Related Research Articles

The Cretaceous is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin creta, "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation Kreide.
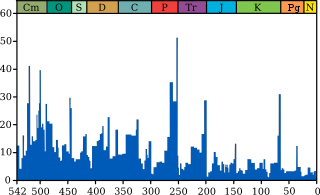
An extinction event is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp fall in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occurs when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the background extinction rate and the rate of speciation. Estimates of the number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. These differences stem from disagreement as to what constitutes a "major" extinction event, and the data chosen to measure past diversity.

The Triassic–Jurassic (Tr-J) extinction event (TJME), often called the end-Triassic extinction, was a Mesozoic extinction event that marks the boundary between the Triassic and Jurassic periods, 201.4 million years ago, and is one of the top five major extinction events of the Phanerozoic eon, profoundly affecting life on land and in the oceans. In the seas, the entire class of conodonts and 23–34% of marine genera disappeared. On land, all archosauromorphs other than crocodylomorphs, pterosaurs, and non-avian dinosaurs became extinct; some of the groups which died out were previously abundant, such as aetosaurs, phytosaurs, and rauisuchids. Some remaining non-mammalian therapsids and many of the large temnospondyl amphibians had become extinct prior to the Jurassic as well. However, there is still much uncertainty regarding a connection between the Tr-J boundary and terrestrial vertebrates, due to a lack of terrestrial fossils from the Rhaetian (uppermost) stage of the Triassic. Plants, crocodylomorphs, dinosaurs, pterosaurs and mammals were left largely untouched; this allowed the dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and crocodylomorphs to become the dominant land animals for the next 135 million years.

The Late Ordovician mass extinction (LOME), sometimes known as the end-Ordovician mass extinction or the Ordovician-Silurian extinction, is the first of the "big five" major mass extinction events in Earth's history, occurring roughly 445 million years ago (Ma). It is often considered to be the second-largest known extinction event just behind the end-Permian mass extinction, in terms of the percentage of genera that became extinct. Extinction was global during this interval, eliminating 49–60% of marine genera and nearly 85% of marine species. Under most tabulations, only the Permian-Triassic mass extinction exceeds the Late Ordovician mass extinction in biodiversity loss. The extinction event abruptly affected all major taxonomic groups and caused the disappearance of one third of all brachiopod and bryozoan families, as well as numerous groups of conodonts, trilobites, echinoderms, corals, bivalves, and graptolites. Despite its taxonomic severity, the Late Ordovician mass extinction did not produce major changes to ecosystem structures compared to other mass extinctions, nor did it lead to any particular morphological innovations. Diversity gradually recovered to pre-extinction levels over the first 5 million years of the Silurian period.

The Late Devonian extinction consisted of several extinction events in the Late Devonian Epoch, which collectively represent one of the five largest mass extinction events in the history of life on Earth. The term primarily refers to a major extinction, the Kellwasser event, also known as the Frasnian-Famennian extinction, which occurred around 372 million years ago, at the boundary between the Frasnian stage and the Famennian stage, the last stage in the Devonian Period. Overall, 19% of all families and 50% of all genera became extinct. A second mass extinction called the Hangenberg event, also known as the end-Devonian extinction, occurred 359 million years ago, bringing an end to the Famennian and Devonian, as the world transitioned into the Carboniferous Period.
Orbital forcing is the effect on climate of slow changes in the tilt of the Earth's axis and shape of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. These orbital changes modify the total amount of sunlight reaching the Earth by up to 25% at mid-latitudes. In this context, the term "forcing" signifies a physical process that affects the Earth's climate.
An anoxic event describes a period wherein large expanses of Earth's oceans were depleted of dissolved oxygen (O2), creating toxic, euxinic (anoxic and sulfidic) waters. Although anoxic events have not happened for millions of years, the geologic record shows that they happened many times in the past. Anoxic events coincided with several mass extinctions and may have contributed to them. These mass extinctions include some that geobiologists use as time markers in biostratigraphic dating. On the other hand, there are widespread, various black-shale beds from the mid-Cretaceous which indicate anoxic events but are not associated with mass extinctions. Many geologists believe oceanic anoxic events are strongly linked to the slowing of ocean circulation, climatic warming, and elevated levels of greenhouse gases. Researchers have proposed enhanced volcanism (the release of CO2) as the "central external trigger for euxinia."
The Early Cretaceous or the Lower Cretaceous is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
The Aptian is an age in the geologic timescale or a stage in the stratigraphic column. It is a subdivision of the Early or Lower Cretaceous Epoch or Series and encompasses the time from 121.4 ± 1.0 Ma to 113.0 ± 1.0 Ma, approximately. The Aptian succeeds the Barremian and precedes the Albian, all part of the Lower/Early Cretaceous.

The Caribbean large igneous province (CLIP) consists of a major flood basalt, which created this large igneous province (LIP). It is the source of the current large eastern Pacific oceanic plateau, of which the Caribbean-Colombian oceanic plateau is the tectonized remnant. The deeper levels of the plateau have been exposed on its margins at the North American and South American plates. The volcanism took place between 139 and 69 million years ago (Ma), with the majority of activity appearing to lie between 95 and 88 Ma. The plateau volume has been estimated as on the order of 4 million km3 (0.96 million cu mi). It has been linked to the Galápagos hotspot.

The Cretaceous Thermal Maximum (CTM), also known as Cretaceous Thermal Optimum, was a period of climatic warming that reached its peak approximately 90 million years ago (90 Ma) during the Turonian age of the Late Cretaceous epoch. The CTM is notable for its dramatic increase in global temperatures characterized by high carbon dioxide levels.
Three Western Interior Seaway anoxic events occurred during the Cretaceous in the shallow inland seaway that divided North America in two island continents, Appalachia and Laramidia. During these anoxic events much of the water column was depleted in dissolved oxygen. While anoxic events impact the world's oceans, Western Interior Seaway anoxic events exhibit a unique paleoenvironment compared to other basins. The notable Cretaceous anoxic events in the Western Interior Seaway mark the boundaries at the Aptian-Albian, Cenomanian-Turonian, and Coniacian-Santonian stages, and are identified as Oceanic Anoxic Events I, II, and III respectively. The episodes of anoxia came about at times when very high sea levels coincided with the nearby Sevier orogeny that affected Laramidia to the west and Caribbean large igneous province to the south, which delivered nutrients and oxygen-adsorbing compounds into the water column.
The Neoproterozoic Oxygenation Event (NOE), also called the Second Great Oxidation Event, was a time interval between around 850 and 540 million years ago which saw a very significant increase in oxygen levels in Earth's atmosphere and oceans. Bringing an end to the Boring Billion, an euxinic period of extremely low atmospheric oxygen spanning from the Statherian to the Tonian, the NOE was the second major increase in atmospheric and oceanic oxygen concentration on Earth, though it was not as large as the Great Oxidation Event (GOE) of the Neoarchean-Paleoproterozoic boundary. Unlike the GOE, it is unclear whether the NOE was a synchronous, global event or a series of asynchronous, regional oxygenation intervals with unrelated causes.
The Toarcian extinction event, also called the Pliensbachian-Toarcian extinction event, the Early Toarcian mass extinction, the Early Toarcian palaeoenvironmental crisis, or the Jenkyns Event, was an extinction event that occurred during the early part of the Toarcian age, approximately 183 million years ago, during the Early Jurassic. The extinction event had two main pulses, the first being the Pliensbachian-Toarcian boundary event (PTo-E). The second, larger pulse, the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event (TOAE), was a global oceanic anoxic event, representing possibly the most extreme case of widespread ocean deoxygenation in the entire Phanerozoic eon. In addition to the PTo-E and TOAE, there were multiple other, smaller extinction pulses within this span of time.
The Selli Event, also known as OAE1a, was an oceanic anoxic event (OAE) of global scale that occurred during the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous, about 120.5 million years ago (Ma). The OAE is associated with large igneous province volcanism and an extinction event of marine organisms driven by global warming, ocean acidification, and anoxia.
