Related Research Articles

A rotary dial is a component of a telephone or a telephone switchboard that implements a signaling technology in telecommunications known as pulse dialing. It is used when initiating a telephone call to transmit the destination telephone number to a telephone exchange.
Direct distance dialing (DDD) is a telecommunication service feature in North America by which a caller may, without operator assistance, call any other user outside the local calling area. Direct dialing by subscribers typically requires extra digits to be dialed as prefixes to the directory telephone number of the destination. International Direct Distance Dialing (IDDD) extends the system beyond the geographic boundaries of the North American Numbering Plan (NANP).

In electronics and telecommunications, a crossbar switch is a collection of switches arranged in a matrix configuration. A crossbar switch has multiple input and output lines that form a crossed pattern of interconnecting lines between which a connection may be established by closing a switch located at each intersection, the elements of the matrix. Originally, a crossbar switch consisted literally of crossing metal bars that provided the input and output paths. Later implementations achieved the same switching topology in solid-state electronics. The crossbar switch is one of the principal telephone exchange architectures, together with a rotary switch, memory switch, and a crossover switch.

The Strowger switch is the first commercially successful electromechanical stepping switch telephone exchange system. It was developed by the Strowger Automatic Telephone Exchange Company founded in 1891 by Almon Brown Strowger. Because of its operational characteristics, it is also known as a step-by-step (SXS) switch.
The Pacific Bell Telephone Company (Pac Bell) is a telephone company that provides telephone service in California. The company is owned by AT&T through AT&T Teleholdings, and, though separate, is now marketed as “AT&T”. The company has been known by a number of names during which its service area has changed. The formal name of the company from the 1910s through the 1984 Bell System divestiture was The Pacific Telephone and Telegraph Company. As of 2002, the name “Pacific Bell” is no longer used in marketing, although Pacific Bell is still the holder of record for the infrastructure of cables and fiber through much of California.
A sender is a type of circuit and system module in 20th-century electromechanical telephone exchanges. It registered the telephone numbers dialed by the subscriber, and transmitted that information to another part of the exchange or another exchange for the purpose of completing a telephone call. Some American exchange designs, for example, of the No. 1 Crossbar switch used originating senders and terminating senders. The corresponding device in the British director telephone system was called a "director" and, in other contexts, "register".
CLLI code is a Common Language Information Services identifier used within the North American telecommunications industry to specify the location and function of telecommunications equipment or of a relevant location such as an international border or a supporting equipment location, like a manhole or pole. Originally, they were used by Bell Telephone companies, but since all other telecommunications carriers needed to interconnect with the dominant Bell companies, CLLI code adoption eventually became universal. CLLI codes are now maintained and issued by iconectiv, which claims trademarks on the names "Common Language" and "CLLI".
A Class-5 telephone switch is a telephone exchange in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) that directly serves subscribers and manages subscriber calling features. Class-5 services include basic dial-tone, calling features, and additional digital and data services to subscribers connected to a local loop.

A telephone exchange name or central office name was a distinguishing and memorable name assigned to a central office. It identified the switching system to which a telephone was connected, and facilitated the connection of telephone calls between switching systems in different localities.

A marker is a type of special purpose control system that was used in electromechanical telephone central office switches. Switches employing markers belong to a class of switches known as "common control", as the purpose of a marker is to control the closure of contacts in the switching fabric that connect a circuit between the calling party and the called party. This is in contrast to "direct control" switches, where the switching elements were controlled directly by the customer's dial, such as the Step by Step switch. The term marker came from its use to mark a path of links through the switching fabric. A marker's comprehensive view of the switching fabric allowed it to find and assemble a path from one terminal to another, if the links were available, unlike the earlier graded progressive systems in which a path might not be found.

Area codes 408 and 669 are telephone area codes in the North American Numbering Plan (NANP) in the U.S. state of California. The numbering plan area comprises most of Santa Clara County and Northern Santa Cruz County, and includes Gilroy, Morgan Hill, Saratoga, Los Gatos, Monte Sereno, Milpitas, Sunnyvale, Santa Clara, Cupertino, Campbell, and San Jose.
The Number Five Crossbar Switching System is a telephone switch for telephone exchanges designed by Bell Labs and manufactured by Western Electric starting in 1947. It was used in the Bell System principally as a Class 5 telephone switch in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) until the early 1990s, when it was replaced with electronic switching systems. Variants were used as combined Class 4 and Class 5 systems in rural areas, and as a TWX switch.
A class-4, or tandem, telephone switch is a U.S. telephone company central office telephone exchange used to interconnect local exchange carrier offices for long distance communications in the public switched telephone network.
The Number One Crossbar Switching System (1XB), was the primary technology for urban telephone exchanges served by the Bell System in the mid-20th century. Its switch fabric used the electromechanical crossbar switch to implement the topology of the panel switching system of the 1920s. The first No. 1 Crossbar was installed in the PResident-2 central office at Troy Avenue in Brooklyn, New York which became operational in February 1938.
Historically, a foreign exchange service (FX) was an access service in a telecommunications network in which a telephone in a given exchange area is connected, via a private line, as opposed to a switched line, to a telephone exchange or central office in another exchange area, called the foreign exchange, rather than the local exchange area where the subscriber station equipment is located. To call originators, it appears that the called party having the FX service is located in the foreign exchange area. It is assigned a telephone number of the foreign exchange. The telecommunication circuit between central offices that implements foreign exchange service has complementary interface types at each end. At the foreign central office that provides the service, the interface is called the foreign exchange office (FXO) end, and at the end where the subscriber station is connected, it provides the foreign exchange station (FXS) interface.
The original North American area codes were established by the American Telephone and Telegraph Company (AT&T) in 1947, after the demonstration of regional Operator Toll Dialing during the World War II period. The program had the goal of speeding the connecting times for long-distance calling by eliminating intermediary telephone operators. Expanding this technology for national use required a comprehensive and universal, continent-wide telephone numbering plan.

A push-button telephone is a telephone that has buttons or keys for dialing a telephone number, in contrast to a rotary dial used in earlier telephones.

A telephone exchange, also known as a telephone switch or central office, is a crucial component in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or large enterprise telecommunications systems. It facilitates the interconnection of telephone subscriber lines or digital system virtual circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers.
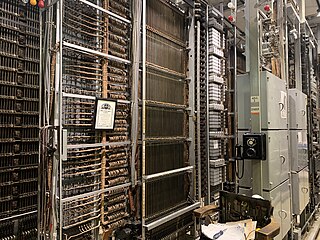
The Panel Machine Switching System is a type of automatic telephone exchange for urban service that was used in the Bell System in the United States for seven decades. The first semi-mechanical types of this design were installed in 1915 in Newark, New Jersey, and the last were retired in the same city in 1983.
References
- ↑ "For 15 years, the mark of an Atlanta newcomer: a 678 phone number". Saporta Report. 2013-01-28. Retrieved 2013-06-02.
- ↑ "Survey of Telephone Switching - Chapter 4". Telephone Tribute. Retrieved 2013-06-02.
- ↑ "Goliath's Fall | 2012-05-15". Microwave Journal. Retrieved 2013-06-02.
{{cite magazine}}: Cite magazine requires|magazine=(help) - ↑ "Telecommunications Virtual Museum". Telcomhistory.org. Archived from the original on 2013-06-19. Retrieved 2013-06-02.