Related Research Articles

Arabic is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece.
Aramaic is a Northwest Semitic language that originated in the ancient region of Syria, and quickly spread to Mesopotamia and eastern Anatolia where it has been continually written and spoken, in different varieties, for over three thousand years. Aramaic served as a language of public life and administration of ancient kingdoms and empires, and also as a language of divine worship and religious study. Several modern varieties, the Neo-Aramaic languages, are still spoken by Assyrians, and some Mandeans and Mizrahi Jews.

The Iraqi people are people originating from the country of Iraq.

The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Hebrew, and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis.

The Culture of Iraq or The Culture of Mesopotamia is one of the world's oldest cultural histories and is considered one of the most influential cultures in the world. The region between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, historically known as Mesopotamia, is often referred to as the Cradle of civilisation. Mesopotamian legacy went on to influence and shape the civilizations of the Old World in different ways such as inventing writing system, mathematics, law, astrology and many more. Iraq is home to diverse ethnic groups who have contributed to the wide spectrum of the Iraqi Culture. The country is known for its poets، architects، painters and sculptors who are among the best in the region, some of them being world-class. The country has one of the longest written traditions in the world including architecture, literature, music, dance, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, stonemasonry and metalworking.

Cypriot Arabic, also known as Cypriot Maronite Arabic or Sanna, is a moribund variety of Arabic spoken by the Maronite community of Cyprus. Formerly speakers were mostly situated in Kormakitis, but following the Turkish invasion of Cyprus in 1974, the majority relocated to the south and dispersed, leading to the decline of the language. Traditionally bilingual in Cypriot Greek, as of some time prior to 2000, all remaining speakers of Cypriot Arabic were over 30 years of age. A 2011 census reported that, of the 3,656 Maronite Cypriots in Republic of Cyprus-controlled areas, none declared Cypriot Arabic as their first language.
Suret, also known as Assyrian or Chaldean, refers to the varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic (NENA) spoken by Christians, largely ethnic Assyrians. The various NENA dialects descend from Old Aramaic, the lingua franca in the later phase of the Assyrian Empire, which slowly displaced the East Semitic Akkadian language beginning around the 10th century BC. They have been further heavily influenced by Classical Syriac, the Middle Aramaic dialect of Edessa, after its adoption as an official liturgical language of the Syriac churches, but Suret is not a direct descendant of Classical Syriac.

Mesopotamian Arabic is a group of varieties of Arabic spoken in the Mesopotamian basin of Iraq as well as spanning into southeastern Turkey, Iran, Syria, Kuwait, and spoken in Iraqi diaspora communities.
Barzani Jewish Neo-Aramaic is a modern Jewish Aramaic language, often called Neo-Aramaic or Judeo-Aramaic. It was originally spoken in three villages near Aqrah in Iraqi Kurdistan. The native name of the language is Lishanid Janan, which means 'our language', and is similar to names used by other Jewish Neo-Aramaic dialects .

Iraqis are people who originate from the country of Iraq.
Targum is used by the Jews of northern Iraq and Kurdistan to refer to a variety of Aramaic dialects spoken by them till recent times. For details of these dialects, see Judeo-Aramaic language. The word "targum" simply means "translation" in Hebrew, and the primary reference of the term is the Aramaic Bible translations of that name. The Jewish use of "Targum" to mean the Aramaic language in general dates back to the early Middle Ages. An analogy is the use of "Ladino" to mean Judeo-Spanish, and of sharħ to mean Judeo-Arabic.
Baghdad Jewish Arabic or autonymhaki mal yihud or el-haki malna is the Arabic dialect spoken by the Jews of Baghdad and other towns of Southern Iraq. This dialect differs from the dialect spoken by the Jews in Northern Iraq, such as Mosul and 'Ana. The Baghdadi and Northern dialects may be regarded as subvarieties of Judeo-Iraqi Arabic. As with most Judeo-Arabic communities, there are likely to be few, if any, speakers of the Judeo-Iraqi Arabic dialects who still reside within Iraq. Rather these dialects have been maintained or are facing critical endangerment within respective Judeo-Iraqi diasporas, namely those of Israel and the United States. In 2014, the film Farewell Baghdad, which is performed mostly in Jewish Baghdadi Arabic dialect, became the first film to be almost completely performed in Judeo-Iraqi Arabic.

Arabic is the official language of Syria and is the most widely spoken language in the country. Several modern Arabic dialects are used in everyday life, most notably Levantine in the west and Mesopotamian in the northeast.
The Arabic language family is divided into several categories which are: Old Arabic, the literary varieties, and the modern vernaculars.
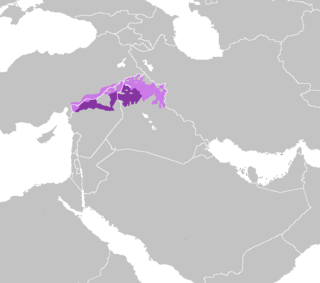
North Mesopotamian Arabic, also known as Moslawi, Mesopotamian Qeltu Arabic, or Syro-Mesopotamian Arabic, is one of the two main varieties of Mesopotamian Arabic, together with Gilit Mesopotamian Arabic.

The Arab world consists of 22 states. As of 2021, the combined population of all the Arab states was around 475 million people.

There are a number of languages spoken in Iraq, but Mesopotamian Arabic is by far the most widely spoken in the country. Arabic and Kurdish are both official languages in Iraq.
The Eastern Aramaic languages have developed from the varieties of Aramaic that developed in and around Mesopotamia, as opposed to western varieties of the Levant. Most speakers are ethnic Assyrians, although there are a minority of Assyrian Jews and Mandaeans, who also speak varieties of Eastern Aramaic.
The varieties of Arabic, a Semitic language within the Afroasiatic family originating in the Arabian Peninsula, are the linguistic systems that Arabic speakers speak natively. There are considerable variations from region to region, with degrees of mutual intelligibility that are often related to geographical distance and some that are mutually unintelligible. Many aspects of the variability attested to in these modern variants can be found in the ancient Arabic dialects in the peninsula. Likewise, many of the features that characterize the various modern variants can be attributed to the original settler dialects as well as local native languages and dialects. Some organizations, such as SIL International, consider these approximately 30 different varieties to be separate languages, while others, such as the Library of Congress, consider them all to be dialects of Arabic.
Gilit Mesopotamian Arabic, also known as Iraqi Arabic, Mesopotamian Gelet Arabic, or simply Mesopotamian Arabic is one of the two main varieties of Mesopotamian Arabic, together with North Mesopotamian Arabic.
References
- ↑ "In Iraq's marshlands, researchers are racing to document a disappearing dialect - Equal Times". 2022-01-19. Archived from the original on 19 January 2022. Retrieved 2022-02-09.
- ↑ UCL (2021-09-28). "Dictionary of Marsh Arab dialects". The Nahrein Network. Retrieved 2022-02-09.
- ↑ Müller-Kessler, Christa (2003). "Aramaic ?k?, lyk? and Iraqi Arabic ?aku, maku: The Mesopotamian Particles of Existence". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 123 (3): 641–646. doi:10.2307/3217756. ISSN 0003-0279. JSTOR 3217756.
- ↑ "الجيم العراقية: حقائق وأوهام". 2022-02-08. Archived from the original on 8 February 2022. Retrieved 2022-02-09.
![]() This article incorporates text by Saja Albuarabi available under the CC BY 4.0 license.
This article incorporates text by Saja Albuarabi available under the CC BY 4.0 license.