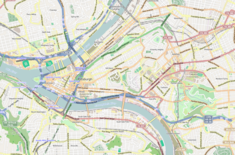
The Strip District is a neighborhood in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania in the United States. It is a one-half square mile area of land northeast of the central business district bordered to the north by the Allegheny River and to the south by portions of the Hill District. The Strip District runs between 11th and 33rd Streets and includes three main thoroughfares — Smallman St., Penn Ave., and Liberty Ave. — as well as various side streets.

The Allegheny County Courthouse in downtown Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, is part of a complex designed by H. H. Richardson. The buildings are considered among the finest examples of the Romanesque Revival style for which Richardson is well known.

The David McCullough Bridge, commonly and historically known as the 16th Street Bridge, is a steel trussed through arch bridge that spans the Allegheny River in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.

Fifth Avenue High School is a defunct school located at 1800 Fifth Avenue in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania's Bluff neighborhood, United States.

The Union Trust Building, was erected in 1915–16 by the industrialist Henry Clay Frick. The Flemish-Gothic structure's original purpose was to serve as a shopping arcade.

The Livestock Exchange Building in Omaha, Nebraska was built in 1926 at 4920 South 30 Street in South Omaha. It was designed as the centerpiece of the Union Stockyards by architect George Prinz and built by Peter Kiewit and Sons in the Romanesque revival and Northern Italian Renaissance Revival styles. In 1999 it was designated an Omaha Landmark and listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The Union Stockyards were closed in 1999, and the Livestock Exchange Building underwent an extensive renovation over the next several years.

Bedford School, located at 910 Bingham Street in the historic South Side Flats neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, has been listed in the National Register of Historic Places since 1986. According to Pittsburgh History and Landmarks Foundation, it is the oldest public school building still standing within the city of Pittsburgh.

Harmony Mills, in Cohoes, New York, United States, is an industrial district that is bordered by the Mohawk River and the tracks of the former Troy and Schenectady Railroad. It was listed as Harmony Mills Historic District on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978. A portion of the district encompassing the industrial buildings and some of the housing built for millworkers was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1999. The centerpiece building, Harmony Mill No. 3 was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1971.

Ruskin Hall is a residence hall at the University of Pittsburgh and a contributing property to the Schenley Farms National Historic District.. Constructed in 1921-22 by H. L. Stevens & Company, with an annex added in 1925-26, it is an eight-story building which is located between the Music Building and Information Sciences Building between Ruskin and Bellefield Avenues near Fifth Avenue on Pitt's main campus in the Oakland neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. Ruskin Hall recently underwent a $19.4 million conversion and renovation from medical student housing into undergraduate apartment-style housing that opened in 2008.

The Schenley Farms Historic District, also referred to as the Schenley Farms–Oakland Civic District, is a historic district listed on the National Register of Historic Places that is located in the Oakland section of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States.

The architectural firm of Starrett & van Vleck, often spelled Starrett & Van Vleck, specialized in the design of early 20th century department stores primarily in New York City. The partner Goldwin Starrett, brother of Colonel William A. Starrett, had worked for four years in the Chicago office of Daniel Burnham. Included in their designs were the New York City flagship stores of Lord & Taylor, Bloomingdales, Saks Fifth Avenue, Abraham & Straus, and Alexander's. The Lord & Taylor store, located on Fifth Avenue between 38th and 39th streets, was completed in 1914 and was Starrett & van Vleck’s first major department store. In December 2007, the store was named a New York City landmark.

The Pittsburgh Plate Glass Company Building, also known as the Northern Implement Company and the American Trio Building, is a warehouse building in downtown Minneapolis, Minnesota. PPG Industries of Pittsburgh constructed the structure. It was designed by thearchitectural firm Kees and Colburn and shows strong influences of architect Louis Sullivan. The arches in the top floor windows are modeled after Louis Sullivan's designs, which in turn were influenced by Henry Hobson Richardson's Richardsonian Romanesque style. The corners of the building are subtly chamfered in at the bottom and rise toward a flaring cornice at the top, echoing John Wellborn Root's design of the Monadnock Building in Chicago.

Heiser, Rosenfeld, and Strauss Buildings, also known as Inner Harbor Lofts I, is a historic loft building located at Baltimore, Maryland, United States. It is a complex of three structures. The Heiser Building is a Romanesque Revival style, six-story brick, stone, and iron structure, eight bays wide and 14 bays deep, built as a show factory in 1886. The Rosenfeld Building is a six-story, five-bay loft building, with Beaux Arts styling and built for E. Rosenfeld and Company in 1905. The Strauss Building is a six-story high, six-bay wide, and 11-bay deep loft structure built in 1887 for the Kinny Tobacco Company, cigarette manufacturers, and later occupied by the Strauss Brothers, clothing manufacturers and became part of the Rosenfeld complex around 1910.

Public School 9 and Public School 9 Annex are two historic school buildings located at 249 and 251 Sterling Place, respectively, at Vanderbilt Avenue in the Prospect Heights neighborhood of Brooklyn, New York City.

The Brockman Building is a 12-story Beaux-Arts, Classical, and Romanesque Revival style building located on 7th Street in the Financial District of Downtown Los Angeles, California.

The Armstrong Cork Company was a cork manufacturer located at 2349 Railroad Street in the Strip District neighborhood of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The company's building was built circa 1901, and designed by architect Frederick J. Osterling. The building was added to the National Register of Historic Places on May 10, 2005, and to the List of Pittsburgh History and Landmarks Foundation Historic Landmarks in 2007.

The Hopewell High School Complex, also known as James E. Mallonee Middle School, is a historic former school campus located at 1201 City Point Road in Hopewell, Virginia, United States. Contributing properties in the complex include the original school building, athletic field, club house, concession stand, press box, Home Economics Cottage, gymnasium and Science and Library Building. There are two non-contributing structures on the property.

Southern Stove Works is a historic factory complex located in the Three Corners District of Richmond, Virginia. The complex includes four contributing red brick buildings built between 1902 and 1920. The buildings housed the foundry, assembly operations, warehouse storage, and metal storage. In 1920, Southern Stove Works vacated the buildings and moved to their new facility, Southern Stove Works, Manchester. By 1921, these buildings were occupied by the J. P. Taylor Leaf Tobacco Company.

H. Lauter Company Complex, also known as J. Solotken Company, Lauter Lofts, and Harding Street Lofts, is a historic factory complex located at Indianapolis, Indiana. It was built between 1894 and 1912, and includes the South Factory, the North Factory, and the Office Building. The factory buildings are in the Italianate and the office building is in the Classical Revival style. The North Factory is a four-story brick building with a raised full basement constructed sometime between 1908 and 1912. The Office Building is a two-story brick building constructed between 1899 and 1908 and has a truncated hipped roof. The four-story, "U"-shaped core of the South Factory was built in two phases; the eastern portion between 1894 and 1898 and the western portion in 1899. The H. Lauter Company furniture manufacturer began in 1894 and they continued to operate at the location until 1936. The buildings have been converted to condominiums and apartments.

The Sioux City Central High School and Central Annex, also known as the Castle on the Hill, are historic buildings located in Sioux City, Iowa, United States. The high school building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974. The annex was added to the historic designation in 2016.