Related Research Articles

Bowie is a city in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States. Per the 2020 census, the population was 58,329. Bowie has grown from a small railroad stop to the largest municipality in Prince George's County, and the fifth most populous city and third largest city by area in the U.S. state of Maryland. In 2014, CNN Money ranked Bowie 28th in its Best Places to Live list.

Upper Marlboro, officially the Town of Upper Marlboro, is the seat of Prince George's County, Maryland. As of the 2020 census, the population within the town limits was 652, although Greater Upper Marlboro, which covers a large area outside the town limits, is many times larger.

Stormwater, also written storm water, is water that originates from precipitation (storm), including heavy rain and meltwater from hail and snow. Stormwater can soak into the soil (infiltrate) and become groundwater, be stored on depressed land surface in ponds and puddles, evaporate back into the atmosphere, or contribute to surface runoff. Most runoff is conveyed directly as surface water to nearby streams, rivers or other large water bodies without treatment.

The Patuxent River is a tributary of the Chesapeake Bay in the state of Maryland. There are three main river drainages for central Maryland: the Potomac River to the west passing through Washington, D.C., the Patapsco River to the northeast passing through Baltimore, and the Patuxent River between the two. The 908-square-mile (2,352 km2) Patuxent watershed had a rapidly growing population of 590,769 in 2000. It is the largest and longest river entirely within Maryland, and its watershed is the largest completely within the state.

The Anacostia River is a river in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States. It flows from Prince George's County in Maryland into Washington, D.C., where it joins with the Washington Channel and ultimately empties into the Potomac River at Buzzard Point. It is about 8.7 miles (14.0 km) long. The name "Anacostia" derives from the area's early history as Nacotchtank, a settlement of Necostan or Anacostan Native Americans on the banks of the Anacostia River.

The Patapsco River mainstem is a 39-mile (63 km) river in central Maryland that flows into the Chesapeake Bay. The river's tidal portion forms the harbor for the city of Baltimore. With its South Branch, the Patapsco forms the northern border of Howard County, Maryland. The name "Patapsco" is derived from the Algonquian pota-psk-ut, which translates to "backwater" or "tide covered with froth".

Rock Creek is a tributary of the Potomac River, in the United States, that empties into the Atlantic Ocean via the Chesapeake Bay. The 32.6-mile (52.5 km) creek drains about 76.5 square miles (198 km2). Its final quarter-mile is affected by tides.

Antietam Creek is a 41.7-mile-long (67.1 km) tributary of the Potomac River located in south central Pennsylvania and western Maryland in the United States, a region known as the Hagerstown Valley. The creek became famous as a focal point of the Battle of Antietam during the American Civil War.

Daylighting is the opening up and restoration of a previously buried watercourse, one which had at some point been diverted below ground. Typically, the rationale behind returning the riparian environment of a stream, wash, or river to a more natural above-ground state is to reduce runoff, create habitat for species in need of it, or improve an area's aesthetics. In the United Kingdom, the practice is also known as deculverting.
Collington was a settlement in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States, dating from colonial times. Collington has been subsumed by the city of Bowie.
Queen Anne in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States, is a former port on the Patuxent River. It was delineated as a CDP for the 2010 census, at which time it had a population of 1,280. Per the 2020 census, the population was 1,405.

Tryon Creek is a 4.85-mile (7.81 km) tributary of the Willamette River in the U.S. state of Oregon. Part of the drainage basin of the Columbia River, its watershed covers about 6.5 square miles (16.8 km2) in Multnomah and Clackamas counties. The stream flows southeast from the Tualatin Mountains through the Multnomah Village neighborhood of Portland and the Tryon Creek State Natural Area to the Willamette in the city of Lake Oswego. Parks and open spaces cover about 21 percent of the watershed, while single-family homes dominate most of the remainder. The largest of the parks is the state natural area, which straddles the border between the two cities and counties.

Paint Branch is a 17.0-mile-long (27.4 km) tributary stream of the Anacostia River that flows Southeastwards through Montgomery County and Prince George's County, Maryland. Specifically, its primary tributary is of the Northeast Branch, which flows to the Anacostia River, Potomac River and the Chesapeake Bay. The beginning elevation of the stream is 480 feet above sea level and it subsequently drops to 30 feet when its flows meet the Indian Creek in College Park, Maryland.

Watts Branch is a tributary stream of the Anacostia River in Prince George's County, Maryland, and Washington, D.C.
Hickey Run is a tributary stream of the Anacostia River in Washington, D.C.

Urban runoff is surface runoff of rainwater, landscape irrigation, and car washing created by urbanization. Impervious surfaces are constructed during land development. During rain, storms, and other precipitation events, these surfaces, along with rooftops, carry polluted stormwater to storm drains, instead of allowing the water to percolate through soil. This causes lowering of the water table and flooding since the amount of water that remains on the surface is greater. Most municipal storm sewer systems discharge untreated stormwater to streams, rivers, and bays. This excess water can also make its way into people's properties through basement backups and seepage through building wall and floors.
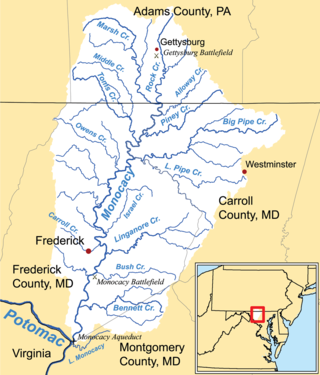
Double Pipe Creek, sometimes called Pipe Creek, is a major tributary of the Monocacy River in Carroll County and Frederick County in Maryland, located several miles north and west of Westminster. The creek is only 1.6 miles (2.6 km) long, but is formed by the confluence of two much longer streams, Big Pipe Creek and Little Pipe Creek.
Collington Branch is a stream that flows into the Western Branch of the Patuxent River in Prince George's County, Maryland.
Mill Branch of the Patuxent River in Prince George's County, Maryland is part of the Upper Patuxent Watershed.
Oxon Run is a tributary stream of Oxon Creek and the Potomac River in Prince George's County, Maryland, and Washington, D.C.
References
- ↑ "City of Bowie Environmental Infrastructure Action Strategy Plan Staff Findings and Recommendations By Sub-watershed". City of Bowie. p. ii. Archived from the original on 21 June 2013. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ↑ "Governor Bridge Natural Area / Patuxent River Park Trail Map" (PDF). Maryland-National Capital Park and Planning Commission . Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ↑ Geology and Water Resources of Prince George's County: Bulletin, Issue 10. Baltimore, Maryland: Maryland Geological Survey. 1952. p. 29.
- 1 2 3 4 "City of Bowie Environmental Infrastructure Action Strategy Plan Staff Findings and Recommendations By Sub-watershed". City of Bowie. p. 26. Archived from the original on 21 June 2013. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
- ↑ "Green Branch Fish Passage Project" (PDF). Patuxent Riverkeeper Newsletter. Patuxent Riverkeeper. p. 5. Retrieved 2 January 2014.