Related Research Articles

Edward Teach, better known as Blackbeard, was an English pirate who operated around the West Indies and the eastern coast of Britain's North American colonies. Little is known about his early life, but he may have been a sailor on privateer ships during Queen Anne's War before he settled on the Bahamian island of New Providence, a base for Captain Benjamin Hornigold, whose crew Teach joined around 1716. Hornigold placed him in command of a sloop that he had captured, and the two engaged in numerous acts of piracy. Their numbers were boosted by the addition to their fleet of two more ships, one of which was commanded by Stede Bonnet, but Hornigold retired from piracy toward the end of 1717, taking two vessels with him.

The Chesapeake & Delaware Canal is a 14-mile (22.5 km)-long, 450-foot (137.2 m)-wide and 35-foot (10.7 m)-deep ship canal that connects the Delaware River with the Chesapeake Bay in the states of Delaware and Maryland in the United States.
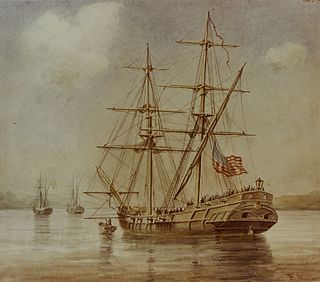
The first USS Lexington of the Thirteen Colonies was a brig purchased in 1776. The Lexington was an 86-foot (26 m) two-mast wartime sailing ship for the fledgling Continental Navy of the Colonists during the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783).

Alfred was the merchant vessel Black Prince, named for Prince Edward, Duke of Cornwall and launched in 1774. The Continental Navy acquired her in 1775, renaming her Alfred after 9th century English monarch Alfred of Wessex, and commissioned her as a 24-gun frigate. During the American Revolutionary War, the Alfred participated in two major naval operations; the battles of Nassau and Block Island. The Royal Navy captured her in 1778, took her into service as HMS Alfred, and sold her in 1782. She then became the merchantman Alfred, and sailed between London and Jamaica.

Stede Bonnet was a Barbadian-born pirate and military officer, known as the Gentleman Pirate because he was a moderately wealthy landowner before turning to a life of crime. Bonnet was born into a wealthy English family on the island of Barbados, and inherited the family estate after his father's death in 1694. Despite his lack of sailing experience, Bonnet decided he should turn to piracy in the spring of 1717. He bought a sailing vessel, the Revenge, and travelled with his paid crew along the Eastern Seaboard of what is now the United States, capturing other vessels and burning other Barbadian ships.

Edward Low was a pirate of English origin during the latter days of the Golden Age of Piracy, in the early 18th century. Low was born into poverty in Westminster, London, and was a thief from an early age. He moved to Boston, Massachusetts, as a young man. His wife died in childbirth in late 1719. Two years later, he became a pirate, operating off the coasts of New England and the Azores, and in the Caribbean.

Sinepuxent Bay is an inland waterway which connects Chincoteague Bay to Isle of Wight Bay, and is connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Ocean City Inlet. It separates Sinepuxent Neck, in Worcester County, Maryland from Assateague Island, and West Ocean City, Maryland from downtown Ocean City. Islands in the Sinepuxent Bay include Horn Island and Skimmer Island. It is crossed by the Harry W. Kelley Memorial Bridge on U.S. Route 50 and the Verrazano Bridge on Maryland Route 611. The bay is the location of the islands that compose the Sinepuxent Bay Wildlife Management Area. Historically the area was referred to by various names including Sinepuxent, Sene Puxon, Synepuxent, Cinnepuxon, et al.

Charles Vane was an English pirate who operated in the Bahamas during the end of the Golden Age of Piracy.
Henry Jennings was an English privateer-turned-pirate. Jennings's first recorded act of piracy took place in early 1716 when, with three vessels and 150–300 men, Jennings's fleet ambushed the Spanish salvage camp from the 1715 Treasure Fleet. After the Florida raid, Jennings and his crew also linked up with Benjamin Hornigold's "three sets of pirates" from New Providence Island.