The Breistroffer Event (OAE1d) was an oceanic anoxic event (OAE) that occurred during the middle Cretaceous period, specifically in the latest Albian, around 101 million years ago (Ma).
The Paquier Event (OAE1b) was an oceanic anoxic event (OAE) that occurred around 111 million years ago (Ma), in the Albian geologic stage, during a climatic interval of Earth's history known as the Middle Cretaceous Hothouse (MKH).
The Amadeus Event (OAE1c) was an oceanic anoxic event (OAE). It occurred 106 million years ago (Ma), during the Albian age of the Cretaceous period, in a climatic interval known as the Middle Cretaceous Hothouse (MKH).
The Mid-Cenomanian Event (MCE) was an oceanic anoxic event that took place during the middle Cenomanian, as its name suggests, around 96.5 Ma.
The Hesseltal Formation or Blackcoloured Formation is a Late Cretaceous geological formation from northern Germany. It consists of lithified marls and limestone, with a unique series of black shales deposited in anoxic conditions during the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary event.
References
- ↑ "International Chronostratigraphic Chart". www.stratigraphy.org.
- ↑ Cetean, Claudia G.; Balc, Ramona; Kaminski, Michael A.; Filipescu, Sorin (August 2008). "Biostratigraphy of the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary in the Eastern Carpathians (Dâmboviţa Valley): preliminary observations". Studia Universitatis Babeş-Bolyai, Geologia. 53 (1): 11–23. doi: 10.5038/1937-8602.53.1.2 .
- ↑ Petrizzo, Maria Rose; Amaglio, Giulia; Watkins, David K.; MacLeod, Kenneth G.; Huber, Brian T.; Hasegawa, Takashi; Wolfgring, Erik (19 August 2022). "Biotic and Paleoceanographic Changes Across the Late Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 in the Southern High Latitudes (IODP Sites U1513 and U1516, SE Indian Ocean)". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 37 (9): e2022PA004474. Bibcode:2022PaPa...37.4474P. doi:10.1029/2022PA004474. PMC 9545577 . PMID 36247808.
- ↑ Paul, C. R. C.; Lamolda, M. A.; Mitchell, S. F.; Vaziri, M. R.; Gorostidi, A.; Marshall, J. D. (15 June 1999). "The Cenomanian–Turonian boundary at Eastbourne (Sussex, UK): a proposed European reference section". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 150 (1–2): 83–121. Bibcode:1999PPP...150...83P. doi:10.1016/S0031-0182(99)00009-7 . Retrieved 28 January 2023.
- ↑ Arthur, Michael A.; Dean, Walter E.; Pratt, Lisa M. (20 October 1988). "Geochemical and climatic effects of increased marine organic carbon burial at the Cenomanian/Turonian boundary". Nature . 335 (6192): 714–717. Bibcode:1988Natur.335..714A. doi:10.1038/335714a0. S2CID 4277249 . Retrieved 28 January 2023.
- 1 2 Grosheny, Danièle; Beaudoin, Bernard; Morel, Laurence; Desmares, Delphine (October 2006). "High-resolution biotratigraphy and chemostratigraphy of the Cenomanian/Turonian boundary event in the Vocontian Basin, southeast France". Cretaceous Research . 27 (5): 629–640. Bibcode:2006CrRes..27..629G. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2006.03.005 . Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- 1 2 Jarvis, Ian; Gale, Andrew S.; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Pearce, Martin A. (3 July 2006). "Secular variation in Late Cretaceous carbon isotopes: a new δ13C carbonate reference curve for the Cenomanian–Campanian (99.6–70.6 Ma)". Geological Magazine . 143 (5): 561–608. Bibcode:2006GeoM..143..561J. doi:10.1017/S0016756806002421. S2CID 55903093 . Retrieved 18 March 2023.
- 1 2 Jarvis, Ian; Carson, G. A.; Cooper, M. K. E.; Hart, M. B.; Leary, P. N.; Tocher, B. A.; Horne, D.; Rosenfeld, A. (March 1988). "Microfossil Assemblages and the Cenomanian-Turonian (late Cretaceous) Oceanic Anoxic Event". Cretaceous Research . 9 (1): 3–103. Bibcode:1988CrRes...9....3J. doi:10.1016/0195-6671(88)90003-1 . Retrieved 27 April 2023.
- 1 2 Junium, Christopher K.; Arthur, Michael A. (3 March 2007). "Nitrogen cycling during the Cretaceous, Cenomanian-Turonian Oceanic Anoxic Event II". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems . 8 (3): 1–18. Bibcode:2007GGG.....8.3002J. doi:10.1029/2006GC001328. S2CID 127888121 . Retrieved 25 April 2023.
- 1 2 Peryt, D.; Wyrwicka, K. (September 1993). "The Cenomanian/Turonian boundary event in Central Poland". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 104 (1–4): 185–197. Bibcode:1993PPP...104..185P. doi:10.1016/0031-0182(93)90130-B . Retrieved 28 January 2023.
- 1 2 Mort, Haydon P.; Adatte, Thierry; Föllmi, Karl B.; Keller, Gerta; Steinmann, Philipp; Matera, Virginie; Berner, Zsolt; Stüben, Doris (1 June 2007). "Phosphorus and the roles of productivity and nutrient recycling during oceanic anoxic event 2". Geology . 35 (6): 483–486. Bibcode:2007Geo....35..483M. doi:10.1130/G23475A.1 . Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- 1 2 Papadomanolaki, Nina M.; Lenstra, Wytze K.; Wolthers, Mariette; Slomp, Caroline P. (1 July 2022). "Enhanced phosphorus recycling during past oceanic anoxia amplified by low rates of apatite authigenesis". Science Advances . 8 (26): eabn2370. Bibcode:2022SciA....8N2370P. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn2370 . hdl: 1874/421467 . PMC 10883373 . PMID 35776794. S2CID 250218660.
- 1 2 Handoh, Itsuki C.; Lenton, Timothy M. (8 October 2003). "Periodic mid-Cretaceous oceanic anoxic events linked by oscillations of the phosphorus and oxygen biogeochemical cycles". Global Biogeochemical Cycles. 17 (4): 3-1–3-11. Bibcode:2003GBioC..17.1092H. doi:10.1029/2003GB002039. S2CID 140194325 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- 1 2 Gomes, Maya L.; Hurtgen, Matthew T.; Sageman, Bradley B. (21 December 2015). "Biogeochemical sulfur cycling during Cretaceous oceanic anoxic events: A comparison of OAE1a and OAE2". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 31 (2): 233–251. doi:10.1002/2015PA002869 . Retrieved 19 December 2022.
- 1 2 Okhouchi, N.; Kawamura, K.; Kajiwara, Y.; Wada, E.; Okada, M.; Kanamatsu, T.; Taira, A. (1 June 1999). "Sulfur isotope records around Livello Bonarelli (northern Apennines, Italy) black shale at the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary". Geology . 27 (6): 535–538. Bibcode:1999Geo....27..535O. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1999)027<0535:SIRALB>2.3.CO;2 . Retrieved 19 December 2022.
- ↑ Sageman, Bradley B.; Meyers, Stephen R.; Arthur, Michael A. (1 February 2006). "Orbital time scale and new C-isotope record for Cenomanian-Turonian boundary stratotype". Geology . 34 (2): 125. Bibcode:2006Geo....34..125S. doi:10.1130/G22074.1. S2CID 16899894 . Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- 1 2 3 Li, Yong-Xiang; Montañez, Isabel P.; Liu, Zhonghui; Ma, Lifeng (March 2017). "Astronomical constraints on global carbon-cycle perturbation during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (OAE2)". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 462: 35–46. Bibcode:2017E&PSL.462...35L. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2017.01.007. ISSN 0012-821X . Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ↑ G. Bonarelli, Il territorio di Gubbio - Notizie geologiche, Roma 1891
- ↑ G. Parisi, F. Piergiovanni e M. Marcucci, Il livello Bonarelli nell'area umbro-marchigiana, in Stratigrafia del Mesozoico e Cenozoico nell'area Umbro-Marchigiana, Roma, 1989
- ↑ Bryant, Raquel; Belanger, Christina L. (19 January 2023). "Spatial heterogeneity in benthic foraminiferal assemblages tracks regional impacts of paleoenvironmental change across Cretaceous OAE2". Paleobiology . 49 (3): 431–453. Bibcode:2023Pbio...49..431B. doi: 10.1017/pab.2022.47 . S2CID 256132544.
