Related Research Articles

Essaouira, known until the 1960s as Mogador, is a port city in the western Moroccan region of Marrakesh-Safi, on the Atlantic coast. It has 77,966 inhabitants as of 2014.

Oujda is a major city in northeast Morocco near the border with Algeria. Oujda is the capital city of the Oriental region of northeastern Morocco and has a population of 720,618 people. It is located about 15 kilometres west of the Moroccan-Algerian border in the south of the Beni Znassen Mountains and about 55 km south of the Mediterranean Sea coast.

The French protectorate in Morocco, also known as French Morocco, was the period of French colonial rule in Morocco that lasted from 1912 to 1956. The protectorate was officially established 30 March 1912, when Sultan Abd al-Hafid signed the Treaty of Fez, though the French military occupation of Morocco had begun with the invasion of Oujda and the bombardment of Casablanca in 1907.

MoulayAbd al-Aziz bin Hassan, born on 24 February 1881 in Marrakesh and died on 10 June 1943 in Tangier, was a sultan of Morocco from 9 June 1894 to 21 August 1908, as a ruler of the 'Alawi dynasty. He was proclaimed sultan at the age of sixteen after the death of his father Hassan I. Moulay Abdelaziz tried to strengthen the central government by implementing a new tax on agriculture and livestock, a measure which was strongly opposed by sections of the society. This in turn led Abdelaziz to mortgage the customs revenues and to borrow heavily from the French, which was met with widespread revolt and a revolution that deposed him in 1908 in favor of his brother Abd al-Hafid.

Algerian Arabic, natively known as Dziria, Darja or Derja, is a variety of Arabic spoken in Algeria. It belongs to the Maghrebi Arabic dialect continuum and is mostly intelligible with the Tunisian and Moroccan dialects. Darja (الدارجة) means "everyday/colloquial dialect".

Moulay Al-Rashid ibn Sharif, known as Moulay Al-Rashid or Moulay Rachid, sometimes called Tafiletta by the English, was Sultan of Morocco from 1666 to 1672. He was the son of the founder of the 'Alawi dynasty, Moulay Sharif, who took power in the Tafilalt region in 1631.
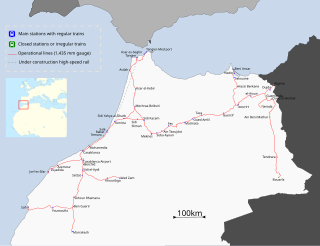
ONCF is Morocco's national railway operator. ONCF is a state-owned company that is under the control of the Ministry of Equipment, Transport and Logistics and is responsible for all passenger and freight traffic on the national railway network. The company is also responsible for building and maintaining the rail infrastructure.

Fouad Laroui is a Moroccan economist and writer, born in Oujda, Morocco. After his studies at the Lycée Lyautey (Casablanca), he joined the prestigious École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, where he studied engineering. After working shortly for the Office Cherifien des Phosphates company in Khouribga (Morocco), he moved to the United Kingdom where he spent several years in Cambridge and York. Later he obtained a PhD in economics and moved to Amsterdam where he started his career as a writer. He has published about twenty books between novels, collections of short stories and essays and two collections of poetry in Dutch. He has won several literary prizes, amongst which the Prix Goncourt de la nouvelle, the Prix Jean-Giono and the Grande Médaille de la littérature de l'Académie française.
Moroccan rap music is a Moroccan musical style related to rap and hip hop culture.
Moroccan Arabic, also known as Darija, is the dialectal, vernacular form or forms of Arabic spoken in Morocco. It is part of the Maghrebi Arabic dialect continuum and as such is mutually intelligible to some extent with Algerian Arabic and to a lesser extent with Tunisian Arabic. It is spoken by 90.9% of the population of Morocco. While Modern Standard Arabic is used to varying degrees in formal situations such as religious sermons, books, newspapers, government communications, news broadcasts and political talk shows, Moroccan Arabic is the predominant spoken language of the country and has a strong presence in Moroccan television entertainment, cinema and commercial advertising. Moroccan Arabic has many regional dialects and accents as well, with its mainstream dialect being the one used in Casablanca, Rabat, Tangier, Marrakesh and Fez, and therefore it dominates the media and eclipses most of the other regional accents.

Fadel Benyaich or Benaich is a senior member of the royal cabinet of King Mohammed VI, reportedly in charge of relations with Spain. He studied at the Collège Royal with Mohammed VI.

The General Directorate of Studies and Documentation is the foreign intelligence agency of Morocco, under authority of the Administration for National Defense. It is officially tasked with maintaining national security and the safety of national institutions.

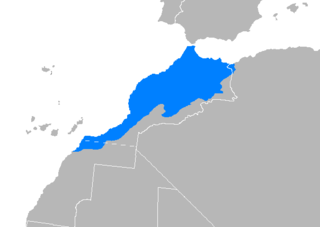
Western Morocco Arabic, Western Moroccan Arabic or ʿAroubi Darija is a dialectal continuum of Hilalian Arabic, mainly spoken in the western and central-western plains of Morocco.
Moroccans and people of Moroccan descent, who come from various ethnic groups, form a distinct community in Belgium and part of the wider Moroccan diaspora. They represent the largest non-European immigrant population in Belgium and are widely referred to as Belgo-Marocains in French and Belgische Marokkanen in Dutch.

The Battle of Moulouya took place in May 1692 at a ford on the Moulouya river in Morocco. It was fought between the armies of the Alawi sultan Moulay Ismail and those of the Dey of Algiers Hadj Chabane.
The Capture of the Rif took place in 1792 and was orchestrated by the Bey of Oran, Mohammed el-Kebir, to capture the eastern Rif region in northern Morocco.
The 1953 Oujda revolt was an anti-colonial revolt against the French protectorate, in the context of the Revolution of the King and the People, that took place in Oujda August 16, 1953. It was followed by a second insurrection in Tafoughalt the next day.

Si El Madani El Glaoui, born Madani El Mezouari El Glaoui, nicknamed the faqih was a prominent statesman in Morocco during the late 19th century and early 20th century. He was largely responsible for establishing the Glaoui family's power in the country.
References
- ↑ M. El Himer, Zones linguistiques du Maroc arabophone : contacts et effets à Salé, in: Between the Atlantic and Indian Oceans, Studies on Contemporary Arabic, 7th AIDA Conference, 2006, held in Vienna Archived 2015-04-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ M. El Himer, Variations linguistiques de l’arabe marocain: de la démarcation régionale à la neutralisation urbaine (unpublished) Archived 2015-04-13 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ S. Elbaz, « La subordination en arabe d'Oujda », Arabica, No. 28, 1981, n.333-344.
- ↑ P. Behnstedt & M. Benabbou, « Données nouvelles sur les parlers arabes du nord-est marocain », Zeitschrift für arabische Linguistik, n.44, 2005, p.17-70.