The pre-American Civil War practice of kidnapping into slavery in the United States occurred in both free and slave states, and both fugitive slaves and free negroes were transported to slave markets and sold, often multiple times. There were also rewards for the return of fugitives. Three types of kidnapping methods were employed: physical abduction, inveiglement of free blacks, and apprehension of fugitives. The enslavement, or re-enslavement, of free blacks occurred for 85 years, from 1780 to 1865.

Edward Davis or Davies was an English buccaneer active in the Caribbean during the 1680s and would lead successful raids against Leon and Panama in 1685, the latter considered one of the last major buccaneer raids against a Spanish stronghold. Much of his career was later recorded by writer William Dampier in A New Voyage Round the World (1697).

Richard Worley was a pirate who was active in the Caribbean Sea and the East Coast of the American Colonies during the early 18th century.
See also 1697 in piracy, 1699 in piracy, and Timeline of piracy.
See also 1717 in piracy, 1719 in piracy, and Timeline of piracy.

Francis Reynolds-Moreton, 3rd Baron Ducie was a Royal Navy officer, politician and peer who sat in the British House of Commons representing the constituency of Lancaster from 1784 to 1785. He is best known for his service in the American Revolutionary War and Fourth Anglo-Dutch War. Reynolds fought at the 1777 Battle of Red Bank during the Philadelphia campaign. During the battle, he was commander of a British squadron onboard HMS Augusta in an attempt to clear the way along the Delaware River to Philadelphia. His ship ran aground while being pursued by American Commodore John Hazelwood's squadron, and Augusta mysteriously caught fire shortly thereafter and exploded before all of the crew could abandon ship. Reynolds also commanded HMS Jupiter and HMS Monarch in several operations and saw service against the French and Dutch in the North Sea, Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea.

The Battle of Delaware Bay, or the Battle of Cape May, was a naval engagement fought between the Kingdom of Great Britain and the United States during the American Revolutionary War. A British squadron of three vessels attacked three American privateers that were escorting a fleet of merchantmen. The ensuing combat in Delaware Bay near Cape May ended with an American victory over a superior British force.

The capture of the sloop Ranger was a naval battle which occurred on June 10, 1723 near Block Island in the Atlantic Ocean. Two pirate ships under the command of Englishmen Edward Low and Charles Harris attacked HMS Greyhound, a post ship of the British Royal Navy which they mistook for a civilian whaler. The resulting engagement lasted for several hours and ended with Harris' sloop Ranger being captured by Greyhound while Low's schooner Fancy escaped. All surviving crew of Ranger were captured and brought to Newport, Rhode Island, where they were placed on trial, sentenced to death and executed.
Richard Glover was a pirate and slave-trader active in the Caribbean and the Red Sea in the late 1690s.
Captain Grinnaway was a pirate from Bermuda, best known for being briefly and indirectly involved with Edward Teach.

The Delaware Railroad was the major railroad in the US state of Delaware, traversing almost the entire state north to south. It was planned in 1836 and built in the 1850s. It began in Porter and was extended south through Dover, Seaford and finally reached Delmar on the border of Maryland in 1859. Although operated independently, in 1857 it was leased by and under the financial control of the Philadelphia, Wilmington, and Baltimore Railroad. In 1891, it was extended north approximately 14 miles (23 km) with the purchase of existing track to New Castle and Wilmington. With this additional track, the total length was 95.2 miles (153.2 km).
References
- 1 2 3 Hazard, Samuel (1851). Minutes of the Provincial Council of Pennsylvania, from the organization to the termination of the proprietary government. [Mar. 10, 1683-Sept. 27, 1775]. Philadelphia: Philadelphia : Printed by J. Severns. Retrieved 8 November 2024.
- ↑ Productions, Moonshell. "Legends of Eastern Shore Pirates - Delmarva Almanac". delmarva-almanac.com. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- 1 2 3 Scharf, John Thomas (1888). History of Delaware : 1609–1888: General history. Philadelphia: L. J. Richards. p. 100 . Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- ↑ Mervine, William M. (1908). "Pirates and Privateers in the Delaware Bay and River". The Pennsylvania Magazine of History and Biography. 32 (4): 459–470. JSTOR 20085447.
