Rheumatology is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and therapy of rheumatic diseases. Physicians who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists. Rheumatologists deal mainly with immune-mediated disorders of the musculoskeletal system, soft tissues, autoimmune diseases, vasculitides, and heritable connective tissue disorders.

The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is the rate at which red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood descend in a standardized tube over a period of one hour. It is a common hematology test, and is a non-specific measure of inflammation. To perform the test, anticoagulated blood is traditionally placed in an upright tube, known as a Westergren tube, and the distance which the red blood cells fall is measured and reported in mm at the end of one hour.

Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily caused by leukocyte migration and resultant damage.

Takayasu's arteritis is a form of large vessel granulomatous vasculitis with massive intimal fibrosis and vascular narrowing, most commonly affecting young or middle-age women of Asian descent, though anyone can be affected. It mainly affects the aorta and its branches, as well as the pulmonary arteries. Females are about 8–9 times more likely to be affected than males.

Arteritis is the inflammation of the walls of arteries, usually as a result of infection or autoimmune response. Arteritis, a complex disorder, is still not entirely understood. Arteritis may be distinguished by its different types, based on the organ systems affected by the disease. A complication of arteritis is thrombosis, which can be fatal. Arteritis and phlebitis are forms of vasculitis.
Polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is a syndrome with pain or stiffness, usually in the neck, shoulders, upper arms, and hips, but which may occur all over the body. The pain can be very sudden, or can occur gradually over a period. Most people with PMR wake up in the morning with pain in their muscles; however, cases have occurred in which the person has developed the pain during the evenings or has pain and stiffness all day long.
Posterior ischemic optic neuropathy (PION) is a medical condition characterized by damage to the retrobulbar portion of the optic nerve due to inadequate blood flow (ischemia) to the optic nerve. Despite the term posterior, this form of damage to the eye's optic nerve due to poor blood flow also includes cases where the cause of inadequate blood flow to the nerve is anterior, as the condition describes a particular mechanism of visual loss as much as the location of damage in the optic nerve. In contrast, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (AION) is distinguished from PION by the fact that AION occurs spontaneously and on one side in affected individuals with predisposing anatomic or cardiovascular risk factors.
Bruit, also called vascular murmur, is the abnormal sound generated by turbulent flow of blood in an artery due to either an area of partial obstruction or a localized high rate of blood flow through an unobstructed artery.

A giant cell is a mass formed by the union of several distinct cells, often forming a granuloma. Although there is typically a focus on the pathological aspects of multinucleate giant cells (MGCs), they also play many important physiological roles. Osteoclasts specifically are invaluable to healthy physiological functions and are key players in the skeletal system. Osteoclasts are frequently classified and discussed separately from other MGCs which are more closely linked with human pathologies.
Retroperitoneal fibrosis or Ormond's disease is a disease featuring the proliferation of fibrous tissue in the retroperitoneum, the compartment of the body containing the kidneys, aorta, renal tract, and various other structures. It may present with lower back pain, kidney failure, hypertension, deep vein thrombosis, and other obstructive symptoms. It is named after John Kelso Ormond, who rediscovered the condition in 1948.
Arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy is the cause of vision loss that occurs in temporal arteritis. Temporal arteritis is an inflammatory disease of medium-sized blood vessels that happens especially with advancing age. AAION occurs in about 15-20 percent of patients with temporal arteritis. Damage to the blood vessels supplying the optic nerves leads to insufficient blood supply (ischemia) to the nerve and subsequent optic nerve fiber death. Most cases of AAION result in nearly complete vision loss first to one eye. If the temporal arteritis is left untreated, the fellow eye will likely suffer vision loss as well within 1–2 weeks. Arteritic AION falls under the general category of anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, which also includes non-arteritic AION. AION is considered an eye emergency, immediate treatment is essential to rescue remaining vision.

Neuromuscular disease is a broad term that encompasses many diseases and ailments that impair the functioning of the muscles, either directly, being pathologies of the voluntary muscle, or indirectly, being pathologies of nerves or neuromuscular junctions.
Aortitis is the inflammation of the aortic wall. The disorder is potentially life-threatening and rare. It is reported that there are only 1–3 new cases of aortitis per year per million people in the United States and Europe. Aortitis is most common in people 10 to 40 years of age.

Kimura's disease is a benign rare chronic inflammatory disorder. Its primary symptoms are subdermal lesions in the head or neck or painless unilateral inflammation of cervical lymph nodes.
Cerebral vasculitis is vasculitis involving the brain and occasionally the spinal cord. It affects all of the vessels: very small blood vessels (capillaries), medium-size blood vessels, or large blood vessels. If blood flow in a vessel with vasculitis is reduced or stopped, the parts of the body that receive blood from that vessel begins to die. It may produce a wide range of neurological symptoms, such as headache, skin rashes, feeling very tired, joint pains, difficulty moving or coordinating part of the body, changes in sensation, and alterations in perception, thought or behavior, as well as the phenomena of a mass lesion in the brain leading to coma and herniation. Some of its signs and symptoms may resemble multiple sclerosis. 10% have associated bleeding in the brain.
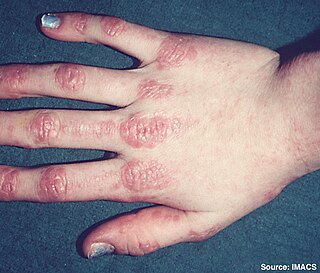
Inflammatory myopathy is disease featuring weakness and inflammation of muscles and muscle pain. The cause of much inflammatory myopathy is unknown (idiopathic), and such cases are classified according to their symptoms and signs and electromyography, MRI and laboratory findings. It can also be associated with underlying cancer. The main classes of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy are polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), and inclusion-body myositis (IBM).
Necrotizing vasculitis also called Systemic necrotizing vasculitus (SNV) is a category of vasculitis, comprising vasculitides that present with necrosis.
Cryofibrinogenemia refers to a condition classified as a fibrinogen disorder in which the chilling of an individual's blood plasma from the normal body temperature of 37 °C to the near-freezing temperature of 4 °C causes the reversible precipitation of a complex containing fibrinogen, fibrin, fibronectin, and, occasionally, small amounts of fibrin split products, albumin, immunoglobulins and other plasma proteins. Returning this plasma to 37 °C resolubilizes the precipitate.

Inflammatory aortic aneurysm (IAA), also known as Inflammatory abdominal aortic aneurysm (IAAA), is a type of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) where the walls of the aneurysm become thick and inflamed. Similar to AAA, IAA occurs in the abdominal region. IAA is closely associated and believed to be a response to and extensive peri-anuerysmal fibrosis, which is the formation of excess fibrous connective tissue in an organ or tissue in a reparative or reactive process IAA accounts for 5-10% of aortic aneurysms. IAA occurs mainly in a population that is on average younger by 10 years than most AAA patients. Some common symptoms of IAA may include back pain, abdominal tenderness, fevers, weight loss or elevated Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) levels. Corticosteroids and other immunosuppressive drugs have been found to decrease symptoms and the degree of peri-aortic inflammation and fibrosis

Acute visual loss is a rapid loss of the ability to see. It is commonly caused by four conditions retinal detachment, glaucoma, macular degeneration, and giant cell arteritis.












