Related Research Articles

An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include eponymous and eponymic.

In geology, a boulder is a rock fragment with size greater than 25.6 centimetres (10.1 in) in diameter. Smaller pieces are called cobbles and pebbles. While a boulder may be small enough to move or roll manually, others are extremely massive. In common usage, a boulder is too large for a person to move. Smaller boulders are usually just called rocks or stones. The word boulder derives from boulder stone, from the Middle English bulderston or Swedish bullersten.
Webster's Dictionary is any of the English language dictionaries edited in the early 19th century by American lexicographer Noah Webster (1758–1843), as well as numerous related or unrelated dictionaries that have adopted the Webster's name in honor. "Webster's" has since become a genericized trademark in the United States for English dictionaries, and is widely used in dictionary titles.

Merriam-Webster, Inc. is an American company that publishes reference books and is especially known for its dictionaries. It is the oldest dictionary publisher in the United States.

Iceland spar, formerly called Iceland crystal and also called optical calcite, is a transparent variety of calcite, or crystallized calcium carbonate, originally brought from Iceland, and used in demonstrating the polarization of light. It occurs in large readily cleavable crystals, is easily divisible into parallelepipeds, and is remarkable for its birefringence. This means that the refractive index of the crystal is different for light of different polarization. A ray of unpolarized light passing through the crystal is divided into two rays of perpendicular polarization directed at different angles. This double refraction causes objects seen through the crystal to appear doubled.

The western Orphean warbler is a typical warbler of the genus Curruca. This species occurs in summer around the Mediterranean, through western Europe and extending into northwest Africa. It is migratory, wintering in Sub-Saharan Africa. It is a rare vagrant to northern and north-western Europe.
A precept is a commandment, instruction, or order intended as an authoritative rule of action.

Fustian is a variety of heavy cloth woven from cotton, chiefly prepared for menswear. It is also used figuratively to refer to pompous, inflated or pretentious writing or speech, from at least the time of Shakespeare. This literary use is because the cloth type was often used as padding, hence, the purposeless words are fustian.
Despite the various English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of the differences between American and British English date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States.

Hessian, burlap in the United States and Canada, or crocus in Jamaica and the wider Caribbean, is a woven fabric usually made from skin of the jute plant or sisal fibres, which may be combined with other vegetable fibres to make rope, nets, and similar products. Gunny is similar in texture and construction.

Rock butter is a soft mineral substance found oozing from alum slates.
A pronunciation respelling for English is a notation used to convey the pronunciation of words in the English language, which does not have a phonemic orthography.

Broadcloth is a dense, plain woven cloth, historically made of wool. The defining characteristic of broadcloth is not its finished width but the fact that it was woven much wider and then heavily milled in order to shrink it to the required width. The effect of the milling process is to draw the yarns much closer together than could be achieved in the loom and allow the individual fibres of the wool to bind together in a felting process, which results in a dense, blind face cloth with a stiff drape which is highly weather-resistant, hard wearing and capable of taking a cut edge without the need for being hemmed.

In classical antiquity, a crotalum was a kind of clapper or castanet used in religious dances by groups in ancient Greece and elsewhere, including the Korybantes.

Sachems and sagamores are paramount chiefs among the Algonquians or other Native American tribes of northeastern North America, including the Iroquois. The two words are anglicizations of cognate terms from different Eastern Algonquian languages. The sagamore was a lesser chief elected by a single band, while the sachem was the head or representative elected by a tribe or group of bands. The positions are elective, not hereditary.

Grosgrain is a type of fabric or ribbon defined by the fact that its weft is heavier than its warp, creating prominent transverse ribs. Grosgrain is a plain weave corded fabric, with heavier cords than poplin but lighter than faille, and is known for being a firm, close-woven, fine-corded fabric. Grosgrain has a dull appearance, with little luster in comparison to many fabric weaves, such as satin, often used for ribbons; however, it is comparatively very strong. Grosgrain fabric is most commonly available in black, but grosgrain ribbon comes in a large variety of colors and patterns. The ribbon is very similar to Petersham ribbon in its appearance, but it does not have the ability to follow the curves of a surface or edge the way that the latter does.
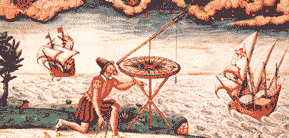
The cosmolabe was an ancient astronomical instrument resembling the astrolabe, formerly used for measuring the angles between heavenly bodies. It is also called pantacosm. Jacques Besson also uses this name, or universal instrument, for his invention described in Le cosmolabe (1567), which could be used for astrometry, cartography, navigation, and surveying.
Cyphonism was a form of punishment using a κύφων, a kind of wooden pillory in which the neck of a malefactor would be fastened. Formerly, this term was widely believed to refer to scaphism, a form of punishment or torture in which a person's naked body was smeared with honey, and exposed to flies, wasps, and other pests.

Dornix, also known as dornicks and darnacle, is a wool and linen fabric, first used in the 16th century.
References
- "drugget" . Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)