- ↑ Selby, David; Mutterlose, Jörg; Condon, Daniel J. (July 2009). "U–Pb and Re–Os geochronology of the Aptian/Albian and Cenomanian/Turonian stage boundaries: Implications for timescale calibration, osmium isotope seawater composition and Re–Os systematics in organic-rich sediments". Chemical Geology . 265 (3–4): 394–409. Bibcode:2009ChGeo.265..394S. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.05.005 . Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ↑ Leckie, R; Bralower, T.; Cashman, R. (2002). "Oceanic anoxic events and plankton evolution: Biotic response to tectonic forcing during the mid-Cretaceous" (PDF). Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 17 (3): 1–29. Bibcode:2002PalOc..17.1041L. doi:10.1029/2001pa000623.
- ↑ Meyers, Stephen R.; Siewert, Sarah E.; Singer, Brad S.; Sageman, Bradley B.; Condon, Daniel J.; Obradovich, John D.; Jicha, Brian R.; Sawyer, David A. (January 2012). "Intercalibration of radioisotopic and astrochronologic time scales for the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary interval, Western Interior Basin, USA". Geology . 40 (1): 7–10. Bibcode:2012Geo....40....7M. doi:10.1130/g32261.1. ISSN 1943-2682 . Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ↑ Kulenguski, Joseph T.; Gilleaudeau, Geoffrey J.; Kaufman, Alan J.; Kipp, Michael A.; Tissot, François L.H.; Goepfert, Tyler J.; Pitts, Alan D.; Pierantoni, Pietropaolo; Evans, Michael N.; Elrick, Maya (15 October 2023). "Carbonate uranium isotopes across Cretaceous OAE 2 in southern Mexico: New constraints on the global spread of marine anoxia and organic carbon burial". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 628: 111756. Bibcode:2023PPP...62811756K. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2023.111756 . Retrieved 19 May 2024– via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ↑ Eldrett, James S.; Ma, Chao; Bergman, Steven C.; Lutz, Brendan; Gregory, F. John; Dodsworth, Paul; Phipps, Mark; Hardas, Petros; Minisini, Daniel; Ozkan, Aysen; Ramezani, Jahander; Bowring, Samuel A.; Kamo, Sandra L.; Ferguson, Kurt; Macaulay, Calum; Kelly, Amy E. (September–December 2015). "An astronomically calibrated stratigraphy of the Cenomanian, Turonian and earliest Coniacian from the Cretaceous Western Interior Seaway, USA: Implications for global chronostratigraphy". Cretaceous Research . 56: 316–344. Bibcode:2015CrRes..56..316E. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.04.010 . Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- ↑ Xu, Kang; Zhong, Yi; Tsikos, H.; Chen, Hongjin; Li, Yawei (16 December 2023). "Orbital-paced Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 evolution and astrochronology in the Mentelle Basin (Australia) at southern high latitudes". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology : 111973. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2023.111973 . Retrieved 30 December 2023– via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ↑ Coccioni, Rodolfo; Luciani, Valeria (1 April 2004). "Planktonic foraminifera and environmental changes across the Bonarelli Event (OAE2, latest Cenomanian) in its type area: A high-resolution study from the tethyan reference Bottaccione section (Gubbio, Central Italy)". Journal of Foraminiferal Research. 34 (2): 109–129. Bibcode:2004JForR..34..109C. doi:10.2113/0340109 . Retrieved 30 December 2022.
- ↑ Bottini, Cinzia; Erba, Elisabetta (10 August 2018). "Mid-Cretaceous paleoenvironmental changes in the western Tethys". Climate of the Past . 14 (8): 1147–1163. Bibcode:2018CliPa..14.1147B. doi: 10.5194/cp-14-1147-2018 . hdl: 2434/593369 . S2CID 55431939 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- ↑ Scotese, Christopher Robert; Song, Haijun; Mills, Benjamin J. W.; Van der Meer, Douwe G. (April 2021). "Phanerozoic paleotemperatures: The earth's changing climate during the last 540 million years". Earth-Science Reviews . 215: 103503. Bibcode:2021ESRv..21503503S. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103503. S2CID 233579194 . Retrieved 10 June 2023.
- ↑ Hong, Sung Kyung; Lee, Yong Il (15 April 2012). "Evaluation of atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations during the Cretaceous". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 327–328: 23–28. Bibcode:2012E&PSL.327...23H. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.01.014 . Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- 1 2 Forster, Astrid; Schouten, Stephan; Moriya, Kazuyoshi; Wilson, Paul A.; Sinninghe Damsté, Jaap S. (14 March 2007). "Tropical warming and intermittent cooling during the Cenomanian/Turonian oceanic anoxic event 2: Sea surface temperature records from the equatorial Atlantic". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 22 (1): 1–14. Bibcode:2007PalOc..22.1219F. doi: 10.1029/2006PA001349 .
- ↑ Voigt, Silke; Gale, Andrew S.; Flögel, Sascha (8 December 2004). "Midlatitude shelf seas in the Cenomanian-Turonian greenhouse world: Temperature evolution and North Atlantic circulation: CENOMANIAN-TURONIAN TEMPERATURE EVOLUTION". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 19 (4): 1–17. doi: 10.1029/2004PA001015 .
- ↑ Wilson, Paul A.; Norris, Richard D.; Cooper, Matthew J. (1 July 2002). "Testing the Cretaceous greenhouse hypothesis using glassy foraminiferal calcite from the core of the Turonian tropics on Demerara Rise". Geology . 30 (7): 607–610. Bibcode:2002Geo....30..607W. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0607:TTCGHU>2.0.CO;2 . Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ↑ O'Brien, Charlotte L.; Robinson, Stuart A.; Pancost, Richard D.; Sinninghe Damsté, Jaap S.; Schouten, Stefan; Lunt, Daniel J.; Alsenz, Heiko; Bornemann, André; Bottini, Cinzia; Brassell, Simon C.; Farnsworth, Alexander; Forster, Astrid; Huber, Brian T.; Inglis, Gordon N.; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Linnert, Christian; Littler, Kate; Markwick, Paul; McAnena, Alison; Mutterlose, Jörg; Naafs, B. David A.; Püttmann, Wilhelm; Sluijs, Appy; Van Helmond, Niels A. G. M.; Vellekoop, Johan; Wagner, Thomas; Wrobel, Neil A. (September 2017). "Cretaceous sea-surface temperature evolution: Constraints from TEX86 and planktonic foraminiferal oxygen isotopes". Earth-Science Reviews . 172: 224–247. Bibcode:2017ESRv..172..224O. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.07.012 . hdl: 2434/521617 . S2CID 55405082.
- ↑ Forster, Astrid; Schouten, Stefan; Baas, Marianne; Sinninghe Damsté, Jaap S. (1 October 2007). "Mid-Cretaceous (Albian–Santonian) sea surface temperature record of the tropical Atlantic Ocean". Geology . 35 (10): 919–922. Bibcode:2007Geo....35..919F. doi:10.1130/G23874A.1. ISSN 0091-7613 . Retrieved 4 September 2023.
