Hudson Strait in Nunavut links the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley in Newfoundland and Labrador and Nunavut and Resolution Island, off Baffin Island. The strait is about 750 km (470 mi) long with an average width of 125 km (78 mi), varying from 70 km (43 mi) at the eastern entrance to 240 km (150 mi) at Deception Bay.

Ellesmere Island is Canada's northernmost and third largest island, and the tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of 196,236 km2 (75,767 sq mi), slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total length of the island is 830 km (520 mi).

Baffin Island, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut, is the largest island in Canada, the second-largest island in the Americas, and the fifth-largest island in the world. Its area is 507,451 km2 (195,928 sq mi) with a population density of 0.03/km2; the population was 13,039 according to the 2021 Canadian census; and it is located at 68°N70°W. It also contains the city of Iqaluit, which is the capital of Nunavut.

Igloolik is an Inuit hamlet in Foxe Basin, Qikiqtaaluk Region in Nunavut, northern Canada. Because its location on Igloolik Island is close to Melville Peninsula, it is often mistakenly thought to be on the peninsula. The name "Igloolik" means "there is a house here". It derives from iglu meaning house or building, and refers to the sod houses that were originally in the area, not to snow igloos. In Inuktitut the residents are called Iglulingmiut.

The Dorset was a Paleo-Eskimo culture, lasting from 500 BCE to between 1000 CE and 1500 CE, that followed the Pre-Dorset and preceded the Thule people (proto-Inuit) in the North American Arctic. The culture and people are named after Cape Dorset in Nunavut, Canada, where the first evidence of its existence was found. The culture has been defined as having four phases due to the distinct differences in the technologies relating to hunting and tool making. Artifacts include distinctive triangular end-blades, oil lamps (qulliq) made of soapstone, and burins.
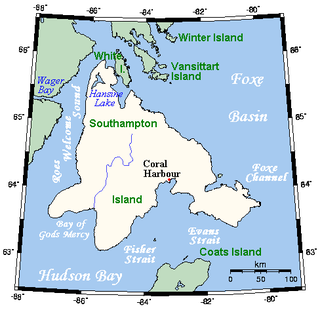
Southampton Island is a large island at the entrance to Hudson Bay at Foxe Basin. One of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago, Southampton Island is part of the Kivalliq Region in Nunavut, Canada. The area of the island is stated as 41,214 km2 (15,913 sq mi) by Statistics Canada. It is the 34th largest island in the world and Canada's ninth largest island. The only settlement on Southampton Island is Coral Harbour, called Salliq in Inuktitut.

Bylot Island lies off the northern end of Baffin Island in Nunavut Territory, Canada. Eclipse Sound to the southeast and Navy Board Inlet to the southwest separate it from Baffin Island. Parry Channel lies to its northwest. At 11,067 km2 (4,273 sq mi) it is ranked 71st largest island in the world and Canada's 17th largest island. The island measures 180 km (110 mi) east to west and 110 km (68 mi) north to south and is one of the largest uninhabited islands in the world. While there are no permanent settlements on this Canadian Arctic island, Inuit from Pond Inlet and elsewhere regularly travel to Bylot Island. An Inuit seasonal hunting camp is located southwest of Cape Graham Moore.

Kinngait, known as Cape Dorset until 27 February 2020, is an Inuit hamlet located on Dorset Island near Foxe Peninsula at the southern tip of Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada.
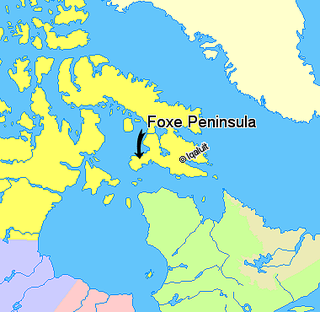
Foxe Peninsula is a peninsula found at the southern end of Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It juts out from the southern end of the island in a southwestern direction, dividing Foxe Basin and Hudson Strait. Its western extremity is Cape Queen; to the southeast lies the Inuit hamlet of Kinngait. At the western coast is Inuksuk Point, which contains more than 100 inuksuit.
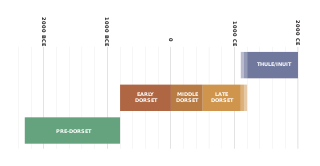
The history of Nunavut covers the period from the arrival of the Paleo-Eskimo thousands of years ago to present day. Prior to the colonization of the continent by Europeans, the lands encompassing present-day Nunavut were inhabited by several historical cultural groups, including the Pre-Dorset, the Dorsets, the Thule and their descendants, the Inuit.

Nunavut is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for self-government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.

Amadjuak Lake is a lake in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Along with Nettilling Lake, it is located in south-central Baffin Island's Great Plain of the Koukdjuak. It is 154 km (96 mi) south of Burwash Bay. The closest community is Iqaluit.
Saqajaa {Inuktitut syllabics: ᓴᖃᔮ) formerly Sakkiak Island is one of the uninhabited Canadian arctic islands located in Hudson Strait, Nunavut, Canada. It is a Baffin Island offshore island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, separated by deep water from Cape Dorset 64°10′40″N76°29′00″W, 1.5 mi (2.4 km) to the south-southwest. The island is approximately 6 km2 (2.3 sq mi) in size, 2.25 mi (3.62 km) long, and 1 mi (1.6 km) wide. The elevation is approximately 65 m (213 ft) above sea level.
Ukaliqtuuq formerly Okolli Island is one of the Canadian arctic islands located in Hudson Strait, Nunavut, Canada. It is a Baffin Island offshore island in Qikiqtaaluk Region. The island is 7.2 km (4.5 mi) long and 2.4 km (1.5 mi) wide. The elevation is 107 m (351 ft) above sea level.

Mallik Island is one of the uninhabited Canadian arctic islands of Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in Hudson Strait between Baffin Island's Foxe Peninsula and Dorset Island. Mallik Island and Dorset Island are joined by sand and boulders. Cape Dorset, an Inuit hamlet, is approximately 4.5 km (2.8 mi) away.
Nunarijjait formerly Nunajuak Island is one of the uninhabited Canadian arctic islands located in the Hudson Strait, Nunavut, Canada. It is a Baffin Island offshore island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region. The elevation is approximately 1 m above sea level.
Gudmusson Island is one of the Canadian arctic islands located in Hudson Strait, Nunavut, Canada. It is a Baffin Island offshore island in Qikiqtaaluk Region. Cape Dorset, an Inuit hamlet on Dorset Island, is approximately 37.7 km (23.4 mi) away.

Dundas Harbour is an abandoned settlement in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located on Devon Island at the eastern shore of the waterway also named Dundas Harbour. Baffin Bay's Croker Bay is immediately to the west.

Inuksuk Point is a small peninsula on Foxe Peninsula, approximately 88.5 km (55.0 mi) from Kinngait on the southwest of Baffin Island in Nunavut, Canada.