
The Great Victoria Desert is a sparsely populated desert ecoregion and interim Australian bioregion in Western Australia and South Australia.

The North Western Ghats montane rain forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of southwestern Indian peninsula. It covers an area of 30,900 square kilometers (11,900 sq mi), extending down the spine of the Western Ghauts range, from southernmost Gujarat through Damaon, Maharashtra, Goa & Karnataka. The montane rain forests are found above 1000 meters elevation, and are surrounded at lower elevations by the North Western Ghats moist deciduous forests.

The Carnarvon xeric shrublands is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion of Western Australia. The ecoregion is coterminous with the Carnarvon Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) bioregion.
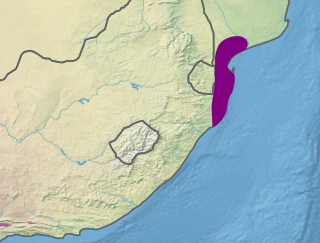
The Maputaland coastal forest mosaic is a subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the Indian Ocean coast of Southern Africa. It covers an area of 29,961 square kilometres (11,568 sq mi) in southern Mozambique, Eswatini, and the KwaZulu-Natal Province of South Africa. Mozambique's capital Maputo lies within the ecoregion.

The Western Guinean lowland forests ecoregion is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of West Africa. It is centered on Liberia, with portions in surrounding countries. It is the westernmost tropical rainforest in Africa, and has high levels of species endemism, with over 200 species of endemic plants.

The Crimean Submediterranean forest complex is an ecoregion on the Black Sea coast of Russia and Ukraine. It is in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome.

Warren, also known as Karri Forest Region and the Jarrah-Karri forest and shrublands ecoregion, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located in the southwest corner of Western Australia between Cape Naturaliste and Albany, it is bordered to the north and east by the Jarrah Forest region. Its defining characteristic is an extensive tall forest of Eucalyptus diversicolor (karri). This occurs on dissected, hilly ground, with a moderately wet climate. Karri is a valuable timber and much of the karri forest has been logged over, but less than a third has been cleared for agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), and as a terrestrial ecoregion by the World Wide Fund for Nature, it was first defined by Ludwig Diels in 1906.

The Tyrrhenian-Adriatic sclerophyllous and mixed forests is an ecoregion in southern Italy, Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica, the Dalmatian Islands of Croatia, and Malta.

The Einasleigh Uplands is an interim Australian bioregion, with vegetation consisting of savanna and woodland located on a large plateau in inland Queensland, Australia. It corresponds to the Einasleigh Uplands savanna ecoregion, as identified by the World Wildlife Fund.

The Southeast Australia temperate savanna ecoregion is a large area of grassland dotted with eucalyptus trees running north–south across central New South Wales, Australia.

The Coolgardie woodlands is an ecoregion in southern Western Australia. The predominant vegetation is woodlands and mallee scrub. The ecoregion is a transitional zone between the Mediterranean-climate forests, woodlands, and shrublands of Southwest Australia and the deserts and dry scrublands of the Australian interior.

The Eyre Yorke Block, also known as the Eyre and Yorke mallee, is an interim Australian (IBRA) bioregion and a World Wildlife Fund ecoregion covering part of the Eyre Peninsula and all of Yorke Peninsula as well as land to its immediate east in South Australia.

The Murray Darling Depression , also known as the Murray-Darling woodlands and mallee, is a 19,717,651 HA biogeographic region and an ecoregion in southeastern Australia consisting of a wooded plain through which flow two of Australia's biggest rivers, the Murray and the Darling. There are several modern human settlements in the bioregion including Ivanhoe and Manilla, but the region also contains some of the oldest known human occupation sites in Australia.

The Naracoorte woodlands is an ecoregion in southern Australia. It covers the Naracoorte coastal plain in southeastern South Australia and southwestern Victoria. It is coterminous with the Naracoorte Coastal Plain IBRA region. Only 10% of the ecoregion's area still has its original vegetation; most has been converted to agriculture and pasture.

The Southwest Australia savanna is an ecoregion in Western Australia.

The Central Ranges xeric scrub is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion of Australia.

The Great Sandy-Tanami desert is a ecoregion of Western Australia extending into the Northern Territory. It is designated as a World Wildlife Fund region.

The Irrawaddy dry forests is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in central Myanmar. The ecoregion occupies portions of the Irrawaddy, Sittaung, and Salween river basins, in areas with less than 800 mm of annual rainfall.

The Cape York Peninsula tropical savanna is a tropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion in northern Australia. It occupies the Cape York Peninsula in Queensland, mainland Australia's northernmost point. It is coterminous with the Cape York Peninsula, an interim Australian bioregion.

The Peninsular Malaysian rain forests is an ecoregion on the Malay Peninsula and adjacent islands. It is in the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome.

