- ↑ Poulsen, Christopher J.; Gendaszek, Andrew S.; Jacob, Robert L. (1 February 2003). "Did the rifting of the Atlantic Ocean cause the Cretaceous thermal maximum?". Geology . 31 (2): 115–118. Bibcode:2003Geo....31..115P. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0115:DTROTA>2.0.CO;2 . Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ↑ Bédard, Jean H.; Dewing, Keith; Grasby, Stephen E.; Nabelek, Peter; Heimdal, Thea Hatlen; Yakymchuk, Chris; Shieh, Sean R.; Rumney, Justin; Deegan, Frances M.; Troll, Valentin R. (13 September 2023). "Basaltic sills emplaced in organic-rich sedimentary rocks: Consequences for organic matter maturation and Cretaceous paleo-climate". Geological Society of America Bulletin . doi:10.1130/B36982.1. ISSN 0016-7606 . Retrieved 23 March 2024– via GeoScienceWorld.
- 1 2 Scaife, J. D.; Ruhl, Micha; Dickson, A. J.; Mather, Tamsin A.; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Percival, L. M. E.; Hesselbo, Stephen P.; Cartwright, J.; Eldrett, J. S.; Bergman, S. C.; Minisini, D. (1 November 2017). "Sedimentary Mercury Enrichments as a Marker for Submarine Large Igneous Province Volcanism? Evidence From the Mid-Cenomanian Event and Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (Late Cretaceous)". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems . 18 (12): 4253–4275. Bibcode:2017GGG....18.4253S. doi: 10.1002/2017GC007153 . S2CID 133798453.
- ↑ Sinton, C. W.; Duncan, R. A. (1 December 1997). "Potential links between ocean plateau volcanism and global ocean anoxia at the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary". Economic Geology . 92 (7–8): 836–842. Bibcode:1997EcGeo..92..836S. doi:10.2113/gsecongeo.92.7-8.836. ISSN 1554-0774 . Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ Serrano, Lina; Ferrari, Luca; López Martínez, Margarita; Petrone, Chiara Maria; Jaramillo, Carlos (15 September 2011). "An integrative geologic, geochronologic and geochemical study of Gorgona Island, Colombia: Implications for the formation of the Caribbean Large Igneous Province". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 309 (3–4): 324–336. Bibcode:2011E&PSL.309..324S. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2011.07.011 . Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ↑ Du Vivier, Alice D. C.; Selby, David; Sageman, Bradley B.; Jarvis, Ian; Gröcke, Darren R.; Voigt, Silke (1 March 2014). "Marine 187Os/188Os isotope stratigraphy reveals the interaction of volcanism and ocean circulation during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 389: 23–33. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.12.024 . ISSN 0012-821X.
- ↑ Joo, Young Ji; Sageman, Bradley B.; Hurtgen, Matthew T. (1 April 2020). "Data-model comparison reveals key environmental changes leading to Cenomanian-Turonian Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Earth-Science Reviews . 203: 103123. Bibcode:2020ESRv..20303123J. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103123 . ISSN 0012-8252.
- ↑ Kerr, Andrew C.; Tarney, John (1 April 2005). "Tectonic evolution of the Caribbean and northwestern South America: The case for accretion of two Late Cretaceous oceanic plateaus". Geology . 33 (4): 269–272. Bibcode:2005Geo....33..269K. doi:10.1130/G21109.1 . Retrieved 8 April 2023.
- ↑ Naber, T.V.; Grasby, S.E.; Cuthbertson, J.P.; Rayner, N.; Tegner, C. (16 December 2020). "New constraints on the age, geochemistry, and environmental impact of High Arctic Large Igneous Province magmatism: Tracing the extension of the Alpha Ridge onto Ellesmere Island, Canada". Geological Society of America Bulletin . 133 (7–8): 1695–1711. doi: 10.1130/B35792.1 . ISSN 0016-7606.
- ↑ Davis, William J.; Schröder-Adams, Claudia J.; Galloway, Jennifer M.; Herrle, Jens O.; Pugh, Adam T. (24 June 2016). "U–Pb geochronology of bentonites from the Upper Cretaceous Kanguk Formation, Sverdrup Basin, Arctic Canada: constraints on sedimentation rates, biostratigraphic correlations and the late magmatic history of the High Arctic Large Igneous Province". Geological Magazine . 154 (4): 757–776. doi:10.1017/S0016756816000376. ISSN 0016-7568 . Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- ↑ Schröder-Adams, Claudia J.; Herrle, Jens O.; Selby, David; Quesnel, Alex; Froude, Gregory (1 April 2019). "Influence of the High Arctic Igneous Province on the Cenomanian/Turonian boundary interval, Sverdrup Basin, High Canadian Arctic". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 511: 76–88. Bibcode:2019E&PSL.511...76S. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2019.01.023. S2CID 133942033 . Retrieved 22 April 2023.
- ↑ Maher, Jr., Harmon D. (January 2001). "Manifestations of the Cretaceous High Arctic Large Igneous Province in Svalbard". The Journal of Geology . 109 (1): 91–104. Bibcode:2001JG....109...91M. doi:10.1086/317960. ISSN 0022-1376 . Retrieved 16 September 2023.
- ↑ Ernst, Richard E.; Youbi, Nasrrddine (July 2017). "How Large Igneous Provinces affect global climate, sometimes cause mass extinctions, and represent natural markers in the geological record". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 478: 30–52. Bibcode:2017PPP...478...30E. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.03.014 . Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ↑ Kuroda, J.; Ogawa, N.; Tanimizu, M.; Coffin, M.; Tokuyama, H.; Kitazato, H.; Ohkouchi, N. (15 April 2007). "Contemporaneous massive subaerial volcanism and late cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 256 (1–2): 211–223. Bibcode:2007E&PSL.256..211K. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.01.027. ISSN 0012-821X. S2CID 129546012 . Retrieved 28 March 2023.
- ↑ Matsumoto, Hironao; Coccioni, Rodolfo; Frontalini, Fabrizio; Shirai, Kotaro; Jovane, Luigi; Trindade, Ricardo; Savian, Jairo F.; Koroda, Junichiro (11 January 2022). "Mid-Cretaceous marine Os isotope evidence for heterogeneous cause of oceanic anoxic events". Nature Communications . 13 (1): 239. Bibcode:2022NatCo..13..239M. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-27817-0. PMC 8752794 . PMID 35017487.
- ↑ Du Vivier, A. D. C.; Selby, David; Condon, Daniel J.; Takashima, R.; Nishi, H. (15 October 2015). "Pacific 187Os/188Os isotope chemistry and U–Pb geochronology: Synchroneity of global Os isotope change across OAE 2". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 428: 204–216. Bibcode:2015E&PSL.428..204D. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.07.020 .
- ↑ Li, Yong-Xiang; Liu, Xinyu; Selby, David; Liu, Zhonghui; Montañez, Isabel P.; Li, Xianghui (15 January 2022). "Enhanced ocean connectivity and volcanism instigated global onset of Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (OAE2) ∼94.5 million years ago". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 578: 117331. Bibcode:2022E&PSL.57817331L. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2021.117331 . Retrieved 4 September 2023.
