
Emausaurus is a genus of thyreophoran or armored dinosaur from the Early Jurassic. Its fossils have been found in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, northern Germany. Emausaurus is the only known Toarcian thyreophoran, as well as the only dinosaur from the zone of the same age with a formal name.

Dapedium is an extinct genus of primitive marine neopterygian ray-finned fish. The first-described finding was an example of D. politum, found in the Lower Lias of Lyme Regis, on the Jurassic Coast of England. Dapedium lived in the Late Triassic to the Middle Jurassic period, from the late Norian to the early Aalenian.

Ohmdenosaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic epoch in what is now Germany. The only specimen – a tibia (shinbone) and ankle – was discovered in rocks of the Posidonia Shale near the village of Ohmden. The specimen, which was originally identified as a plesiosaur, is exhibited in a local museum, the Urweltmuseum Hauff. In the 1970s, it caught the attention of German palaeontologist Rupert Wild, who recognised it as the remains of a sauropod. Wild named Ohmdenosaurus in a 1978 publication; the only known species is Ohmdenosaurus liasicus.

Bittacidae is a family of scorpionflies commonly called hangingflies or hanging scorpionflies.

Stenopterygius is an extinct genus of thunnosaur ichthyosaur known from Europe.

Rhomaleosaurus is an extinct genus of Early Jurassic rhomaleosaurid pliosauroid known from Northamptonshire and from Yorkshire of the United Kingdom. It was first named by Harry Seeley in 1874 and the type species is Rhomaleosaurus cramptoni. It was one of the earliest large marine reptile predators which hunted in the seas of Mesozoic era, measuring about 7 metres (23 ft) long. Like other pliosaurs, Rhomaleosaurus fed on ichthyosaurs, ammonites and other plesiosaurs.

Microcleidus is an extinct genus of sauropterygian reptile belonging to the Plesiosauroidea. The species has 40 neck vertebrae and a short tail of 28 vertebrae. Fossils of the genus have been found in France, the Posidonia Shale in Germany and Luxembourg, and the Alum Shale Formation of England.

Excalibosaurus is a monotypic genus of marine prehistoric reptiles (ichthyosaurs) that lived during the Sinemurian stage of the Early Jurassic period in what is now England. It is characterized by the extreme elongation of the rostrum, with the lower jaw about three-quarters the length of the upper jaw, giving the animal a swordfish-like look. The only known species is Excalibosaurus costini.

Hauffiosaurus is an extinct genus of Early Jurassic pliosaurid plesiosaur known from Holzmaden of Germany and from Yorkshire of the United Kingdom. It was first named by Frank Robin O’Keefe in 2001 and the type species is Hauffiosaurus zanoni. In 2011, two additional species were assigned to this genus: H. longirostris and H. tomistomimus.
Eurycleidus is an extinct genus of large-bodied rhomaleosaurid known from the Early Jurassic period of the United Kingdom. It contains a single species, E. arcuatus.

Seeleyosaurus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur from Germany and possibly also Russia.

Plesiopterys is an extinct genus of plesiosaur originating from the Posidonienschiefer of Holzmaden, Germany, and lived during the Early Jurassic period. It is thought to be the sister taxon to all other plesiosauroids including the Plesiosaurus, and is placed outside of the Plesiosauroidea group. Plesiopterys wildi is the one known species within the genus, and is 220 centimeters long, or about 7.2 feet, and its body and skull are both relatively small. It possesses a unique combination of both primitive and derived characters, and is currently displayed at the State Museum of Natural History, Germany.

The Posidonia Shale geologically known as the Sachrang Formation, is an Early Jurassic geological formation of southwestern and northeast Germany, northern Switzerland, northwestern Austria, southern Luxembourg and the Netherlands, including exceptionally well-preserved complete skeletons of fossil marine fish and reptiles.

Trachymetopon is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth from the Jurassic of Europe. Fossils have been found in the Early Jurassic Posidonia Shale of Germany the Middle Jurassic Marnes de Dives of France, and probably the Late Jurassic Kimmeridge Clay of England. Only one species has been named, Trachymetoponliassicum, described by Henning in 1951 from an almost complete specimen found in the Lower Toarcian of Ohmden in Baden-Württemberg. Another specimen is known from the same site, and two older specimens come from the Sinemurian of Holzmaden. The holotype of this species is 1.6 metres in length. A giant specimen of an undetermined species of Trachymetopon found at the Middle Jurassic Falaises des Vaches Noires of Normandy. This specimen, composed of a 53 cm long palatoquadrate, belongs to an individual 4 metres (13 ft) in length. A basisphenoid found in a museum in Switzerland that likely originates from the same locaity probably belonged to an individual around 5 m (16 ft) long, making Trachymetopon the largest of all coelacanths alongside Mawsonia. A study published in 2015 revealed that this coelacanth belongs to the Mawsoniidae. Trachymetopon is one of the few known mawsoniids to have been exclusively marine, while most of the other members of the group have lived in fresh and brackish waters.
Suevoleviathan is an extinct genus of primitive ichthyosaur found in the Early Jurassic (Toarcian) of Holzmaden, Germany.

Meyerasaurus is an extinct genus of rhomaleosaurid plesiosaur known from the Early Jurassic of Holzmaden, Baden-Württemberg in southwestern Germany.

Lusonectes is an extinct genus of microcleidid plesiosaur from the Early Jurassic (Toarcian) São Gião Formation of Portugal.

The Sachrang Formation or "Posidonienschiefer" Formation is a geological formation of southwestern Germany, northern Switzerland, northwestern Austria, southeast Luxembourg and the Netherlands, that spans about 3 million years during the Early Jurassic period. It is known for its detailed fossils, especially sea fauna, listed below. Composed mostly by black shale, the formation is a Lagerstätte, where fossils show exceptional preservation, with a thickness that varies from about 1 m to about 40 m on the Rhine level, being on the main quarry at Holzmaden between 5 and 14 m. Some of the preserved material has been transformed into fossil hydrocarbon Jet, specially wood remains, used for jewelry. The exceptional preservation seen on the Posidonia Shale has been studied since the late 1800s, finding that a cocktail of chemical and environmental factors let to such an impressive conservation of the marine fauna. The most common theory is the changes in the oxygen level, where the different anoxic events of the Toarcian left oxygen-depleted bottom waters, with the biota dying and falling to the bottom without any predator able to eat the dead bodies.
Fulgoridiidae are an extinct family of Mesozoic planthoppers. They are the earliest group of planthoppers known, and appear to be a paraphyletic assemblage ancestral to living planthoppers. The majority of known members of the family lived in the Jurassic period, though the group also includes one Cretaceous taxon. All currently known species are from Eurasia.
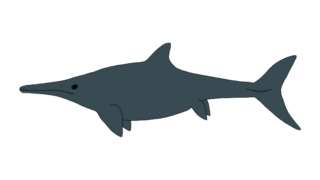
Magnipterygius is an extinct genus of primitive ichthyosaur found in the Early Jurassic Posidonia Shale of Dotternhausen, Germany. The holotype specimen is SMNS96922, a nearly complete articulated skeleton. This genus is well known as a small-sized ichthyosaur, of around 120 centimetres (3.9 ft) length, making it the second genus of that size after the Triassic. Due to the similarities with the genus Stenopterygius it has been classified as a member of the family Stenopterygiidae.

























