
A Reagan Democrat is a traditionally Democratic voter in the United States, referring to working class residents who supported Republican presidential candidates Ronald Reagan in the 1980 and/or the 1984 presidential elections, and/or George H. W. Bush during the 1988 presidential election. The term Reagan Democrat remains part of the lexicon in American political jargon because of Reagan's continued widespread popularity among a large segment of the electorate.

In United States politics, a swing state is any state that could reasonably be won by either the Democratic or Republican candidate in a statewide election, most often referring to presidential elections, by a swing in votes. These states are usually targeted by both major-party campaigns, especially in competitive elections. Meanwhile, the states that regularly lean to a single party are known as "safe states", as it is generally assumed that one candidate has a base of support from which a sufficient share of the electorate can be drawn without significant investment or effort by the campaign.

Starting with the 2000 United States presidential election, the terms "red state" and "blue state" have referred to US states whose voters vote predominantly for one party—the Republican Party in red states and the Democratic Party in blue states—in presidential and other statewide elections. By contrast, states where the vote fluctuates between the Democratic and Republican candidates are known as "swing states" or "purple states". Examining patterns within states reveals that the reversal of the two parties' geographic bases has happened at the state level, but it is more complicated locally, with urban-rural divides associated with many of the largest changes.

Nebraska's 2nd congressional district is a congressional district in the U.S. state of Nebraska that encompasses the core of the Omaha–Council Bluffs metropolitan area. It includes all of Douglas County, which includes the state's largest city Omaha; it also includes Saunders County and areas of western Sarpy County. It has been represented in the United States House of Representatives since 2017 by Don Bacon, a member of the Republican Party. It was one of 18 districts that would have voted for Joe Biden in the 2020 presidential election had they existed in their current configuration while being won or held by a Republican in 2022.

The 2020 United States presidential election was the 59th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. The Democratic ticket of former vice president Joe Biden and the junior U.S. senator from California Kamala Harris defeated the incumbent Republican president Donald Trump, and vice president Mike Pence. The election took place against the backdrop of the global COVID-19 pandemic and related recession. The election saw the highest voter turnout by percentage since 1900. Biden received more than 81 million votes, the most votes ever cast for a candidate in a U.S. presidential election.

The 2020 United States elections were held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. The Democratic Party's nominee, former vice president Joe Biden, defeated incumbent Republican president Donald Trump in the presidential election. Despite losing seats in the House of Representatives, Democrats retained control of the House and gained control of the Senate. As a result, the Democrats obtained a government trifecta, the first time since the elections in 2008 that the party gained unified control of Congress and the presidency. With Trump losing his bid for re-election, he became the first president to have seen his party lose the presidency and control of both the House and the Senate since Herbert Hoover in 1932. This was the first time since 1980 that either chamber of Congress flipped partisan control in a presidential year, and the first time Democrats did so since 1948.
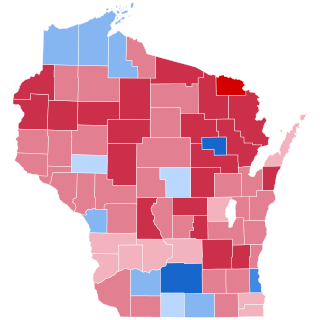
The 2016 United States presidential election in Wisconsin was held on November 8, 2016, as part of the 2016 United States presidential election. Wisconsin voters chose ten electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote pitting Republican nominee Donald Trump against Democratic nominee Hillary Clinton.

The 2016 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania took place on November 8, 2016, as part of the 2016 United States elections in which all 50 states and the District of Columbia participated. Pennsylvania voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Iowa was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Iowa voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump of Florida, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence of Indiana against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden of Delaware, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Iowa has six electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Pennsylvania voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Pennsylvania had 20 electoral votes in the Electoral College.
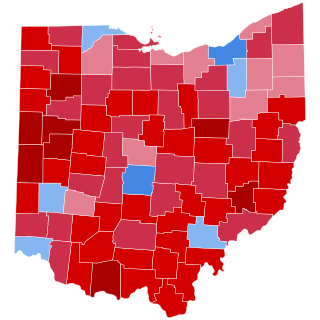
The 2020 United States presidential election in Ohio was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Ohio voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden and his running mate, California Senator Kamala Harris against the Republican Party's nominee—incumbent President Donald Trump and his running mate, Vice President Mike Pence. Ohio had 18 electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Maine was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Maine voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Maine has four electoral votes in the Electoral College. Unlike all other states except Nebraska, Maine awards two electoral votes based on the statewide vote, and one vote for each congressional district.
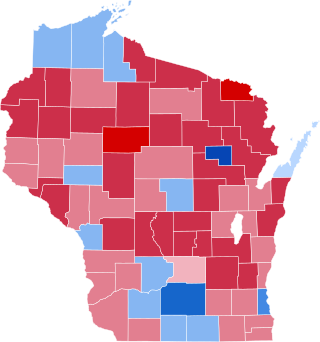
The 2020 United States presidential election in Wisconsin was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Wisconsin voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Wisconsin has 10 electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Nebraska was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Nebraska voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. Nebraska has five electoral votes in the Electoral College, two from the state at large, and one each from the three congressional districts.
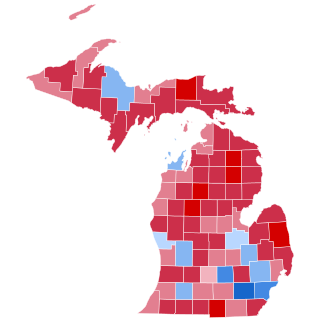
The 2020 United States presidential election in Michigan was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Michigan voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump of Florida, and his running mate, Vice President Mike Pence of Indiana against the Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden of Delaware, and his running mate, Senator Kamala Harris of California. Michigan had 16 electoral votes in the Electoral College.

The 2024 United States presidential election in Maine took place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Maine voters will choose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote. The state of Maine has four electoral votes in the Electoral College, following reapportionment due to the 2020 United States census in which the state neither gained nor lost a seat.

The 2024 United States presidential election in Michigan took place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024, and as part of the 2024 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Michigan voters chose electors for Donald Trump and JD Vance to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote. The state of Michigan has 15 electoral votes in the Electoral College, following reapportionment due to the 2020 United States census in which the state lost a seat. Michigan was considered to be a crucial swing state in 2024.

The 2024 United States presidential election in Nebraska took place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States presidential election in which all 50 states and the District of Columbia participated. Nebraska voters will choose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote. Nebraska has five electoral votes.

The 2024 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania took place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Pennsylvania voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote. The state of Pennsylvania has 19 electoral votes in the Electoral College, following reapportionment due to the 2020 United States census in which the state lost a seat.

The 2024 United States presidential election in Wisconsin took place on Tuesday, November 5, 2024, as part of the 2024 United States elections in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. Wisconsin voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote. The state of Wisconsin has 10 electoral votes in the Electoral College, following reapportionment due to the 2020 United States census in which the state neither gained nor lost a seat.




