- 1 2 3 Sullivan, Daniel L.; Brandon, Alan D.; Eldrett, James; Bergman, Steven C.; Wright, Shawn; Minisini, Daniel (15 September 2020). "High resolution osmium data record three distinct pulses of magmatic activity during cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (OAE-2)". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta . 285: 257–273. Bibcode:2020GeCoA.285..257S. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2020.04.002 . Retrieved 30 December 2023– via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ↑ Zheng, Xin-Yuan; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Gale, Andrew S.; Ward, David J.; Henderson, Gideon M. (1 February 2016). "A climatic control on reorganization of ocean circulation during the mid-Cenomanian event and Cenomanian-Turonian oceanic anoxic event (OAE 2): Nd isotope evidence". Geology . 44 (2): 151–154. Bibcode:2016Geo....44..151Z. doi:10.1130/G37354.1. S2CID 130480845 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- 1 2 Turgeon, Steven; Brumsack, Hans-Jürgen (15 November 2006). "Anoxic vs dysoxic events reflected in sediment geochemistry during the Cenomanian–Turonian Boundary Event (Cretaceous) in the Umbria–Marche Basin of central Italy". Chemical Geology . 234 (3–4): 321–339. Bibcode:2006ChGeo.234..321T. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.008 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- ↑ Holmden, C.; Jacobson, A. D.; Sageman, B. B.; Hurtgen, M. T. (1 August 2016). "Response of the Cr isotope proxy to Cretaceous Ocean Anoxic Event 2 in a pelagic carbonate succession from the Western Interior Seaway". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta . 186: 277–295. Bibcode:2016GeCoA.186..277H. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2016.04.039. ISSN 0016-7037 . Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ Percival, Lawrence M. E.; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Mather, Tamsin A.; Dickson, Alexander J.; Batenburg, Sietske J.; Ruhl, Micha; Hesselbo, Stephen B.; Barclay, Richard; Jarvis, Ian; Robinson, Stuart A.; Woelders, Lineke (October 2018). "Does large igneous province volcanism always perturb the mercury cycle? Comparing the records of Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 and the end-Cretaceous to other Mesozoic events". American Journal of Science . 318 (8): 799–860. Bibcode:2018AmJS..318..799P. doi:10.2475/08.2018.01. hdl: 2262/90923 . S2CID 134682528 . Retrieved 28 March 2023.
- ↑ Flögel, S.; Wallmann, K.; Poulsen, C. J.; Zhou, J.; Oschlies, A.; Voigt, S.; Kuhnt, W. (May 2011). "Simulating the biogeochemical effects of volcanic CO2 degassing on the oxygen-state of the deep ocean during the Cenomanian/Turonian Anoxic Event (OAE2)". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 305 (3–4): 371–384. Bibcode:2011E&PSL.305..371F. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2011.03.018. ISSN 0012-821X . Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- 1 2 Naafs, B. David A.; Monteiro, Fanny M.; Pearson, Ann; Higgins, Meytal B.; Pancost, Richard D.; Ridgwell, Andy (10 December 2019). "Fundamentally different global marine nitrogen cycling in response to severe ocean deoxygenation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America . 116 (50): 24979–24984. Bibcode:2019PNAS..11624979N. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1905553116 . PMC 6911173 . PMID 31767742.
- 1 2 Jarvis, Ian; Lignum, John S.; Gröcke, Darren R.; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Pearce, Martin A. (19 July 2011). "Black shale deposition, atmospheric CO2 drawdown, and cooling during the Cenomanian-Turonian Oceanic Anoxic Event". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 26 (3): 1–17. Bibcode:2011PalOc..26.3201J. doi: 10.1029/2010PA002081 .
- ↑ Sinninghe Damsté, Jaap S.; Van Bentum, Elisabeth C.; Reichart, Gert-Jan; Pross, Jörg; Schouten, Stefan (15 April 2010). "A CO2 decrease-driven cooling and increased latitudinal temperature gradient during the mid-Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 293 (1–2): 97–103. Bibcode:2010E&PSL.293...97S. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2010.02.027 . Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- ↑ Percival, Lawrence M. E.; Van Helmond, N. A. G. M.; Selby, David; Goderis, S.; Claeys, P. (26 September 2020). "Complex Interactions Between Large Igneous Province Emplacement and Global-Temperature Changes During the Cenomanian-Turonian Oceanic Anoxic Event (OAE 2)". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 35 (10). Bibcode:2020PaPa...35.4016P. doi:10.1029/2020PA004016. S2CID 224902886 . Retrieved 13 June 2023.
- ↑ Du Vivier, Alice D. C.; Jacobson, Andrew D.; Lehn, Gregory O.; Selby, David; Hurtgen, Matthew T.; Sageman, Bradley B. (15 April 2015). "Ca isotope stratigraphy across the Cenomanian–Turonian OAE 2: Links between volcanism, seawater geochemistry, and the carbonate fractionation factor". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 416: 121–131. Bibcode:2015E&PSL.416..121D. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.02.001 .
- ↑ Fantle, Matthew S.; Ridgwell, Andy (5 August 2020). "Towards an understanding of the Ca isotopic signal related to ocean acidification and alkalinity overshoots in the rock record". Chemical Geology . 547: 119672. Bibcode:2020ChGeo.54719672F. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.119672 . S2CID 219461270.
- ↑ Kitch, Gabriella Dawn (December 2021). "Calcium isotope ratios of malformed foraminifera reveal biocalcification stress preceded OAE2". Identifying and Constraining Biocalcification Stress from Geologic Ocean Acidification Events (PhD). Northwestern University. ProQuest 2617262217 . Retrieved 4 September 2023.
- ↑ Hönisch, Bärbel; Ridgwell, Andy; Schmidt, Daniela N.; Thomas, Ellen; Gibbs, Samantha J.; Sluijs, Appy; Zeebe, Richard; Kump, Lee; Martindale, Rowan C.; Greene, Sarah E.; Kiessling, Wolfgang; Ries, Justin; Zachos, James C.; Royer, Dana L.; Barker, Stephen; Marchitto Jr., Thomas M.; Moyer, Ryan; Pelejero, Carles; Ziveri, Patrizia; Foster, Gavin L.; Williams, Branwen (2 March 2012). "The Geological Record of Ocean Acidification". Science . 335 (6072): 1058–1063. Bibcode:2012Sci...335.1058H. doi:10.1126/science.1208277. hdl: 1874/385704 . PMID 22383840. S2CID 6361097 . Retrieved 28 June 2023.
- ↑ Jones, Matthew M.; Sageman, Bradley B.; Selby, David; Jacobson, Andrew D.; Batenburg, Sietske J.; Riquier, Laurent; MacLeod, Kenneth G.; Huber, Brian T.; Bogus, Kara A.; Tejada, Maria Luisa G.; Kuroda, Junichiro; Hobbs, Richard W. (19 January 2023). "Abrupt episode of mid-Cretaceous ocean acidification triggered by massive volcanism". Nature Geoscience . 16 (1): 169–174. Bibcode:2023NatGe..16..169J. doi:10.1038/s41561-022-01115-w. S2CID 256137367 . Retrieved 24 April 2023.
- 1 2 "Submarine eruption bled Earth's oceans of oxygen". New Scientist. 16 July 2008. Retrieved 2018-05-09.(subscription required)
- ↑ Charbonnier, Guillaume; Boulila, Slah; Spangenberg, Jorge E.; Adatte, Thierry; Föllmi, Karl B.; Laskar, Jacques (1 October 2018). "Obliquity pacing of the hydrological cycle during the Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 499: 266–277. Bibcode:2018E&PSL.499..266C. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2018.07.029 . Retrieved 23 March 2024– via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ↑ Chen, Hongjin; Xu, Zhaokai; Bayon, Germain; Lim, Dhongil; Batenburg, Sietske J.; Petrizzo, Maria Rose; Hasegawa, Takashi; Li, Tiegang (1 February 2022). "Enhanced hydrological cycle during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 at southern high latitudes: New insights from IODP Site U1516". Global and Planetary Change . 209: 103735. Bibcode:2022GPC...20903735C. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2022.103735. ISSN 0921-8181 . Retrieved 30 December 2023– via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ↑ Meyers, Philip A.; Bernasconi, Stefano M.; Forster, Astrid (December 2006). "Origins and accumulation of organic matter in expanded Albian to Santonian black shale sequences on the Demerara Rise, South American margin". Organic Geochemistry . 37 (12): 1816–1830. Bibcode:2006OrGeo..37.1816M. doi:10.1016/j.orggeochem.2006.08.009 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- ↑ Kalanat, Behnaz; Vaziri-Moghaddam, Hossein (1 November 2019). "The Cenomanian/Turonian boundary interval deep-sea deposits in the Zagros Basin (SW Iran): Bioevents, carbon isotope record and palaeoceanographic model". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 533: 109238. Bibcode:2019PPP...53309238K. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.109238. ISSN 0031-0182 . Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- 1 2 Kerr, Andrew C. (July 1998). "Oceanic plateau formation: a cause of mass extinction and black shale deposition around the Cenomanian–Turonian boundary?". Journal of the Geological Society . 155 (4): 619–626. Bibcode:1998JGSoc.155..619K. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.155.4.0619. S2CID 129178854 . Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ↑ Brčić, Vlatko; Glumac, Bosiljka; Fuček, Ladislav; Grizelj, Anita; Horvat, Marija; Posilović, Hrvoje; Mišur, Ivan (July 2017). "The Cenomanian–Turonian boundary in the northwestern part of the Adriatic Carbonate Platform (Ćićarija Mtn., Istria, Croatia): characteristics and implications". Facies. 63 (3): 17. Bibcode:2017Faci...63...17B. doi:10.1007/s10347-017-0499-7. S2CID 132371872 . Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- ↑ Nagm, Emad; El-Qot, Gamal; Wilmsen, Markus (December 2014). "Stable-isotope stratigraphy of the Cenomanian–Turonian (Upper Cretaceous) boundary event (CTBE) in Wadi Qena, Eastern Desert, Egypt". Journal of African Earth Sciences . 100: 524–531. Bibcode:2014JAfES.100..524N. doi:10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2014.07.023. ISSN 1464-343X . Retrieved 17 March 2023.
