The Isle of Wight is one of the richest dinosaur localities in Europe, with over 20 species of dinosaur having been recognised from the early Cretaceous Period, some of which were first identified on the island, as well as the contemporary non-dinosaurian species of crocodile, turtle and pterosaur.

Yaverlandia is a genus of maniraptoran dinosaur. Known from a partial fossil skull found in Lower Cretaceous strata of the Wessex Formation on the Isle of Wight. it was described as the earliest known member of the pachycephalosaurid family, but research by Darren Naish shows it to have actually been a theropod, seemingly a maniraptoran. The type species is Y. bitholus.

Elasmosauridae is an extinct family of plesiosaurs, often called elasmosaurs. They had the longest necks of the plesiosaurs and existed from the Hauterivian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Cretaceous, and represented one of the two groups of plesiosaurs present at the end of the Cretaceous alongside Polycotylidae. Their diet mainly consisted of crustaceans and molluscs.

The Wealden Group, occasionally also referred to as the Wealden Supergroup, is a group in the lithostratigraphy of southern England. The Wealden group consists of paralic to continental (freshwater) facies sedimentary rocks of Berriasian to Aptian age and thus forms part of the English Lower Cretaceous. It is composed of alternating sands and clays. The sandy units were deposited in a flood plain of braided rivers, the clays mostly in a lagoonal coastal plain.

Istiodactylus is a genus of pterosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous period, about 120 million years ago. The first fossil was discovered on the English Isle of Wight in 1887, and in 1901 became the holotype specimen of a new species, O. latidens, in the genus Ornithodesmus. This species was moved to its own genus, Istiodactylus, in 2001; this name is Greek for "sail finger". More specimens were described in 1913, and Istiodactylus was the only pterosaur known from three-dimensionally preserved fossils for much of the 20th century. In 2006, a species from China, I. sinensis, was assigned to Istiodactylus, but it has also been suggested to belong to a different genus.

Suchosaurus is a spinosaurid dinosaur from Cretaceous England and Portugal, originally believed to be a genus of crocodile. The type material, consisting of teeth, was used by British palaeontologist Richard Owen to name the species S. cultridens in 1841. Later in 1897, French palaeontologist Henri-Émile Sauvage named a second species, S. girardi, based on two fragments from the mandible and one tooth discovered in Portugal. Suchosaurus is possibly a senior synonym of the contemporary spinosaurid Baryonyx, but is usually considered a dubious name due to the paucity of its remains, and is considered an indeterminate baryonychine. In the Wadhurst Clay Formation of what is now southern England, Suchosaurus lived alongside other dinosaurs, as well as plesiosaurs, mammals, and crocodyliforms.

Leptocleidus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur, belonging to the family Leptocleididae. It was a small plesiosaur, measuring only up to 3 m (9.8 ft).

Nichollssaura is an extinct genus of leptocleidid plesiosaur from the Early Cretaceous Boreal Sea of North America. The type species is N. borealis, found in the early Albian age Clearwater Formation near Fort McMurray, Alberta, Canada.
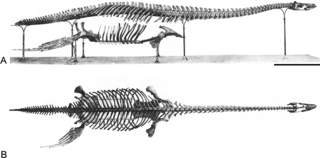
Brancasaurus is a genus of plesiosaur which lived in a freshwater lake in the Early Cretaceous of what is now North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a long neck possessing vertebrae bearing distinctively-shaped "shark fin"-shaped neural spines, and a relatively small and pointed head, Brancasaurus is superficially similar to Elasmosaurus, albeit smaller in size at 3.26 metres (10.7 ft) in length as a subadult.

The Wessex Formation is a fossil-rich English geological formation that dates from the Berriasian to Barremian stages of the Early Cretaceous. It forms part of the Wealden Group and underlies the younger Vectis Formation and overlies the Durlston Formation. The dominant lithology of this unit is mudstone with some interbedded sandstones. It is part of the strata of the Wessex Basin, exposed in both the Isle of Purbeck and the Isle of Wight. While the Purbeck sections are largely barren of vertebrate remains, the Isle of Wight sections are well known for producing the richest and most diverse fauna in Early Cretaceous Europe.

Leptocleididae is a family of small-sized plesiosaurs that lived during the Early Cretaceous period. They had small bodies with small heads and short necks. Leptocleidus and Umoonasaurus had round bodies and triangle-shaped heads. Leptocleidids have been found in what were shallow nearshore, freshwater and brackish habitats. Hilary F. Ketchum and Roger B. J. Benson (2010), transferred Brancasaurus, Kaiwhekea, Nichollssaura and Thililua to this family. However, Ketchum and Benson (2011) reassigned Kaiwhekea and Thililua to their original positions, as an elasmosaurid and a polycotylid, respectively.
The Vectis Formation is a geological formation on the Isle of Wight and Swanage, England whose strata were formed in the lowermost Aptian, approximately 125 million years ago. The environment of deposition was that of a freshwater coastal lagoon with occasional marine influence after the early Aptian marine transgression, transitioning from the floodplain environment of the underlying Wessex Formation. The primary lithology is of laminated grey mudstones. The Vectis Formation is composed of three geological members: the Shepherds Chine member, the Barnes High Sandstone member, and the Cowleaze Chine member. It is overlain by the fully marine Atherfield Clay Formation, part of the Lower Greensand Group. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
Hylaeochampsa is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorphs. It is known only from a partial skull recovered from Barremian-age rocks of the Lower Cretaceous Vectis Formation of the Isle of Wight. This skull, BMNH R 177, is short and wide, with a eusuchian-like palate and inferred enlarged posterior teeth that would have been suitable for crushing. Hylaochampsa was described by Richard Owen in 1874, with H. vectiana as the type species. It may be the same genus as the slightly older Heterosuchus, inferred to have been of similar evolutionary grade, but there is no overlapping material as Heterosuchus is known only from vertebrae. If the two could be shown to be synonyms, Hylaeochampsa would have priority because it is the older name. Hylaeochampsa is the type genus of the family Hylaeochampsidae, which also includes Iharkutosuchus from the Late Cretaceous of Hungary. James Clark and Mark Norell positioned it as the sister group to Crocodylia. Hylaeochampsa is currently the oldest known unambiguous eusuchian.

Hylaeochampsidae is an extinct family of basal eusuchian crocodylomorphs thought to be closely related to the order Crocodylia.
Hastanectes is an extinct genus of a plesiosaurian with possible pliosaurid affinities known from the Early Cretaceous Wadhurst Clay Formation of the United Kingdom. It contains a single species, Hastanectes valdensis, which was originally thought to be a species of Cimoliasaurus.

Vectidraco, is a genus of azhdarchoid pterosaur from the Lower Cretaceous of England.
Wightia is a genus of tapejarid pterosaur recovered from the Lower Cretaceous (Barremian) aged Wessex Formation of the Isle of Wight of England, from which it gets its name. The only species within this genus is W. declivirostris.
The Bulldog Shale is a formation of Early Cretaceous age that forms part of the Marree Subgroup of the Rolling Downs Group, located in the Eromanga Basin of South Australia, Queensland and New South Wales.

Vectiraptor is a genus of dromaeosaurid dinosaur from the Barremian aged Wessex Formation of the United Kingdom. The type and only species is Vectiraptor greeni, known from associated dorsal vertebrae and a partial sacrum.




















