
Calico is a heavy plain-woven textile made from unbleached, and often not fully processed, cotton. It may also contain unseparated husk parts. The fabric is far coarser than muslin, but less coarse and thick than canvas or denim. However, it is still very cheap owing to its unfinished and undyed appearance.

A needlework sampler is a piece of embroidery or cross-stitching produced as a 'specimen of achievement', demonstration or a test of skill in needlework. It often includes the alphabet, figures, motifs, decorative borders and sometimes the name of the person who embroidered it and the date. The word sampler is derived from the Latin exemplum, which means 'example'.

Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms.

Velvet is a type of woven fabric with a dense, even pile that gives it a distinctive soft feel. By extension, the word velvety means "smooth like velvet". Historically, velvet was typically made from silk. Today, velvet can be made from silk, linen, cotton, wool, synthetic fibers, silk-cotton blends, or synthetic-natural fiber blends.
A satin weave is a type of fabric weave that produces a characteristically glossy, smooth or lustrous material, typically with a glossy top surface and a dull back; it is not durable, as it tends to snag. It is one of three fundamental types of textile weaves alongside plain weave and twill weave.

The spinning jenny is a multi-spindle spinning frame, and was one of the key developments in the industrialisation of textile manufacturing during the early Industrial Revolution. It was invented in 1764–1765 by James Hargreaves in Stan hill, Oswaldtwistle, Lancashire in England.

In the manufacture of cloth, warp and weft are the two basic components in weaving to transform thread and yarn into textile fabrics. The vertical warp yarns are held stationary in tension on a loom (frame) while the horizontal weft is drawn through the warp thread. In the terminology of weaving, each warp thread is called a warp end ; a pick is a single weft thread that crosses the warp thread.

Flannel is a soft woven fabric, of varying fineness. Flannel was originally made from carded wool or worsted yarn, but is now often made from either wool, cotton, or synthetic fiber. Flannel is commonly used to make tartan clothing, blankets, bed sheets, sleepwear, and several other uses.

Damask is a woven, reversible patterned fabric. Damasks are woven by periodically reversing the action of the warp and weft threads. The pattern is most commonly created with a warp-faced satin weave and the ground with a weft-faced or sateen weave. Fabrics used to create damasks include silk, wool, linen, cotton, and synthetic fibers, but damask is best shown in cotton and linen. Over time, damask has become a broader term for woven fabrics with a reversible pattern, not just silks.

Cambric or batiste is a fine dense cloth. It is a lightweight plain-weave fabric, originally from the commune of Cambrai, woven greige, then bleached, piece-dyed, and often glazed or calendered. Initially it was made of linen; from the 18th and 19th centuries the term came to apply to cotton fabrics as well.
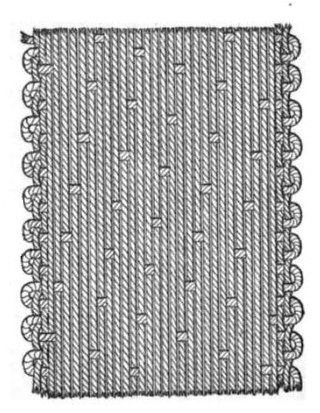
Dimity is a collective term for figured cloths of harness loom decorated with designs and patterns. It is a strong cotton cloth with various stripes and illustrations. It is bleached or washed after looming, less often dyed, unlike fustian, which is usually dyed.
Dowlas was a strong coarse linen cloth of the 16th and 17th centuries, and initially, it was manufactured in Brittany. In the 18th century the fabric was also produced in England and Scotland. Dowlas was identical to sailcloth. The cloth was also imitated in cotton for the same use.

Linsey-woolsey is a coarse twill or plain-woven fabric woven with a linen warp and a woollen weft. Similar fabrics woven with a cotton warp and woollen weft in Colonial America were also called linsey-woolsey or wincey. The name derives from a combination of lin and wool. This textile has been known since ancient times. Known as shatnez (שַׁעַטְנֵז) in Hebrew, the wearing of this fabric was forbidden in the Torah and hence Jewish law.

Plain weave is the most basic of three fundamental types of textile weaves. It is strong and hard-wearing, and is used for fashion and furnishing fabrics. Fabrics with a plain weave are generally strong, durable, and have a smooth surface. They are often used for a variety of applications, including clothing, home textiles, and industrial fabrics.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fiber from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, which turns it into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of colouring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.

Grosgrain is a type of fabric or ribbon defined by the fact that its weft is heavier than its warp, creating prominent transverse ribs. Grosgrain is a plain weave corded fabric, with heavier cords than poplin but lighter than faille, and is known for being a firm, close-woven, fine-corded fabric. Grosgrain has a dull appearance, with little luster in comparison to many fabric weaves, such as satin, often used for ribbons; however, it is comparatively very strong. Grosgrain fabric is most commonly available in black, but grosgrain ribbon comes in a large variety of colors and patterns. The ribbon is very similar to Petersham ribbon in its appearance, but it does not have the ability to follow the curves of a surface or edge the way that the latter does.

Woodblock printing on textiles is the process of printing patterns on fabrics, typically linen, cotton, or silk, by means of carved wooden blocks.

Balinese textiles are reflective of the historical traditions of Bali, Indonesia. Bali has been historically linked to the major courts of Java before the 10th century; and following the defeat of the Majapahit kingdom, many of the Javanese aristocracy fled to Bali and the traditions were continued. Bali therefore may be seen as a repository not only of its own arts but those of Java in the pre-Islamic 15th century. Any attempt to definitively describe Balinese textiles and their use is doomed to be incomplete. The use of textile is a living tradition and so is in constant change. It will also vary from one district to another. For the most part old cloth are not venerated for their age. New is much better. In the tropics cloth rapidly deteriorates and so virtue is generated by replacing them.
Huckaback fabric or Huck is a type of toweling cloth with a bird's eye or honeycomb pattern. It is a loosely woven fabric made of cotton or linen with Huckaback weave.
Diaper is a damask cloth with small geometrical patterns such as bird's eye or diamond shapes. Terms such as “bird’s eye” or “pheasant’s eye” refer to the size of the diamond in the design. Diaper has been used as a tablecloth.