- ↑ Jenkyns, Hugh C. (March 2010). "Geochemistry of oceanic anoxic events: REVIEW". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems . 11 (3): n/a. Bibcode:2010GGG....11.3004J. doi: 10.1029/2009GC002788 .
- ↑ Schlanger, S. O.; Arthur, M. A.; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Scholle, P. A. (1987). "The Cenomanian-Turonian Oceanic Anoxic Event, I. Stratigraphy and distribution of organic carbon-rich beds and the marine δ 13 C excursion". Geological Society, London, Special Publications. 26 (1): 371–399. Bibcode:1987GSLSP..26..371S. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.1987.026.01.24. ISSN 0305-8719. S2CID 129843829.
- 1 2 Sullivan, Daniel L.; Brandon, Alan D.; Eldrett, James; Bergman, Steven C.; Wright, Shawn; Minisini, Daniel (1 December 2020). "Corrigendum to "High resolution osmium data record three distinct pulses of magmatic activity during cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (OAE-2)" [Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 285 (2020) 257–273]". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta . 290: 424–425. Bibcode:2020GeCoA.290..424S. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2020.09.022. ISSN 0016-7037 . Retrieved 30 December 2023– via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ↑ Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Mutterlose, Jorg; Sliter, W. V. (1995). "UPPER CRETACEOUS CARBON- AND OXYGEN-ISOTOPE STRATIGRAPHY OF DEEP-WATER SEDIMENTS FROM THE NORTH-CENTRAL PACIFIC (SITE 869, FLANK OF PIKINNI-WODEJEBATO, MARSHALL ISLANDS)" (PDF). Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results. Retrieved 23 March 2024.
- ↑ Jones, Matthew M.; Sageman, Bradley B.; Meyers, Stephen R. (20 April 2018). "Turonian Sea Level and Paleoclimatic Events in Astronomically Tuned Records From the Tropical North Atlantic and Western Interior Seaway". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 33 (5): 470–492. Bibcode:2018PaPa...33..470J. doi: 10.1029/2017PA003158 . ISSN 2572-4517.
- ↑ Wang, Xiangli; Reinhard, Christopher T.; Planavsky, Noah J.; Owens, Jeremy D.; Lyons, Timothy W.; Johnson, Thomas M. (1 July 2016). "Sedimentary chromium isotopic compositions across the Cretaceous OAE2 at Demerara Rise Site 1258". Chemical Geology . 429: 85–92. Bibcode:2016ChGeo.429...85W. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.03.006 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- ↑ Westermann, Stéphane; Vance, Derek; Cameron, Vyllinniskii; Archer, Corey; Robinson, Stuart A. (15 October 2014). "Heterogeneous oxygenation states in the Atlantic and Tethys oceans during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 404: 178–189. Bibcode:2014E&PSL.404..178W. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2014.07.018 . Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ↑ Goldberg, Tatiana; Poulton, Simon W.; Wagner, Thomas; Kolonic, Sadat F.; Rehkämper, Mark (15 April 2016). "Molybdenum drawdown during Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 440: 81–91. Bibcode:2016E&PSL.440...81G. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2016.02.006. hdl: 10044/1/29929 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- ↑ Wang, Jianpeng; Bulot, Luc G.; Taylor, Kevin G.; Redfern, Jonathan (June 2021). "Controls and timing of Cenomanian-Turonian organic enrichment and relationship to the OAE2 event in Morocco, North Africa". Marine and Petroleum Geology . 128: 105013. doi:10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.105013 . Retrieved 30 June 2024– via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ↑ Sinninghe Damsté, Jaap S.; Köster, Jürgen (30 May 1998). "A euxinic southern North Atlantic Ocean during the Cenomanian/Turonian oceanic anoxic event". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 158 (3–4): 165–173. Bibcode:1998E&PSL.158..165S. doi:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00052-1 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- ↑ Kuypers, Marcel M. M.; Pancost, Richard D.; Nijenhuis, Ivar A.; Sinninghe Damsté, Jaap S. (9 October 2002). "Enhanced productivity led to increased organic carbon burial in the euxinic North Atlantic basin during the late Cenomanian oceanic anoxic event". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 17 (4): 3-1–3-13. Bibcode:2002PalOc..17.1051K. doi:10.1029/2000PA000569. hdl: 21.11116/0000-0001-D2CD-B . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- ↑ Pancost, Richard D.; Crawford, Neal; Magness, Simon; Turner, Andy; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Maxwell, James R. (1 May 2004). "Further evidence for the development of photic-zone euxinic conditions during Mesozoic oceanic anoxic events". Journal of the Geological Society . 161 (3): 353–364. Bibcode:2004JGSoc.161..353P. doi:10.1144/0016764903-059. S2CID 130919916 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- ↑ Abraham, Mohd Al Farid; Naafs, Bernhard David A.; Lauretano, Vittoria; Sgouridis, Fotis; Pancost, Richard D. (20 December 2023). "Warming drove the expansion of marine anoxia in the equatorial Atlantic during the Cenomanian leading up to Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Climate of the Past . 19 (12): 2569–2580. Bibcode:2023CliPa..19.2569A. doi: 10.5194/cp-19-2569-2023 . ISSN 1814-9332 . Retrieved 23 March 2024.
- ↑ Zhai, Ruixiang; Zeng, Zhiyu; Zhang, Ruiling; Yao, Weiqi (August 2023). "The response of nitrogen and sulfur cycles to ocean deoxygenation across the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary". Global and Planetary Change . 227: 104182. Bibcode:2023GPC...22704182Z. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2023.104182 . S2CID 259689748.
- ↑ Elderbak, Khalifa; Leckie, R. Mark (May 2016). "Paleocirculation and foraminiferal assemblages of the Cenomanian–Turonian Bridge Creek Limestone bedding couplets: Productivity vs. dilution during OAE2". Cretaceous Research . 60: 52–77. Bibcode:2016CrRes..60...52E. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2015.11.009 . Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- ↑ Hilbrecht, Heinz; Hubberten, Hans-W.; Oberhänsli, Hedwig (May 1992). "Biogeography of planktonic foraminifera and regional carbon isotope variations: productivity and water masses in late Cretaceous Europe". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 92 (3–4): 407–421. Bibcode:1992PPP....92..407H. doi:10.1016/0031-0182(92)90093-K . Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- ↑ Forster, Astrid; Kuypers, Marcel M. M.; Turgeon, Steven C.; Brumsack, Hans-J.; Petrizzo, Maria Rose; Sinninghe Damsté, Jaap S. (1 October 2008). "The Cenomanian/Turonian oceanic anoxic event in the South Atlantic: New insights from a geochemical study of DSDP Site 530A". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 267 (3–4): 256–283. Bibcode:2008PPP...267..256F. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.07.006 . Retrieved 28 June 2023.
