Related Research Articles

Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive, round-shaped bacterium, a member of the Firmicutes, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. The emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains of S. aureus such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine. Despite much research and development, no vaccine for S. aureus has been approved.
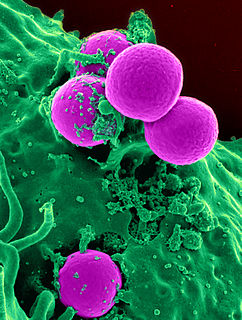
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) refers to a group of Gram-positive bacteria that are genetically distinct from other strains of Staphylococcus aureus. MRSA is responsible for several difficult-to-treat infections in humans. MRSA is any strain of S. aureus that has developed or acquired a multiple drug resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. Beta-lactam (β-lactam) antibiotics are a broad-spectrum group that include some penams and cephems such as the cephalosporins. Strains unable to resist these antibiotics are classified as methicillin-susceptible S. aureus, or MSSA.

Coagulase is a protein enzyme produced by several microorganisms that enables the conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin. In the laboratory, it is used to distinguish between different types of Staphylococcus isolates. Importantly, S. aureus is generally coagulase-positive, meaning that a positive coagulase test would indicate the presence of S. aureus or any of the other 11 coagulase-positive Staphylococci. A negative coagulase test would instead show the presence of coagulase-negative organisms such as S. epidermidis or S. saprophyticus. However, it is now known that not all S. aureus are coagulase-positive.

The classical complement pathway is one of three pathways which activate the complement system, which is part of the immune system. The classical complement pathway is initiated by antigen-antibody complexes with the antibody isotypes IgG and IgM.

The alternative pathway is a type of cascade reaction of the complement system and is a component of the innate immune system, a natural defense against infections.

C3 convertase belongs to family of serine proteases and is necessary in innate immunity as a part of the complement system which eventuate in opsonisation of particles, release of inflammatory peptides, C5 convertase formation and cell lysis.

Staphylococcus epidermidis is a Gram-positive bacterium, and one of over 40 species belonging to the genus Staphylococcus. It is part of the normal human flora, typically the skin flora, and less commonly the mucosal flora. It is a facultative anaerobic bacteria. Although S. epidermidis is not usually pathogenic, patients with compromised immune systems are at risk of developing infection. These infections are generally hospital-acquired. S. epidermidis is a particular concern for people with catheters or other surgical implants because it is known to form biofilms that grow on these devices. Being part of the normal skin flora, S. epidermidis is a frequent contaminant of specimens sent to the diagnostic laboratory.

Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation, the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis.
MSCRAMM adhesin proteins mediate the initial attachment of bacteria to host tissue, providing a critical step to establish infection.
Staphylokinase is a protein produced by Staphylococcus aureus. It contains 136 amino acid residues and has a molecular mass of 15kDa. Synthesis of staphylokinase occurs in late exponential phase. It is similar to streptokinase.
RNAIII is a stable 514 nt regulatory RNA transcribed by the P3 promoter of the Staphylococcus aureus quorum-sensing agr system ). It is the major effector of the agr regulon, which controls the expression of many S. aureus genes encoding exoproteins and cell wall associated proteins plus others encoding regulatory proteins The RNAIII transcript also encodes the 26 amino acid δ-haemolysin peptide (Hld). RNAIII contains many stem loops, most of which match the Shine-Dalgarno sequence involved in translation initiation of the regulated genes. Some of these interactions are inhibitory, others stimulatory; among the former is the regulatory protein Rot. In vitro, RNAIII is expressed post exponentially, inhibiting translation of the surface proteins, notably protein A, while stimulating that of the exoproteins, many of which are tissue-degrading enzymes or cytolysins. Among the latter is the important virulence factor, α-hemolysin (Hla), whose translation RNAIII activates by preventing the formation of an inhibitory foldback loop in the hla mRNA leader.

