
Bald Rock National Park is a national park in northern New South Wales, Australia, just north of Tenterfield on the Queensland border. The border passes over the rock on the Western side. On the other side of the border national park continues as the Girraween National Park.

Girraween National Park is an area of the Granite Belt in the Darling Downs region of Queensland, Australia reserved as a national park. Girraween is known for its spectacular flowers, dramatic landscapes and unique wildlife. Bushwalking and rock climbing are the most popular activities in the park.

Stanthorpe is a rural town and locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, the locality of Stanthorpe had a population of 5,286 people.
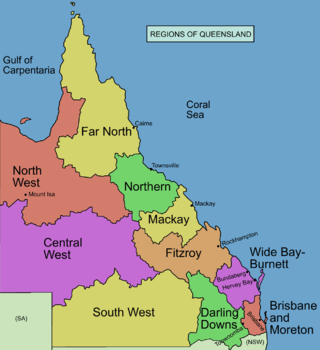
The Darling Downs is a farming region on the western slopes of the Great Dividing Range in southern Queensland, Australia. The Downs are to the west of South East Queensland and are one of the major regions of Queensland. The name was generally applied to an area approximating to that of the Condamine River catchment upstream of Condamine township but is now applied to a wider region comprising the Southern Downs, Western Downs, Toowoomba and Goondiwindi local authority areas. The name Darling Downs was given in 1827 by Allan Cunningham, the first European explorer to reach the area and recognises the then Governor of New South Wales, Ralph Darling.
Liston is a small mountain village in northern New South Wales, Australia in Tenterfield Shire local government area. It lies just inside the eastern boundary of the New South Wales, Queensland border on the old Cobb & Co route, now the Mount Lindesay Highway, which used to extend from Brisbane to Tenterfield, New South Wales.

The Australian wine industry is one of the world's largest exporters of wine, with approximately 800 million out of the 1.2 to 1.3 billion litres produced annually exported to overseas markets. The wine industry is a significant contributor to the Australian economy through production, employment, export, and tourism.

The Shire of Stanthorpe was a local government area of Queensland, Australia on the Queensland-New South Wales border. It was on the Great Dividing Range and was part of the Granite Belt. Its main industries included fruit and vegetable growing, wineries and tourism, and sheep and cattle grazing.

New South Wales wine is Australian wine produced in New South Wales, Australia. New South Wales is Australia's most populous state and its wine consumption far outpaces the region's wine production. The Hunter Valley, located 130 km (81 mi) north of Sydney, is the most well-known wine region but the majority of the state's production takes place in the Big Rivers zone-Perricoota, Riverina and along the Darling and Murray Rivers. The wines produced from the Big Rivers zone are largely used in box wine and mass-produced wine brands such as Yellow Tail. A large variety of grapes are grown in New South Wales, including Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, Shiraz and Sémillon.

Thulimbah is a rural town and locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, the locality of Thulimbah had a population of 351 people. It borders New South Wales.

The Ballandean Pyramid is a man-made stone pyramid near the small village of Ballandean, Queensland, Australia. The pyramid is approximately 15 metres in height and built from blocks of the local granite. It is on private property belonging to a local vineyard and is approximately 25 metres from the nearest road.

Ballandean is a rural town and locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. The town has a number of nearby vineyards which attracted tourists to the area. In the 2021 census, the locality of Ballandean had a population of 316 people.
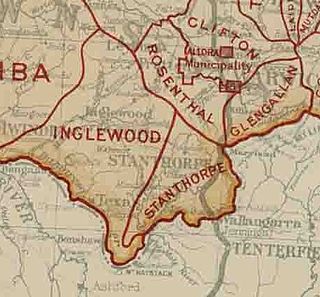
The Ballandean Division was a local government area on the Granite Belt, Queensland, Australia, close to the Queensland-New South Wales border. It only existed between 1879 and 1880.

Lyra is a rural locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Lyra had a population of 35 people.

Ballandean railway station is located on the Southern line in Queensland, Australia. It services the town of Ballandean, a rural district in the Granite Belt.

Eukey is a rural locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. It is on the border with New South Wales. In the 2021 census, Eukey had a population of 140 people.
The Apple & Grape Harvest Festival is a biennial festival held in Stanthorpe, Queensland, Australia, taking place over 10 days at the beginning of March. It is one of Queensland's longest-running festivals, first held in 1966 as a celebration of the Granite Belt region’s wine and produce industry.
Angelo Puglisi is an Australian winemaker, best known for owning and managing the Ballandean Estate on Queensland's Granite Belt with his family.
Fletcher is a rural locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Fletcher had a population of 128 people.

Girraween is an undeveloped locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. It is in the Granite Belt and on the border with New South Wales. In the 2021 census, Girraween had a population of 5 people.
Nundubbermere is a rural locality in the Southern Downs Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2021 census, Nundubbermere had a population of 102 people.



