- ↑ Li, Yong-Xiang; Gill, Benjamin; Montañez, Isabel P.; Ma, Lifeng; LeRoy, Matthew; Kodama, Kenneth P. (2020). "Orbitally driven redox fluctuations during Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (OAE2) revealed by a new magnetic proxy". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 538: 109465. Bibcode:2020PPP...53809465L. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.109465.
- 1 2 3 Mitchell, Ross N.; Bice, David M.; Montanari, Alessandro; Cleaveland, Laura C.; Christianson, Keith T.; Coccioni, Rodolfo; Hinnov, Linda A. (1 March 2008). "Oceanic anoxic cycles? Orbital prelude to the Bonarelli Level (OAE 2)". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 267 (1–2): 1–16. Bibcode:2008E&PSL.267....1M. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.11.026 . Retrieved 2 January 2023.
- 1 2 Coccioni, Rodolfo; Galeotti, Simone (15 January 2003). "The mid-Cenomanian Event: prelude to OAE 2". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 190: 427–440. Bibcode:2003PPP...190..427C. doi:10.1016/S0031-0182(02)00617-X . Retrieved 22 January 2023.
- ↑ Kuhnt, Wolfgang; Holbourn, Ann E.; Beil, Sebastian; Aquit, Mohamed; Krawczyk, Tim; Flögel, Sascha; Chellai, El Hassane; Jabour, Haddou (11 August 2017). "Unraveling the onset of Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 in an extended sediment archive from the Tarfaya-Laayoune Basin, Morocco". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 32 (8): 923–946. Bibcode:2017PalOc..32..923K. doi:10.1002/2017PA003146 . Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ↑ Dickson, Alexander J.; Saker-Clark, Matthew; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Bottini, Cinzia; Erba, Elisabetta; Russo, Fabio; Gorbanenko, Olga; Naafs, Bernhard D. A.; Pancost, Richard D.; Robinson, Stuart A.; Van den Boorn, Sander H.J.M; Idiz, Erdem (14 June 2016). "A Southern Hemisphere record of global trace-metal drawdown and orbital modulation of organic-matter burial across the Cenomanian–Turonian boundary (Ocean Drilling Program Site 1138, Kerguelen Plateau)". Sedimentology. 64 (1): 186–203. doi:10.1111/sed.12303. hdl: 2434/451186 . S2CID 133063861 . Retrieved 7 April 2023.
- ↑ Laurin, Jiří; Barclay, Richard S.; Sageman, Bradley B.; Dawson, Robin R.; Pagani, Mark; Schmitz, Mark; Eaton, Jeffrey; McInerney, Francesca A.; McElwain, Jennifer C. (15 June 2019). "Terrestrial and marginal-marine record of the mid-Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (OAE 2): High-resolution framework, carbon isotopes, CO2 and sea-level change". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 524: 118–136. Bibcode:2019PPP...524..118L. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.03.019 . ISSN 0031-0182.
- ↑ Mort, Haydon P.; Adatte, Thierry; Keller, Gerta; Bartels, David; Föllmi, Karl B.; Steinmann, Philipp; Berner, Zsolt; Chellai, E. H. (October–December 2008). "Organic carbon deposition and phosphorus accumulation during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 in Tarfaya, Morocco". Cretaceous Research . 29 (5–6): 1008–1023. Bibcode:2008CrRes..29.1008M. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2008.05.026 . Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- ↑ Beil, Sebastian; Kuhnt, Wolfgang; Holbourn, Ann; Scholtz, Florian; Oxmann, Julian; Wallmann, Klaus; Lorenzen, Janne; Aquit, Mohamed; Chellai, El Hassane (29 April 2020). "Cretaceous oceanic anoxic events prolonged by phosphorus cycle feedbacks". Climate of the Past . 16 (2): 757–782. Bibcode:2020CliPa..16..757B. doi: 10.5194/cp-16-757-2020 . Retrieved 14 June 2023.
- ↑ Poulton, Simon W.; Henkel, Susann; März, Christian; Urquhart, Hannah; Flögel, Sascha; Kasten, Sabine; Sinninghe Damsté, Jaap S.; Wagner, Thomas (1 November 2015). "A continental-weathering control on orbitally driven redox-nutrient cycling during Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Geology . 43 (11): 963–966. Bibcode:2015Geo....43..963P. doi: 10.1130/G36837.1 .
- ↑ Monteiro, F. M.; Pancost, Richard D.; Ridgwell, Andy; Donnadieu, Yannick (15 December 2012). "Nutrients as the dominant control on the spread of anoxia and euxinia across the Cenomanian-Turonian oceanic anoxic event (OAE2): Model-data comparison". Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology . 27 (4): 1–17. Bibcode:2012PalOc..27.4209M. doi: 10.1029/2012PA002351 . hdl: 1983/671e8aee-23c9-4b58-adef-4bb84ba6cab1 .
- ↑ Karakitsios, Vassilis; Tsikos, Harilaos; van Breugel, Yvonne; Koletti, Lyda; Damsté, Jaap S. Sinninghe; Jenkyns, Hugh C. (2006). "First evidence for the Cenomanian–Turonian oceanic anoxic event (OAE2, 'Bonarelli' event) from the Ionian Zone, western continental Greece" (PDF). International Journal of Earth Sciences . 96 (2): 343–352. Bibcode:2007IJEaS..96..343K. doi:10.1007/s00531-006-0096-4. S2CID 54714713. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2020-03-11.
- ↑ Ruebsam, Wolfgang; Schwark, Lorenz (May 2023). "Phytoplankton dynamics and nitrogen cycling during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 (Cenomanian/Turonian) in the upwelling zone of the NE proto-North Atlantic". Global and Planetary Change . 224: 104117. Bibcode:2023GPC...22404117R. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2023.104117. S2CID 258097848 . Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- ↑ Scholz, Florian; Beil, Sebastian; Flögel, Sascha; Lehmann, Moritz F.; Holbourn, Ann; Wallmann, Klaus; Kuhnt, Wolfgang (1 July 2019). "Oxygen minimum zone-type biogeochemical cycling in the Cenomanian-Turonian Proto-North Atlantic across Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 517: 50–60. Bibcode:2019E&PSL.517...50S. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2019.04.008. S2CID 149777356 . Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ↑ Pierce, Martin A.; Jarvis, Ian; Tocher, Bruce A. (1 September 2009). "The Cenomanian–Turonian boundary event, OAE2 and palaeoenvironmental change in epicontinental seas: New insights from the dinocyst and geochemical records". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology . 280 (1–2): 207–234. Bibcode:2009PPP...280..207P. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2009.06.012 . Retrieved 28 January 2023.
- ↑ Jenkyns, Hugh C. (March 1980). "Cretaceous anoxic events: from continents to oceans". Journal of the Geological Society . 137 (2): 171–188. Bibcode:1980JGSoc.137..171J. doi:10.1144/gsjgs.137.2.0171. S2CID 140199289 . Retrieved 8 April 2023.
- ↑ Al-Bassam, Khaldoun; Magna, Tomáš; Vodrážka, Radek; Čech, Stanislav (May 2019). "Mineralogy and geochemistry of marine glauconitic siliciclasts and phosphates in selected Cenomanian–Turonian units, Bohemian Cretaceous Basin, Czech Republic: Implications for provenance and depositional environment". Geochemistry. 79 (2): 347–368. Bibcode:2019ChEG...79..347A. doi:10.1016/j.chemer.2019.05.003. S2CID 164633566 . Retrieved 12 April 2023.
- ↑ Blättler, Clara L.; Jenkyns, Hugh C.; Reynard, Linda M.; Henderson, Gideon M. (1 September 2011). "Significant increases in global weathering during Oceanic Anoxic Events 1a and 2 indicated by calcium isotopes". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 309 (1–2): 77–88. Bibcode:2011E&PSL.309...77B. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2011.06.029 . Retrieved 8 April 2023.