Alpha-toxin, also known as alpha-hemolysin (Hla), is the major cytotoxic agent released by bacterium Staphylococcus aureus and the first identified member of the pore forming beta-barrel toxin family. This toxin consists mostly of beta-sheets (68%) with only about 10% alpha-helices. The hly gene on the S. aureus chromosome encodes the 293 residue protein monomer, which forms heptameric units on the cellular membrane to form a complete beta-barrel pore. This structure allows the toxin to perform its major function, development of pores in the cellular membrane, eventually causing cell death.
Fibronectin binding protein A (FnBPA) is a Staphylococcus aureus MSCRAMM cell surface-bound protein that binds to both fibronectin and fibrinogen.
'Staphylococcus aureus delta toxin is a toxin produced by Staphylococcus aureus. It has a wide spectrum of cytolytic activity.
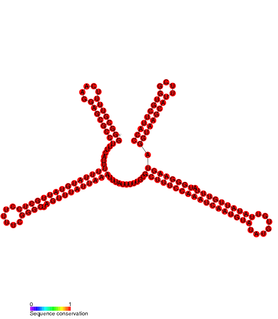
In molecular biology SprD is a non-coding RNA expressed on pathogenicity islands in Staphylococcus aureus. It was identified in silico along with a number of other sRNAs (SprA-G) through microarray analysis which were confirmed using a Northern blot. SprD has been found to significantly contribute to causing disease in an animal model.

Glutamyl endopeptidase is an extracellular bacterial serine protease of the glutamyl endopeptidase I family that was initially isolated from the Staphylococcus aureus strain V8. The protease is, hence, commonly referred to as "V8 protease", or alternatively SspA from its corresponding gene.

Aureolysin is an extracellular metalloprotease expressed by Staphylococcus aureus. This protease is a major contributor to the bacterium's virulence, or ability to cause disease, by cleaving host factors of the innate immune system as well as regulating S. aureus secreted toxins and cell wall proteins. To catalyze its enzymatic activities, aureolysin requires zinc and calcium which it obtains from the extracellular environment within the host.
Staphylococcus pseudintermedius is a gram positive coccus bacteria of the genus Staphylococcus found worldwide. It is primarily a pathogen for domestic animals, but has been known to affect humans as well.S. pseudintermedius is an opportunistic pathogen that secretes immune modulating virulence factors, has many adhesion factors, and the potential to create biofilms, all of which help to determine the pathogenicity of the bacterium. Diagnoses of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius have traditionally been made using cytology, plating, and biochemical tests. More recently, molecular technologies like MALDI-TOF, DNA hybridization and PCR have become preferred over biochemical tests for their more rapid and accurate identifications. This includes the identification and diagnosis of antibiotic resistant strains.
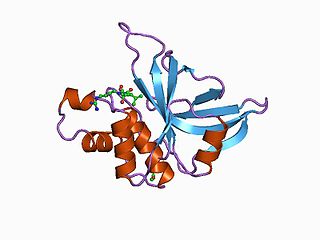
Staphopain A is a secreted cysteine protease produced by Staphylococcus aureus. It was first identified in the S. aureus V8 strain as a papain-like cysteine protease. The protease distinguishes itself from the other major proteases of S. aureus in its very broad specificity and its ability to degrade elastin.

In the contact activation system or CAS, three proteins in the blood, factor XII (FXII), prekallikrein (PK) and high molecular weight kininogen (HK), bind to a surface and cause blood coagulation and inflammation. FXII and PK are proteases and HK is a non-enzymatic co-factor. The CAS can activate the kinin–kallikrein system and blood coagulation through its ability to activate multiple downstream proteins. The CAS is initiated when FXII binds to a surface and reciprocal activation of FXII and PK occurs, forming FXIIa and PKa. FXIIa can initiate the coagulation cascade by cleaving and activating factor XI (FXI), which leads to formation of a blood clot. Additionally, the CAS can activate the kinin–kallikrein system when PKa cleaves HK to form cHK, releasing a peptide known as bradykinin (BK). BK and its derivatives bind to bradykinin receptors B1 and B2 to mediate inflammation.
References
- ↑ Hair PS; Ward MD; Semmes OJ; Foster TJ; Cunnion KM (July 2008). "Staphylococcus aureus clumping factor A binds to complement regulator factor I and increases factor I cleavage of C3b". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 198 (1): 125–33. doi: 10.1086/588825 . PMID 18544012.