A traction control system (TCS), is typically a secondary function of the electronic stability control (ESC) on production motor vehicles, designed to prevent loss of traction of the driven road wheels. TCS is activated when throttle input and engine power and torque transfer are mismatched to the road surface conditions.

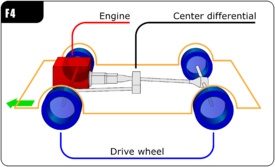
A four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 or 4WD, is a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer case providing an additional output drive shaft and, in many instances, additional gear ranges.

Quattro is the trademark used by the automotive brand Audi to indicate that all-wheel drive (AWD) technologies or systems are used on specific models of its automobiles.

In automotive design, a front-engine, front-wheel-drive (FWD) layout, or FF layout, places both the internal combustion engine and driven roadwheels at the front of the vehicle.

A transfer case is an intermediate gearbox that transfers power from the transmission of a motor vehicle to the driven axles of four-wheel-drive, all-wheel-drive, and other multi-axled on- and off-road machines. A part of the vehicle's drivetrain, it employs drive shafts to mechanically deliver motive power. The transfer case also synchronizes the difference between the rotation of the front and rear wheels, and may contain one or more sets of low range gears for off-road use.

In a motor vehicle, the powertrain comprises the main components that generate power and deliver that power to the road surface, water, or air. This includes the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, and the final drive. Hybrid powertrains also include one or more electric traction motors that operate to drive the vehicle wheels. All-electric vehicles eliminate the engine altogether, relying solely on electric motors for propulsion. Occasionally the term powerplant is casually used to refer to the engine or, less often, the entire powertrain.
4Matic is the marketing name of an all-wheel drive system developed by Mercedes-Benz. It is designed to increase traction in slippery conditions. With the introduction of the 2017 E 63 S sedan, Mercedes-AMG announced a performance-oriented variant of the system called AMG Performance 4MATIC+.

A drive wheel is a wheel of a motor vehicle that transmits force, transforming torque into tractive force from the tires to the road, causing the vehicle to move. The powertrain delivers enough torque to the wheel to overcome stationary forces, resulting in the vehicle moving forwards or backwards.

The Jeep Patriot (MK74) is a front-engine five-door compact crossover SUV manufactured and marketed by Jeep, having debuted with the Jeep Compass in April 2006 at the New York Auto Show for the 2007 model year. Both cars, as well as the Dodge Caliber, shared the GS platform, differentiated by their styling and marketing, with the Patriot exclusively offering a four-wheel drive system, marketed as Freedom Drive II.
ATTESA is a four-wheel drive system used in some automobiles produced by the Japanese automaker Nissan, including some models under its luxury marque Infiniti.
Jeep uses a variety of four-wheel drive systems on their vehicles. These range from basic part-time systems that require the driver to move a control lever to send power to four wheels, to permanent four-wheel systems that monitor and sense traction needs at all four wheels automatically under all conditions.
Super Handling-All Wheel Drive (SH-AWD) is a full-time, fully automatic, all-wheel drive traction and handling system, which combines front-rear torque distribution control with independently regulated torque distribution to the left and right rear wheels. This way the system freely distributes the optimum amount of torque to all four wheels according to the driving conditions. The system was announced in April 2004, and was introduced in the North American market in the second generation 2005 model year Acura RL, and in Japan as the fourth generation Honda Legend.
The powertrain layout of a motorised vehicle such as a car is often defined by the location of the engine or motors and the drive wheels.

Super Select is the brand name of a four-wheel drive system produced by Mitsubishi Motors, used worldwide except for North America, where it was initially known as Active-Trac. It was first introduced in 1991 with the then-new second generation of the Mitsubishi Pajero.

In automotive design, an M4, or Mid-engine, Four-wheel-drive layout places the internal combustion engine in the middle of the vehicle, between both axles and drives all four road wheels.
Torque vectoring is a technology employed in automobile differentials that has the ability to vary the torque to each half-shaft with an electronic system; or in rail vehicles which achieve the same using individually motored wheels. This method of power transfer has recently become popular in all-wheel drive vehicles. Some newer front-wheel drive vehicles also have a basic torque vectoring differential. As technology in the automotive industry improves, more vehicles are equipped with torque vectoring differentials. This allows for the wheels to grip the road for better launch and handling.

A drivetrain or transmission system, is the group of components that deliver mechanical power from the prime mover to the driven components. In automotive engineering, the drivetrain is the components of a motor vehicle that deliver power to the drive wheels. This excludes the engine or motor that generates the power. In marine applications, the drive shaft will drive a propeller, thruster, or waterjet rather than a drive axle, while the actual engine might be similar to an automotive engine. Other machinery, equipment and vehicles may also use a drivetrain to deliver power from the engine(s) to the driven components.

An all-wheel drive vehicle is one with a powertrain capable of providing power to all its wheels, whether full-time or on-demand.
E-Four, eFour, AWD-i, or AWD-e was developed by Toyota. Front wheels are powered directly by the hybrid powertrain, rear wheels are powered by a dedicated electric motor with its own power control unit, reduction gear and differential. Amount of torque transferred to the rear wheels is automatically adjusted by the vehicle's electronic control unit according to driving conditions. E-Four also adds additional regenerative braking. In North America, Toyota uses the term AWD-i. There is no drive shaft between the front combustion engine and rear wheels. The rear wheels only receive power and torque from the rear electric motor(s).
This glossary of automotive terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related to automobiles, including their parts, operation, and manufacture, as well as automotive engineering, auto repair, and the automotive industry in general. For more specific terminology regarding the design and classification of various automobile styles, see Glossary of automotive design; for terms related to transportation by road, see Glossary of road transport terms; for competitive auto racing, see Glossary of motorsport terms.