- ↑ Chen, Hongjin; Bayon, Germain; Xu, Zhaokai; Li, Tiegang (1 January 2023). "Hafnium isotope evidence for enhanced weatherability at high southern latitudes during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Earth and Planetary Science Letters . 601: 117910. Bibcode:2023E&PSL.60117910C. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2022.117910 . S2CID 253650113.
- ↑ Sachs, Sven; Grant-Mackie, Jack A. (March 2003). "An ichthyosaur fragment from the Cretaceous of Northland, New Zealand". Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand . 33 (1): 307–314. Bibcode:2003JRSNZ..33..307S. doi: 10.1080/03014223.2003.9517732 . S2CID 129312766 . Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ↑ Bardet, Nathalie; Houssaye, Alexandra; Rage, Jean-Claude; Pereda Suberbiola, Xabier (1 November 2008). "The Cenomanian-Turonian (late Cretaceous) radiation of marine squamates (Reptilia): the role of the Mediterranean Tethys". Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France . 179 (6): 605–622. doi:10.2113/gssgfbull.179.6.605. ISSN 1777-5817 . Retrieved 30 June 2024– via GeoScienceWorld.
- ↑ Forêt, Tom; Aubier, Paul; Jouve, Stéphane; Cubo, Jorge (23 April 2024). "Biotic and abiotic factors and the phylogenetic structure of extinction in the evolution of Tethysuchia". Paleobiology . 50 (2): 285–307. doi:10.1017/pab.2024.5. ISSN 0094-8373 . Retrieved 30 June 2024– via Cambridge Core.
- ↑ Erbacher, Jochen; Thurow, Jürgen; Littke, Ralf (1 June 1996). "Evolution patterns of radiolaria and organic matter variations: A new approach to identify sea-level changes in mid-Cretaceous pelagic environments". Geology . 24 (6): 499–502. Bibcode:1996Geo....24..499E. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0499:EPORAO>2.3.CO;2 . Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- ↑ Gertsch, B.; Keller, G.; Adatte, Thierry; Berner, Z.; Kassab, A. S.; Tantawy, A. A. A.; El-Sabbagh, A. M.; Stueben, D. (22 October 2008). "Cenomanian–Turonian transition in a shallow water sequence of the Sinai, Egypt". International Journal of Earth Sciences . 99: 165–182. doi:10.1007/s00531-008-0374-4. S2CID 56427056 . Retrieved 11 April 2023.
- ↑ Petrizzo, Maria Rose; Watkins, David K.; MacLeod, Kenneth G.; Hasegawa, Takashi; Huber, Brian T.; Batenburg, Sietske J.; Kato, Tomonori (November 2021). "Exploring the paleoceanographic changes registered by planktonic foraminifera across the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary interval and Oceanic Anoxic Event 2 at southern high latitudes in the Mentelle Basin (SE Indian Ocean)". Global and Planetary Change . 206: 103595. Bibcode:2021GPC...20603595P. doi: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2021.103595 . hdl: 2434/869684 .
- 1 2 Melinte-Dobrinescu, Mihaela Carmen; Bojar, Ana-Voica (October–December 2008). "Biostratigraphic and isotopic record of the Cenomanian–Turonian deposits in the Ohaba-Ponor section (SW Haţeg, Romania)". Cretaceous Research . 29 (5–6): 1024–1034. Bibcode:2008CrRes..29.1024M. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2008.05.018 . Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ↑ Linnert, Christian; Mutterlose, Jörg; Erbacher, Jochen (February 2010). "Calcareous nannofossils of the Cenomanian/Turonian boundary interval from the Boreal Realm (Wunstorf, northwest Germany)". Marine Micropaleontology. 74 (1–2): 38–58. Bibcode:2010MarMP..74...38L. doi:10.1016/j.marmicro.2009.12.002. ISSN 0377-8398.
- ↑ Faucher, G.; Erba, Elisabetta; Bottini, Cinzia (2013). "Life in extreme Oceans: Calcareous Nannoplankton adaptations and strategies during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Journal of Nannoplankton Research. Retrieved 21 April 2023.
- ↑ Erbacher, J.; Thurow, J. (March 1997). "Influence of oceanic anoxic events on the evolution of mid-Cretaceous radiolaria in the North Atlantic and western Tethys". Marine Micropaleontology. 30 (1–3): 139–158. Bibcode:1997MarMP..30..139E. doi:10.1016/S0377-8398(96)00023-0 . Retrieved 19 April 2023.
- ↑ Kunstmüllerová, Lucie; Košťák, Martin (January 2024). "Changes in bivalve assemblages at the onset of the OAE2 event in the Peri-Tethyan area (Bohemian Cretaceous Basin)". Cretaceous Research . 153: 105704. Bibcode:2024CrRes.15305704K. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2023.105704.
- ↑ Johnson, C. C.; Kauffman, Erle G. (23 November 2005). "Originations, radiations and extinctions of Cretaceous rudistid bivalve species in the Caribbean Province". In Kauffman, Erle G.; Walliser, Otto H. (eds.). Extinction Events in Earth History. Berlin: Springer. pp. 305–324. doi:10.1007/BFb0011154. ISBN 978-3-540-47071-7.
- ↑ Naimi, Mohammed Nadir; Cherif, Amine; Mahboubi, Chikh Younes; Benyoucef, Madani (10 June 2022). "Ichnology of the Cenomanian–Turonian boundary event in the southern Tethyan margin (Khanguet Grouz section, Ouled Nail Range, Algeria)". Arabian Journal of Geosciences. 15 (12): 1150. Bibcode:2022ArJG...15.1150N. doi:10.1007/s12517-022-10420-y. S2CID 249551061 . Retrieved 9 April 2023.
- ↑ Prauss, Michael L. (April 2012). "The Cenomanian/Turonian Boundary event (CTBE) at Tarfaya, Morocco: Palaeoecological aspects as reflected by marine palynology". Cretaceous Research . 34: 233–256. Bibcode:2012CrRes..34..233P. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2011.11.004. ISSN 0195-6671.
- ↑ Fonseca, Carolina; Mendonça Filho, João Graciano; Lézin, Carine; de Oliveira, António Donizeti; Duarte, Luís V. (December 2019). "Organic matter deposition and paleoenvironmental implications across the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary of the Subalpine Basin (SE France): Local and global controls". International Journal of Coal Geology. 218: 103364. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2019.103364 .
- ↑ Eaton, Jeffrey G.; Kirkland, James I.; Hutchinson, J. Howard; Denton, Robert; O'Neill, Robert C.; Parrish, J. Michael (1 May 1997). "Nonmarine extinction across the Cenomanian-Turonian boundary, southwestern Utah, with a comparison to the Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction event". Geological Society of America Bulletin . 109 (5): 560–567. Bibcode:1997GSAB..109..560E. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1997)109<0560:NEATCT>2.3.CO;2 . Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ↑ Galasso, Francesca; Heimhofer, Ulrich; Schneebeli-Hermann, Elke (22 February 2023). "The Cenomanian/Turonian boundary in light of new developments in terrestrial palynology". Scientific Reports . 13 (1): 3074. Bibcode:2023NatSR..13.3074G. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-30072-6. PMC 9947001 . PMID 36813802.
- ↑ Heimhofer, Ulrich; Wucherpfennig, Nina; Adatte, Thierry; Schouten, Stefan; Schneebeli-Hermann, Elke; Gardin, Silvia; Keller, Gerta; Kentsch, Sarah; Kujau, Ariane (20 September 2018). "Vegetation response to exceptional global warmth during Oceanic Anoxic Event 2". Nature Communications . 9 (1). doi:10.1038/s41467-018-06319-6. ISSN 2041-1723. PMC 6148089 . PMID 30237441 . Retrieved 30 June 2024.