External links
Arabic language | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overviews | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alphabet | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Letters | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Varieties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Academic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Linguistics | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hasaitic | |
|---|---|
| Region | Arabia |
| Extinct | marginalized by Classical Arabic from the 7th century[ citation needed ] |
| Monumental South Arabian script | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | – |
| Glottolog | hasa1249 |
Hasaitic is an Ancient North Arabian dialect attested in inscriptions in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia at Thaj, Hinna, Qatif, Ras Tanura, Abqaiq in the al-Hasa region, Ayn Jawan, Mileiha and at Uruk. [1] It is written in the Monumental South Arabian script [2] and dates from the 5th to 2nd centuries BC.

Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It spans the vast majority of the Arabian Peninsula, with a land area of approximately 2,150,000 km2 (830,000 sq mi). Saudi Arabia is the largest country in the Middle East, and the second-largest country in the Arab world. It is bordered by Jordan and Iraq to the north, Kuwait to the northeast, Qatar, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates to the east, Oman to the southeast and Yemen to the south; it is separated from Egypt and Israel in the north-west by the Gulf of Aqaba. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of its terrain consists of arid desert, lowland, steppe, and mountains. Its largest and capital city is Riyadh, and the country is home to Mecca and Medina, the two holiest cities in Islam.
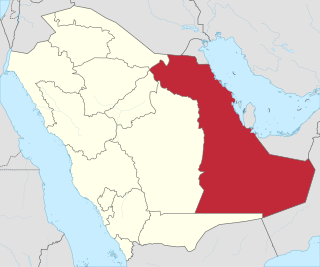
The Eastern Province, also known as the Eastern Region, and officially the Emirate of the Eastern Province, is the easternmost of the 13 provinces of Saudi Arabia. It is the largest province by area and the third most populous after the Riyadh Province and the Mecca Province. In 2017, the population was 4,900,325. Of these, 3,140,362 were Saudi citizens and 1,759,963 were foreign nationals The province accounts for 15.05% of the entire population of Saudi Arabia and is named for its geographical location relative to the rest of the kingdom.

The Mecca Province, also known as the Mecca Region, is one of the 13 provinces of Saudi Arabia. It is the third-largest province by area at 153,128 km2 (59,123 sq mi) and the most populous with a population of 8,557,766 as of 2017, of which 4,041,189 were foreign nationals and 4,516,577 were Saudis. It is located in the historic Hejaz region, and has an extended coastline on the Red Sea. Its capital is Mecca, the holiest city in Islam, and its largest city is Jeddah, which is Saudi Arabia's main port city. The province accounts for 26.29% of the population of Saudi Arabia and is named after the holy city of Mecca.

Dammam is the sixth-most populous city in Saudi Arabia after Riyadh, Jeddah, Mecca, Medina and Khamis Mushait. It is the capital of the Eastern Province. With a total population of 1,252,523 as of 2020. The judicial and administrative bodies of the province, in addition to the administrative offices of other minor governmental departments functioning within the province, are located in the city. The word itself is generally used to refer to the city, but may also refer to its eponymous governorate.

Khobar is a city and governorate in the Eastern Province of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, situated on the coast of the Persian Gulf. With a population of 457,748 as of 2017, Khobar is part of the 'Triplet Cities' area, or Dammam metropolitan area along with Dammam and Dhahran, forming the residential core of the region.

Dhahran is a city located in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. With a total population of 240,742 as of 2021. It is a major administrative center for the Saudi oil industry. Together with the nearby cities of Dammam and Khobar, Dhahran forms part of the Dammam Metropolitan Area, which is commonly known as greater Dammam and has an estimated population of 4,140,000 as of 2012.

Al-Aḥsāʾ, also known as al-Ḥasāʾ (الْحَسَاء) or Hajar (هَجَر), is a traditional oasis historical region in eastern Saudi Arabia whose name is used by the Al-Ahsa Governorate, which makes up much of that country's Eastern Province. The oasis is located about 60 km (37 mi) inland from the coast of the Arabian Gulf.

