This article's lead section may be too long.(November 2025) |

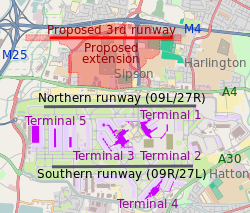
The expansion of Heathrow Airport is a series of proposals to add to the runways at London's busiest airport beyond its two long runways which are intensively used to serve four terminals and a large cargo operation. The plans are those presented by Heathrow Airport Holdings and an independent proposal by Heathrow Hub with the main object of increasing capacity. [1]
Contents
- Plans
- 2009 third runway and additional terminal plan
- 2013 Northwest runway plan
- 2025 Labour government plans
- 2025 Arora Group proposal
- Support
- Reasons for expansion
- Supporters
- Advocacy in support of expansion
- Lobbying
- Opposition
- Greenhouse gas emissions
- Community destruction
- Noise pollution
- Opponents of expansion
- Advocacy against expansion
- Alternatives to expansion
- Greater use of regional airports
- Thames Estuary Airport
- High-speed rail
- See also
- Notes
- References
- External links
In early December 2006, the Department for Transport published a progress report on the strategy which confirmed the original vision of expanding the runways. [2] [3] In November 2007, the government started a public consultation on its proposal for a slightly shorter third runway (2,000 m or 6,560 ft) and a new passenger terminal. [4]
The plan was publicly supported by many businesses, the aviation industry, the British Chambers of Commerce, the Confederation of British Industry, the Trades Union Congress and the then Labour government. It was publicly opposed by Conservative and Liberal Democrat parties as opposition parties and then as a coalition government, by Boris Johnson (then Mayor of London), many environmental, local advocacy groups and prominent individuals. Although the expansion was cancelled on 12 May 2010 by the new coalition government, [5] the Airport Commission published its various-options comparative study "Final Report" on 1 July 2015 which preferred the plan. [6]
On 25 October 2016, a new northwest runway and terminal was adopted as central Government policy. In late June 2018, the resultant National Policy Statement: Airports was debated and voted on by the House of Commons; the House voted 415–119 in favour of the third runway, within which outcome many local MPs, including a majority of those from London, opposed or abstained.
On 27 February 2020, in an application for judicial review brought by environmental campaigning groups, London councils, and the Mayor of London, Sadiq Khan, the Court of Appeal ruled that the government's decision to proceed with building the third runway were unlawful, as the government's commitments to combat climate change under the Paris Agreement were not taken into account. In response, the government announced it would not appeal against the decision, but Heathrow announced its intention to appeal to the Supreme Court. [7]
On 16 December 2020, the UK Supreme Court lifted the ban on the third runway, allowing a planning application via a Development Consent Order to go ahead. [8] The plan stalled in 2023 after post-COVID pandemic falling passenger numbers and concerns about investment costs, [9] but as of June 2024 the third runway is still planned with a projected completion date around 2040. [10] In January 2025, Chancellor of the Exchequer Rachel Reeves confirmed it was the new Labour government's plan to proceed with a third runway within the current parliamentary term. [11]