
Futabasaurus is a genus of plesiosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Fukushima, Japan. It was described and named in 2006, and was assigned to the family Elasmosauridae. The genus contains one species, F. suzukii.

Hydrotherosaurus is an extinct genus of elasmosaurid plesiosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Moreno Formation of Fresno County, California, USA. The only known species, H. alexandrae, was named for its discoverer, Annie Montague Alexander, by Samuel Paul Welles.

Polycotylidae is a family of plesiosaurs from the Cretaceous, a sister group to Leptocleididae. Polycotylids first appeared during the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous, before becoming abundant and widespread during the early Late Cretaceous. Several species survived into the final stage of the Cretaceous, the Maastrichtian.

Dolichorhynchops is an extinct genus of polycotylid plesiosaur from the Late Cretaceous of North America, containing three species, D. osborni, D. bonneri and D. tropicensis, as well as a questionably referred fourth species, D. herschelensis. Dolichorhynchops was a prehistoric marine reptile, but at least one species, D. tropicensis, likely entered rivers to collect gastroliths. Its Greek generic name means "long-nosed face". While typically measuring about 3 metres (9.8 ft) in length, the largest specimens of D. osborni and D. bonneri are estimated to have a total body length more than approximately 4.29 metres (14.1 ft) and 5.09 metres (16.7 ft), respectively.

Suchosaurus is a spinosaurid dinosaur from Cretaceous England and Portugal, originally believed to be a genus of crocodile. The type material, consisting of teeth, was used by British palaeontologist Richard Owen to name the species S. cultridens in 1841. Later in 1897, French palaeontologist Henri-Émile Sauvage named a second species, S. girardi, based on two fragments from the mandible and one tooth discovered in Portugal. Suchosaurus is possibly a senior synonym of the contemporary spinosaurid Baryonyx, but is usually considered a dubious name due to the paucity of its remains, and is considered an indeterminate baryonychine. In the Wadhurst Clay Formation of what is now southern England, Suchosaurus lived alongside other dinosaurs, as well as plesiosaurs, mammals, and crocodyliforms.

Brachauchenius is an extinct genus of pliosaurid that lived in North America and Morocco during the Late Cretaceous.

Leptocleidus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur, belonging to the family Leptocleididae. It was a small plesiosaur, measuring only up to 3 m (9.8 ft).

Aphrosaurus was an extinct genus of plesiosaur from the Maastrichtian. The type species is Aphrosaurus furlongi, named by Welles in 1943. The holotype specimen was discovered in the Moreno Formation in Fresno County, California in 1939 by rancher Frank C. Piava. A second specimen - LACM 2832 - was also found in the same formation and initially diagnosed as a juvenile of the same species, but has since been removed from the genus.

Nichollssaura is an extinct genus of leptocleidid plesiosaur from the Early Cretaceous Boreal Sea of North America. The type species is N. borealis, found in the early Albian age Clearwater Formation near Fort McMurray, Alberta, Canada.

Callawayasaurus is a genus of plesiosaur from the family Elasmosauridae. When the holotype was first described by Samuel Paul Welles in 1962, it was described as Alzadasaurus colombiensis before being moved into its current genus by Kenneth Carpenter in 1999.

Morenosaurus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur from the Cretaceous of what is now California. The type species is Morenosaurus stocki, first named by Samuel Welles in 1943, in honor of Dr. Chester Stock. The species was found by Robert Wallace and Arthur Drescher in the Panoche Hills region of Fresno County. The skeleton they found was fairly complete, and lacked only the head and parts of the neck and paddles; the preserved portion of the trunk and tail is 3.63 metres (11.9 ft) long. The skeleton was originally mounted at Caltech but is now in the Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County.
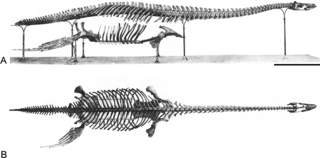
Brancasaurus is a genus of plesiosaur which lived in a freshwater lake in the Early Cretaceous of what is now North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a long neck possessing vertebrae bearing distinctively-shaped "shark fin"-shaped neural spines, and a relatively small and pointed head, Brancasaurus is superficially similar to Elasmosaurus, albeit smaller in size at 3.26 metres (10.7 ft) in length as a subadult.

Polycotylus is a genus of plesiosaur within the family Polycotylidae. The type species is P. latippinis and was named by American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope in 1869. Eleven other species have been identified. The name means 'much-cupped vertebrae', referring to the shape of the vertebrae. It lived in the Western Interior Seaway of North America toward the end of the Cretaceous. One fossil preserves an adult with a single large fetus inside of it, indicating that Polycotylus gave live birth, an unusual adaptation among reptiles.
Sinopliosaurus is a genus of pliosauroid plesiosaur, a type of short-necked marine reptile, alive during the Aptian and Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous of the People's Republic of China - its exact age is unknown. The type species, Sinopliosaurus weiyuanensis, was named and described in 1944 by Yang Zhongjian. One species, "S." fusuiensis, was later shown to be based on teeth from a spinosaurid theropod dinosaur which is now known as Siamosaurus. S. weiyuanensis would have lived near a coastal environment.
Eromangasaurus is an extinct genus of elasmosaurid known from northern Queensland of Australia.

Seeleyosaurus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur that was initially placed within the genus Plesiosaurus in 1895 and was given its own genus in 1940. Two species were known: the type, S. guilelmiimperatoris, and the now obsolete species S. holzmadensis, which has since been absorbed into S. guilelmiimperatoris. It was a relatively small plesiosaur, measuring 2.9–3.6 m (9.5–11.8 ft) long. The holotype was MB.R.1992, a large almost complete skeleton from the Upper Lias (Toarcian) Lias Group Formations of Württemberg, Germany. There seems to be the impression of a rhomboidal flap of skin in a vertical plane; if so, many plesiosaurs may have been equipped in this way. The holotype was destroyed in 1945 (WWII) and only a cast exists today. A second specimen, preserved in 3D, has survived until today. It was once the holotype of the now obsolete species S. holzmadensis.

Alexandronectes is a genus of elasmosaurid plesiosaur, a type of long-necked marine reptile, that lived in the oceans of Late Cretaceous New Zealand. It contains one species, A. zealandiensis. Fossils of Alexandronectes were found in the Conway Formation of Canterbury, which can be dated to the Early Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous. Fossils of it were found around 1872 near the Waipara River, north of Christchurch, New Zealand.
Orophosaurus is an dubious genus of elasmosaurid plesiosaur from the Late Cretaceous of New Mexico.
Vectocleidus is an extinct genus of leptocleidid plesiosaurian known from the Early Cretaceous Vectis Formation of Isle of Wight, in the United Kingdom. It contains a single species, Vectocleidus pastorum.

This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flourished during the Mesozoic Era. The first scientifically documented plesiosaur fossils were discovered during the early 19th century by Mary Anning. Plesiosaurs were actually discovered and described before dinosaurs. They were also among the first animals to be featured in artistic reconstructions of the ancient world, and therefore among the earliest prehistoric creatures to attract the attention of the lay public. Plesiosaurs were originally thought to be a kind of primitive transitional form between marine life and terrestrial reptiles. However, now plesiosaurs are recognized as highly derived marine reptiles descended from terrestrial ancestors.
