Hafar al-Batin, also frequently spelled Hafr al-Batin, is a Saudi Arabian city in the Eastern Province. It is located 430 km north of Riyadh, 94.2 km from the Kuwait border, and about 74.3 from the Iraq border. The city lies in the dry valley of the Wadi al-Batin, which is part of the longer valley of the river Wadi al-Rummah, which leads inland toward Medina and formerly emptied into the Persian Gulf.
Saudi Arabian Cricket Federation is the official governing body of the sport of cricket in Saudi Arabia. Its current headquarters is in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. It is Saudi Arabia's representative at the International Cricket Council, and has been a member of the Council since 2003. It is also a member of the Asian Cricket Council.

Al-Batin Football Club is a Saudi Arabian professional football club based in Hafar Al-Batin, Eastern Province, that competes in the Saudi Professional League. The club was founded in 1979.

The Riyadh Region, also known as the Riyadh Province, and officially the Emirate of Riyadh Province, is a region of Saudi Arabia, located in the geographic center of the country. It has an area of 404,240 km2 (156,080 sq mi) and with a 2017 population of 8,216,284, it is the second-largest region by both area and population, behind the Eastern Province and Mecca Region respectively. The capital governorate of the province is the Riyadh Governorate and it is named after the capital of the kingdom, Riyadh, which is the most populous city in the region and the kingdom, with a little less than two-thirds of the population of the region residing within the city.
The Subdivisions of Saudi Arabia, officially the Organization of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, as provided by the Regions' System, issued on 27 Sha'baan 1412 AH by Royal Order A/92, amended by Royal Order No. A/21 on 30 Rabi' al-Awal 1414 AH, divided the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia into 13 emirates (provinces/regions); the 13 provinces further divided into 118 governorates, classified category (A) or category (B); the 118 governorates divided into a number of centers, category (A) and category (B), taking into consideration the housing, geographical, security, transport, environment and historic conditions of each region.

Saudi Arabian oil was first discovered by the Americans in commercial quantities at Dammam oil well No. 7 in 1938 in what is now modern day Dhahran.

The protests in Saudi Arabia were part of the Arab Spring that started with the 2011 Tunisian revolution. Protests started with a self-immolation in Samtah and Jeddah street protests in late January 2011. Protests against anti-Shia discrimination followed in February and early March in Qatif, Hofuf, al-Awamiyah, and Riyadh. A Facebook organiser of a planned 11 March "Day of Rage", Faisal Ahmed Abdul-Ahad, was allegedly killed by Saudi security forces on 2 March, with several hundred people protesting in Qatif, Hofuf and al-Amawiyah on the day itself. Khaled al-Johani demonstrated alone in Riyadh, was interviewed by BBC Arabic Television, was detained in ʽUlaysha Prison, and became known online as "the only brave man in Saudi Arabia". Many protests over human rights took place in April 2011 in front of government ministry buildings in Riyadh, Ta'if and Tabuk and in January 2012 in Riyadh. In 2011, Nimr al-Nimr encouraged his supporters in nonviolent resistance.

The Society for Development and Change is a Saudi Arabian human rights non-governmental organisation that became active in 2011, campaigning for equal human rights for Shia in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. The organisation called for a constitution and an elected legislature for Eastern Province.

The 1979 Qatif Uprising was a period of unprecedented civil unrest that occurred in Qatif and Al-Hasa, Saudi Arabia, in late November 1979. The unrest resulted in 20–24 people killed in what was described as a sectarian outburst of violence between the Shi'a minority and Sunni majority in Saudi Arabia and the beginning of the modern phase of the Qatif conflict.

The Qatif and Dammam mosque bombings occurred on 22 and 29 May 2015. On Friday May 22, a suicide bomber attacked the Shia "Imam Ali ibn Abi Talib Mosque" situated in Qudeih village of Qatif city in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. The Islamic State of Iraq and Syria claimed responsibility for the blast, which killed at least 21 people. The event is the second deadly attack against Shia in six months.

The General Entertainment Authority was created on May 7, 2016 by a royal decree in Saudi Arabia. The GEA is responsible for the nation’s expanding public entertainment sector.
The 2017–2020 Qatif unrest was a phase of conflict in the Qatif region of Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia, between Saudi security forces and the local Shia community, that arose sporadically starting in 1979, including a series of protests and repression during the 2011–12 Saudi Arabian protests.
The European Saudi Organisation for Human Rights (ESOHR) is a Europe-based human rights organisation for documenting and promoting human rights in Saudi Arabia.