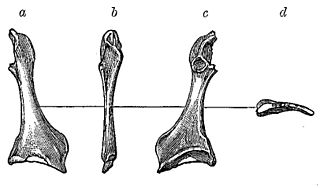
Cimolopteryx is a prehistoric bird genus from the Late Cretaceous Period. It is currently thought to contain only a single species, Cimolopteryx rara. The only specimen confidently attributed to C. rara was found in the Lance Formation of Wyoming, dating to the end of the Maastrichtian age, which ended about 66 million years ago. The dubious species "Cimolopteryx" maxima has been described from both the Lance Formation and the Hell Creek Formation of Montana. The humeral end of a left coracoid from the Frenchman Formation of southern Saskatchewan has also been attributed to the genus.
Palintropus is a prehistoric bird genus from the Late Cretaceous. A single species has been named based on a proximal coracoid from the Lance Formation of Wyoming, dated to the latest Maastrichtian, 66 million years ago. Coracoids and a proximal scapula of two unnamed species from the upper Campanian Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, dating to between 76.5 and 75 million years ago, are also known.
Telmatornis is a valid prehistoric bird genus which has been placed in Charadriiformes. It apparently lived in the Late Cretaceous; its remains were found in the early Maastrichtian Navesink Formation of New Jersey. A single species is included today, Telmatornis priscus.
Palaeotringa is a prehistoric bird genus that was discovered by O. C. Marsh during the late 19th century American bone wars. Its remains were found in the controversial Hornerstown Formation of New Jersey which straddles the Cretaceous-Paleocene boundary some 66 million years ago. Though it cannot be said if these birds lived before or after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, they were in all likelihood wading birds that inhabited the coasts of the northwestern Atlantic.

Cimolopterygidae is an extinct family of ornithurine dinosaurs known from the Late Cretaceous epoch. Remains attributed to cimolopterygids have been found in the Frenchman Formation of Saskatchewan, the Lance Formation of Wyoming, the Fox Hills Formation of Colorado, the Hell Creek Formation of Montana, and the Allen Formation of Rio Negro, Argentina. Most date to the end of the Maastrichtian age, about 66 million years ago, though a much earlier species has also been identified from the Campanian-aged Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, about 75 million years ago.
Bonapartenykus is a monospecific genus of alvarezsauroid dinosaur from Argentina that lived during the Late Cretaceous (Campanian-Maastrichtian) in what is now the upper Allen Formation of the Río Negro Province. The type and only species, Bonapartenykus ultimus, is known from a nearly articulated but partial skeleton that was found in close association to two incomplete eggs and several clusters of eggshells belonging to the oogenus Arriagadoolithus. Bonapartenykus was named in 2012 by Federico L. Agnolin, Jaime E. Powell, Fernando E. Novas and Martin Kundrát. Bonapartenykus has an estimated length of 2.5 m (8.2 ft) and weight of 72 kg (159 lb), making it the largest member of the clade Alvarezsauroidea.

Leptorhynchos is an extinct genus of caenagnathid theropod from the Late Cretaceous of what is now the US state of Texas, although it has been suggested to also exist in Alberta and South Dakota. The type species is L. gaddisi, and it is currently the only widely accepted valid species. The generic name of Leptorhynchos comes from the Greek "leptos" meaning "small" and "rhynchos" meaning "beak". The specific epithet is in honor of the Gaddis family, who owned the land on which the holotype was discovered.
Lamarqueavis is an extinct genus of ornithuran dinosaurs from the family Cimolopterygidae known from Late Cretaceous-aged rocks from Argentina, Canada, and the United States. The type species, L. australis, was named in 2010 and is based on the holotype MML 207, a partial right coracoid found in the Allen Formation, Argentina. Two other species, L. minima, based on the holotype UCMP 53976, a right coracoid found in the Lance Formation, Wyoming, and L. petra, based on the holotype AMNH 21911, a left coracoid also found in the Lance Formation, Wyoming, were transferred over from Cimolopteryx to Lamarqueavis in 2010. A third unnamed species is known from the Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta, Canada.

Maip is a genus of large megaraptorid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Chorrillo Formation of Santa Cruz, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, M. macrothorax, known from an incomplete, disarticulated skeleton. Maip may represent the largest megaraptorid known from South America, and possibly the world.
Kookne is a prehistoric bird genus from the Late Cretaceous. Known from a coracoid, the remains of the only known species Kookne yeutensis were found in rocks from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) Chorrillo Formation of Santa Cruz, Argentina.